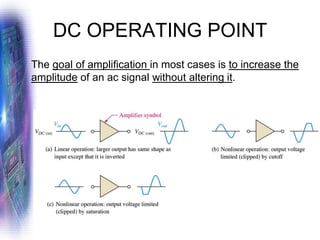
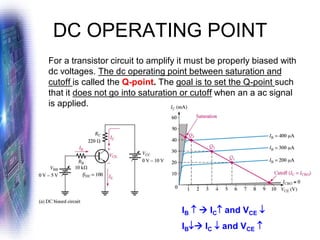
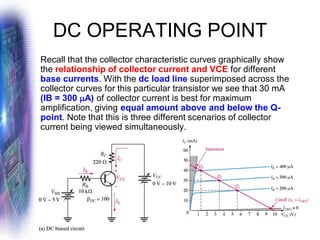
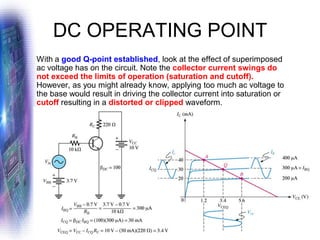
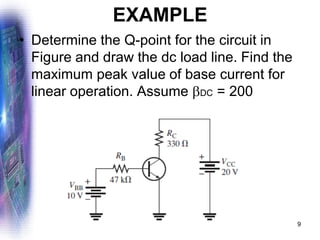
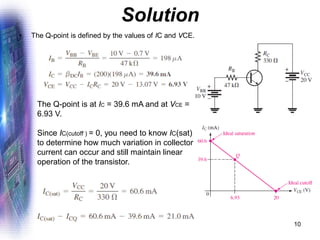
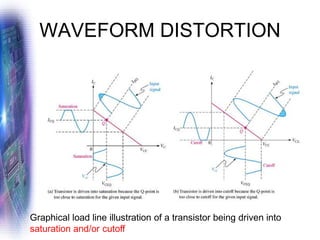
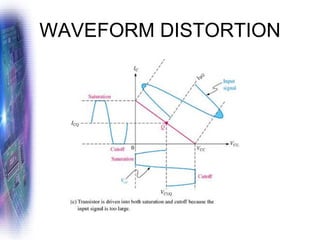
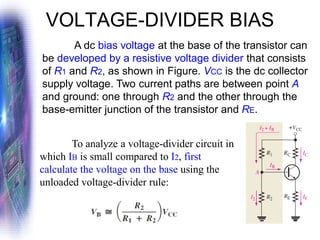
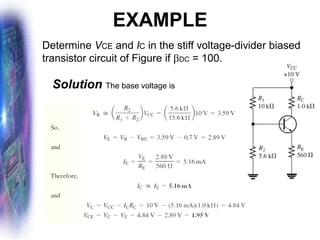
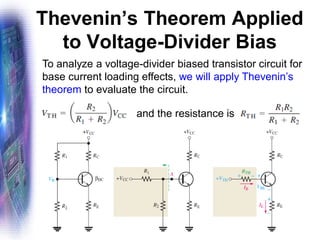
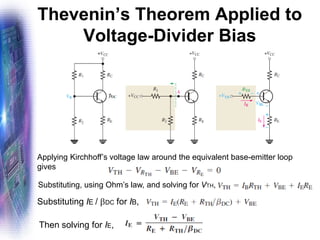
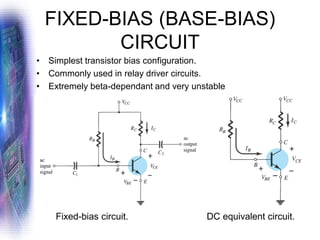
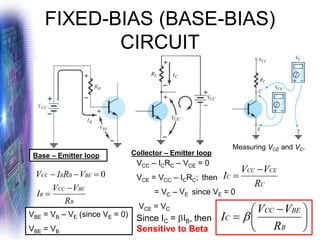
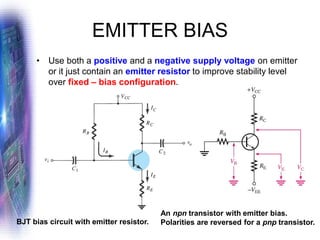
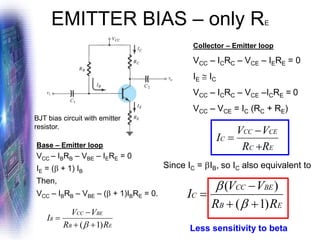
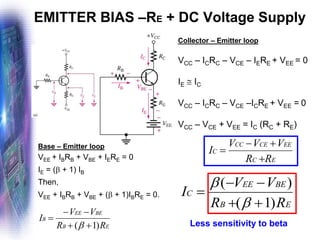
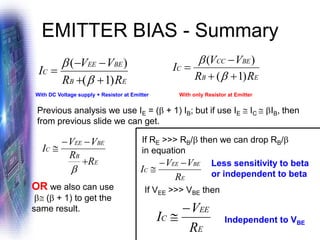
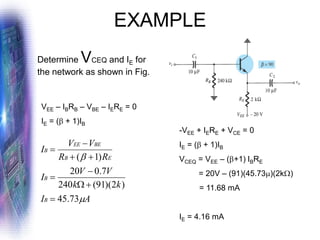
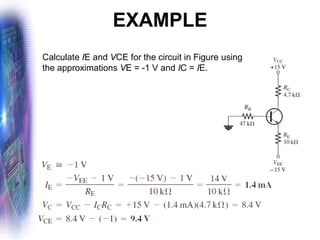
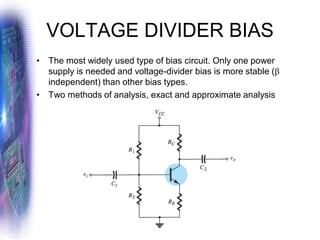
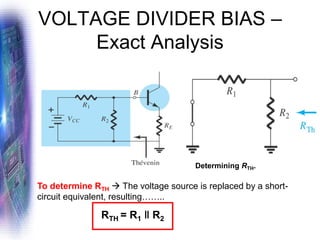
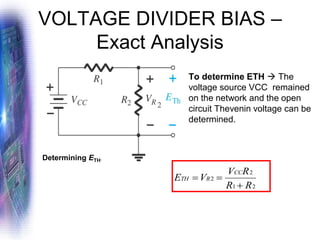
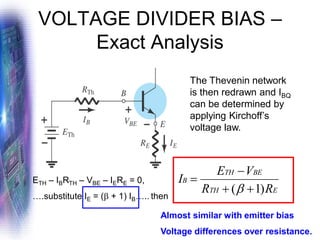
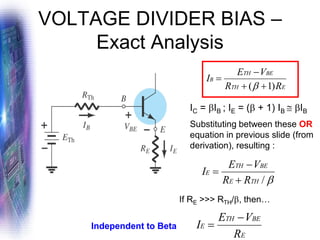
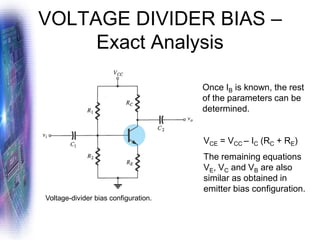
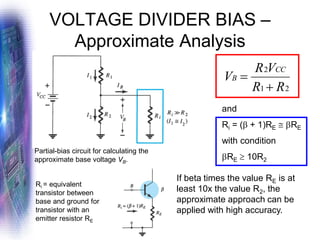
