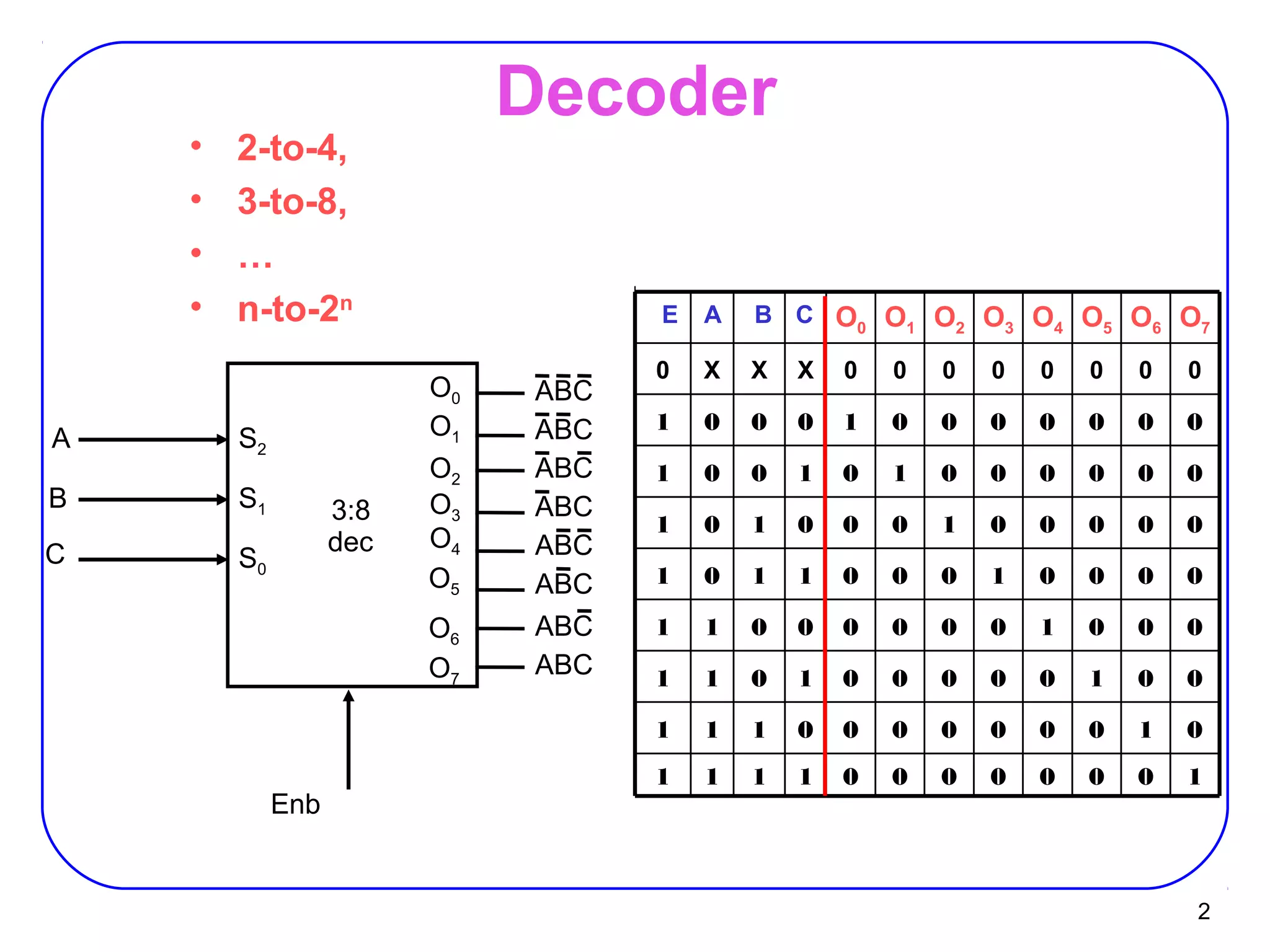
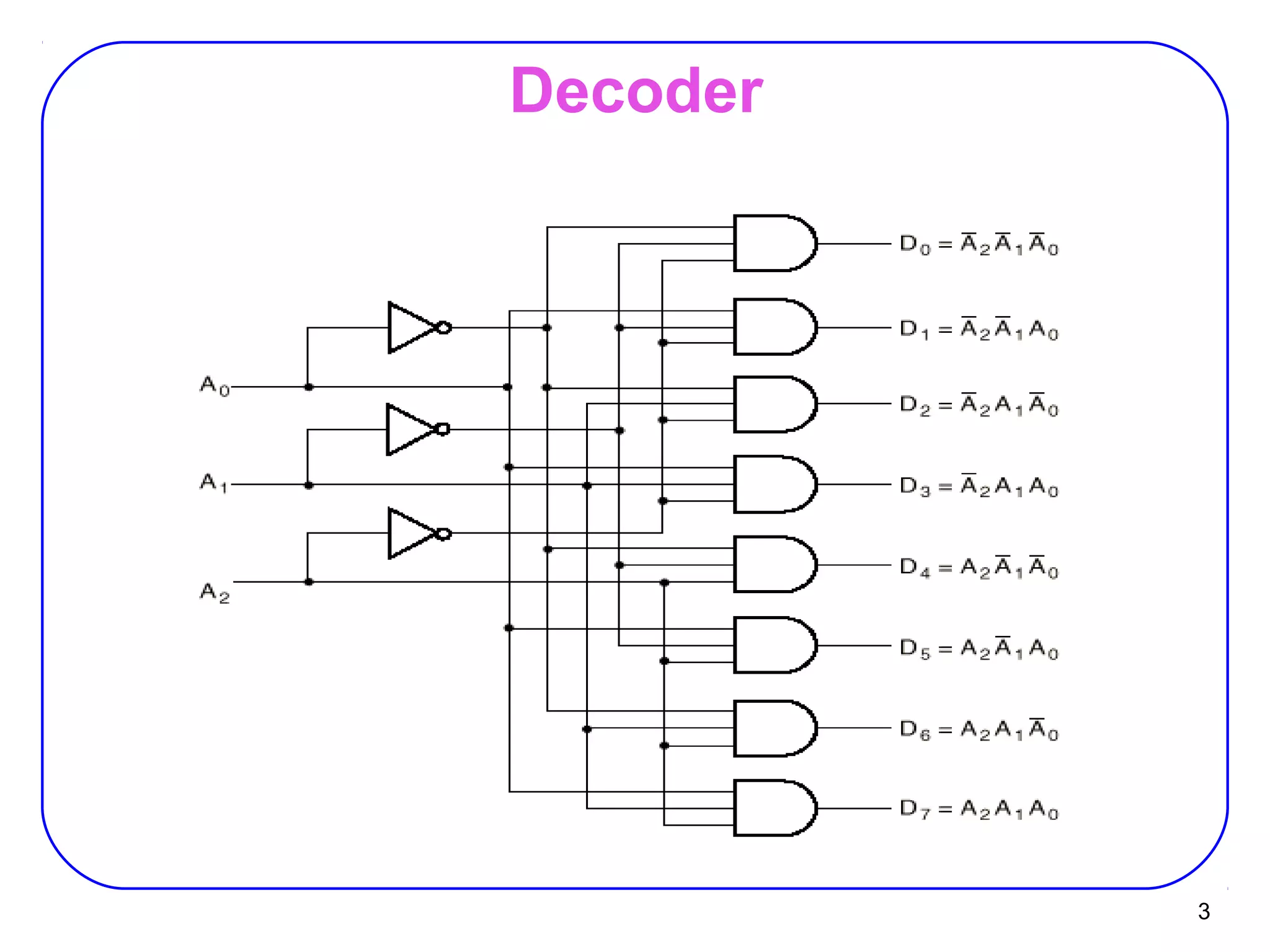