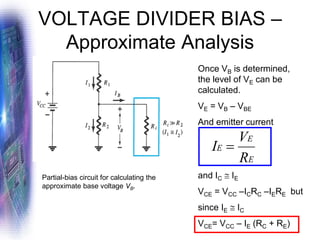
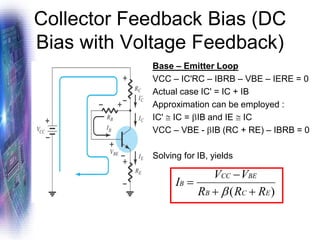
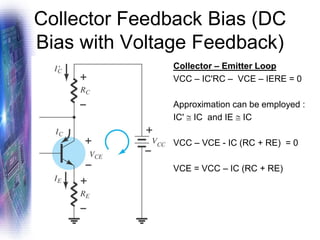
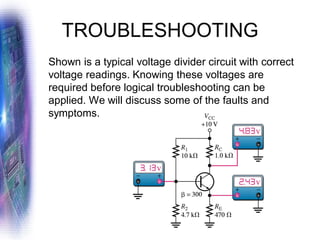
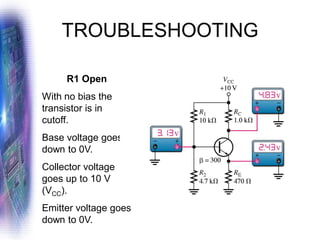
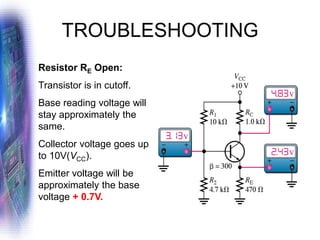
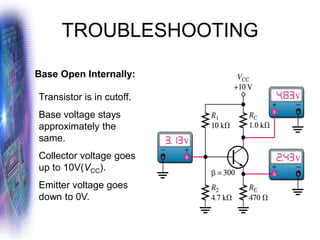
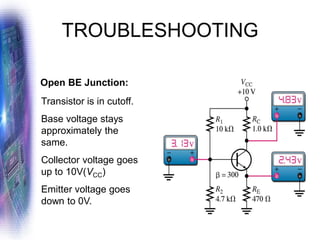
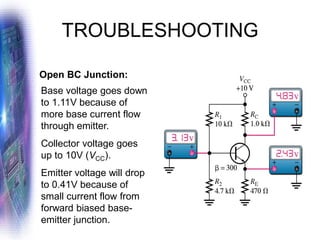
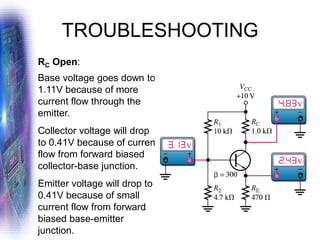
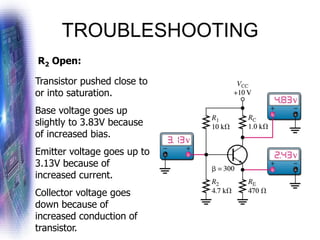
This document discusses various methods of biasing bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) for proper operation, including voltage-divider bias, emitter bias, and collector feedback bias. It explains that transistors must be biased to establish a stable operating point between cutoff and saturation. Various bias circuits are analyzed using Kirchhoff's laws and the transistor model. Key aspects of establishing bias, such as determining the quiescent point and load lines, as well as sources of instability and techniques to improve stability, are covered. Examples are provided to illustrate calculating important bias parameters.