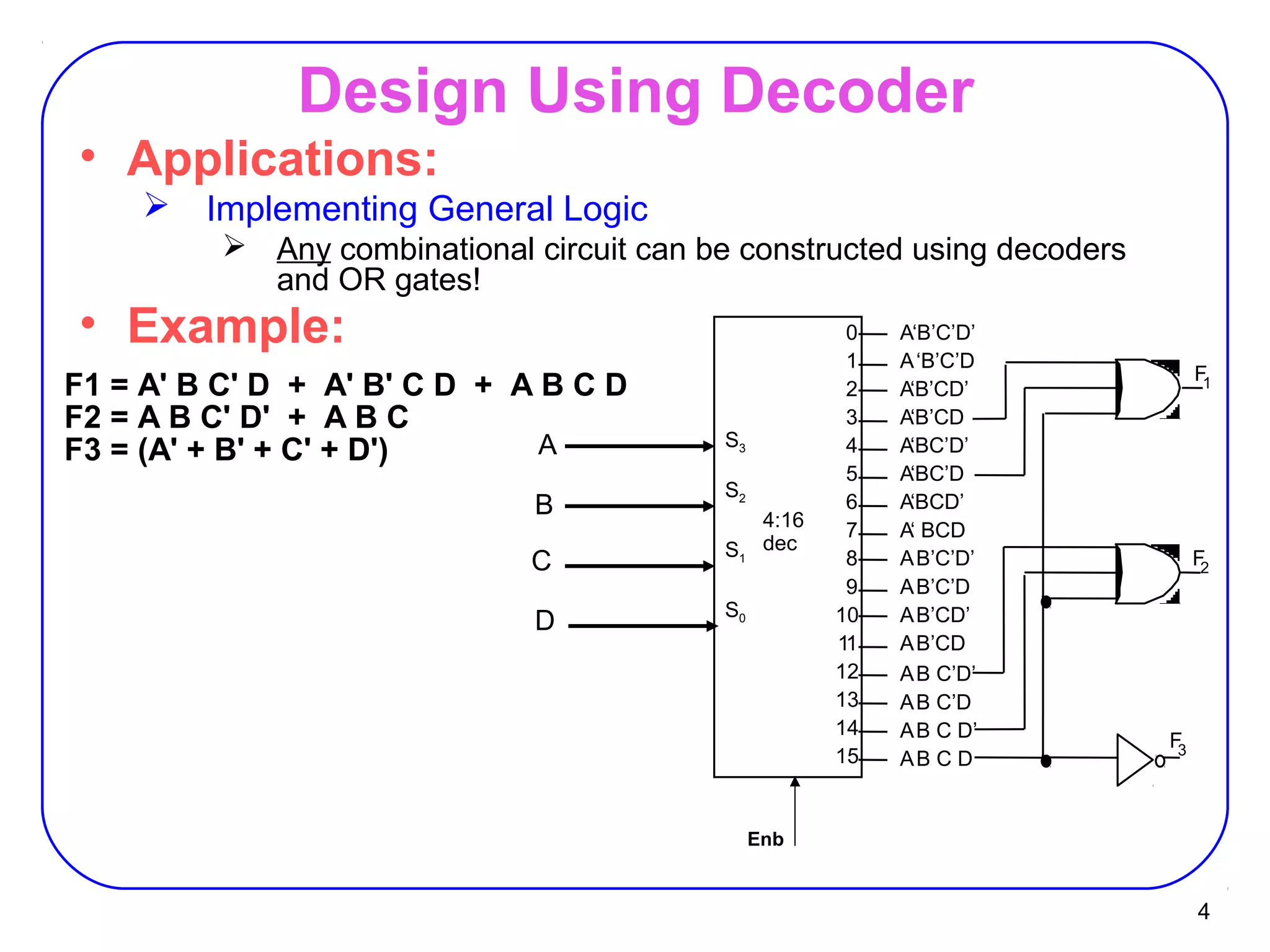
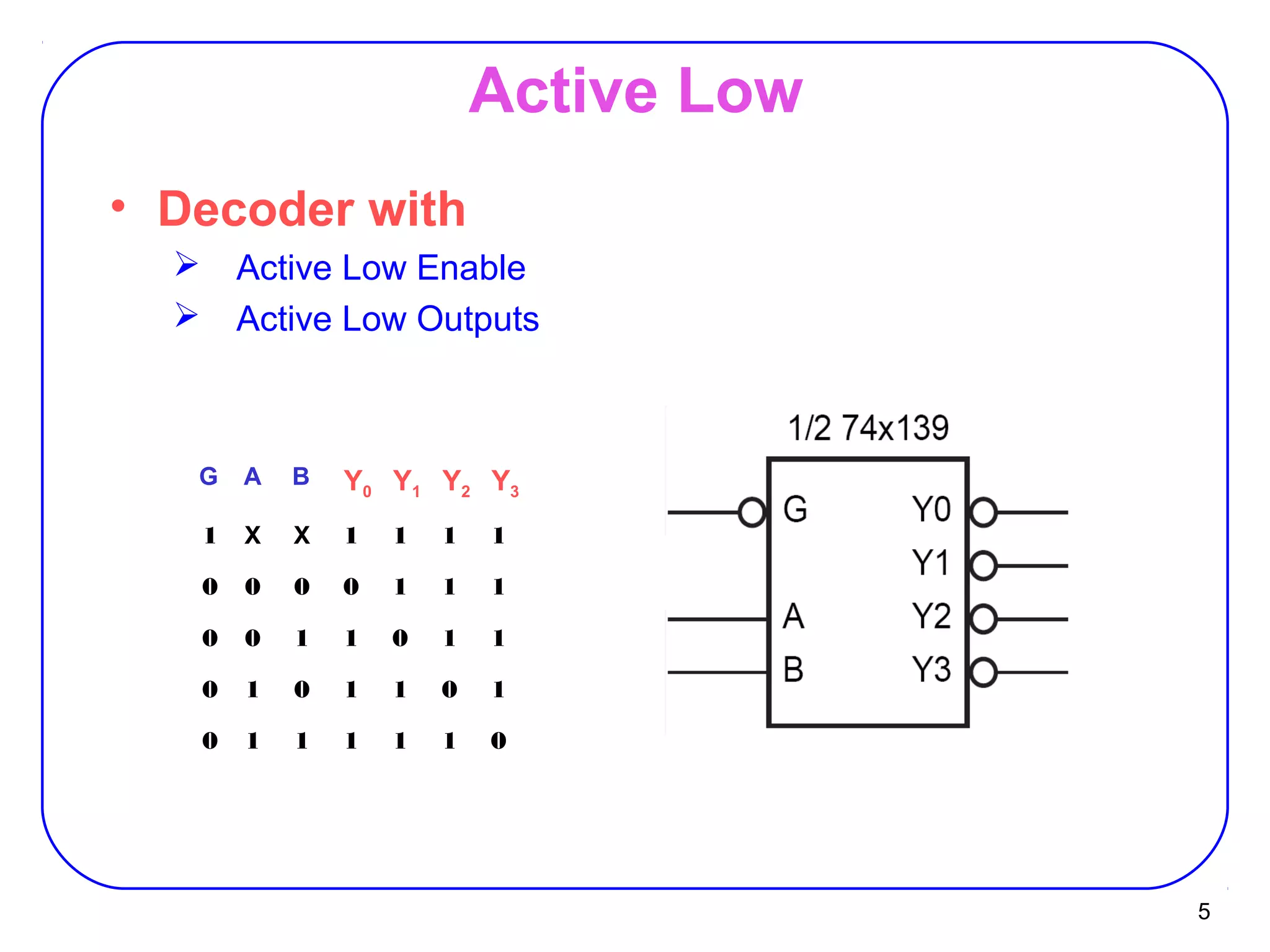
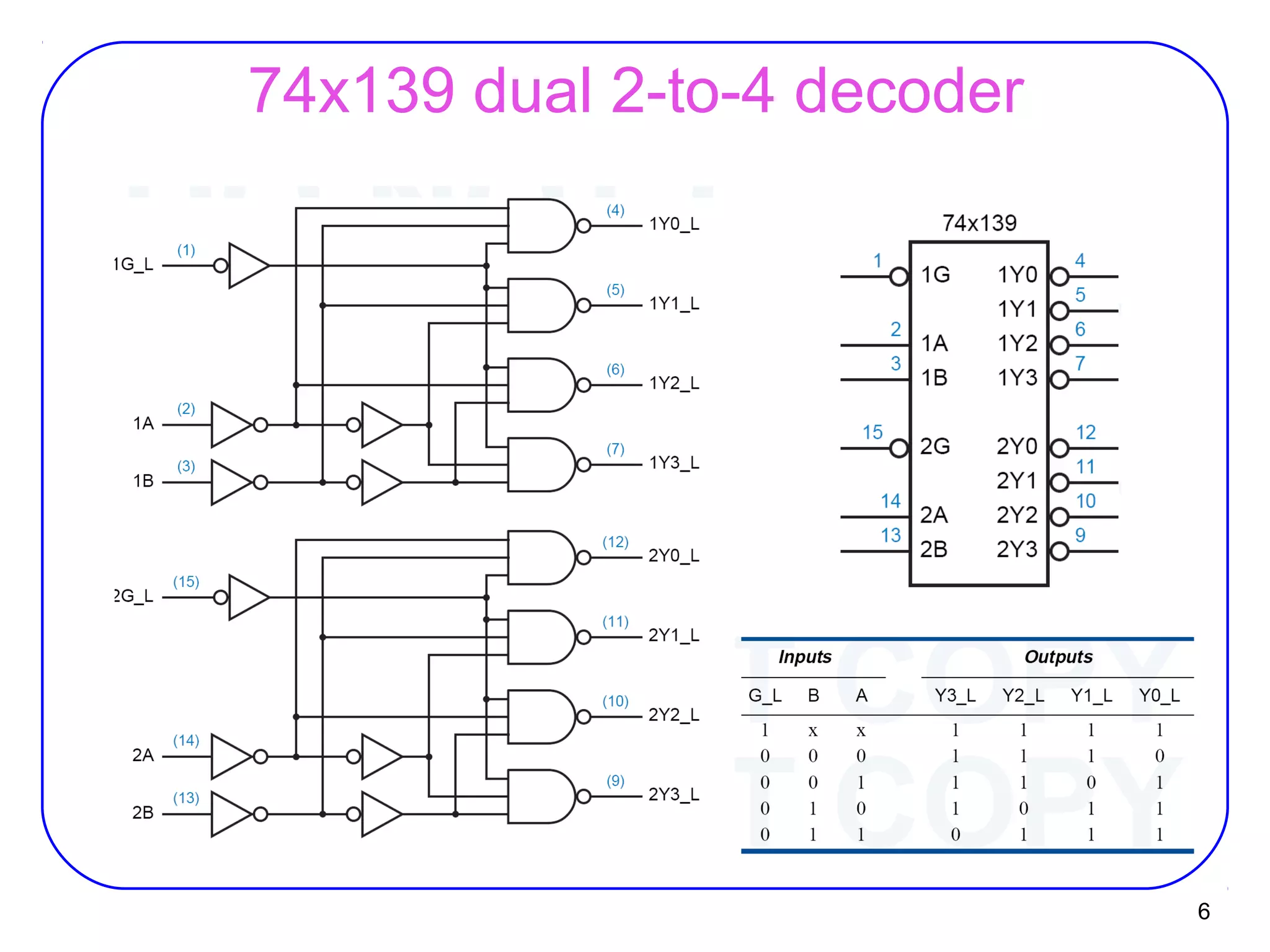
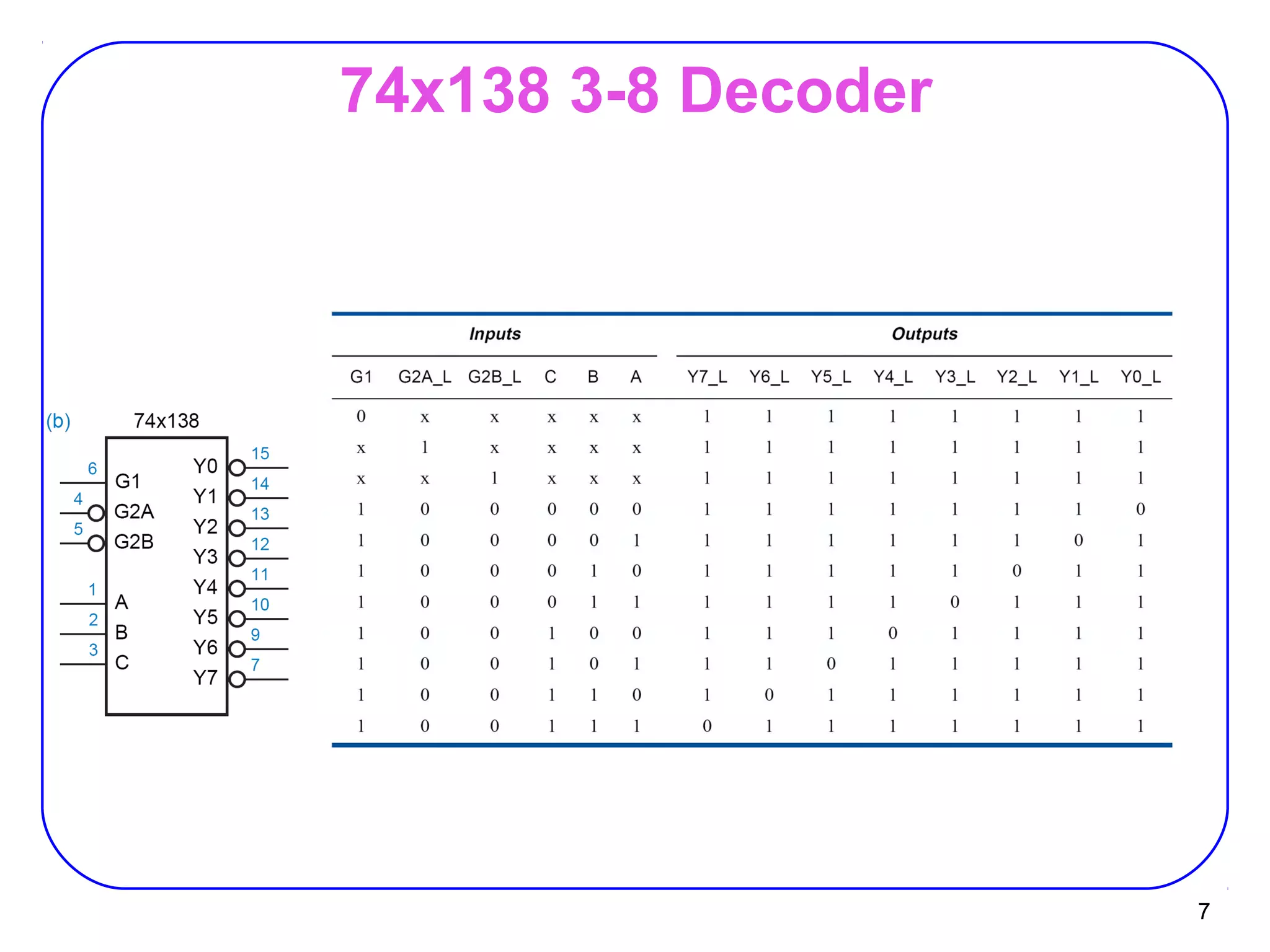
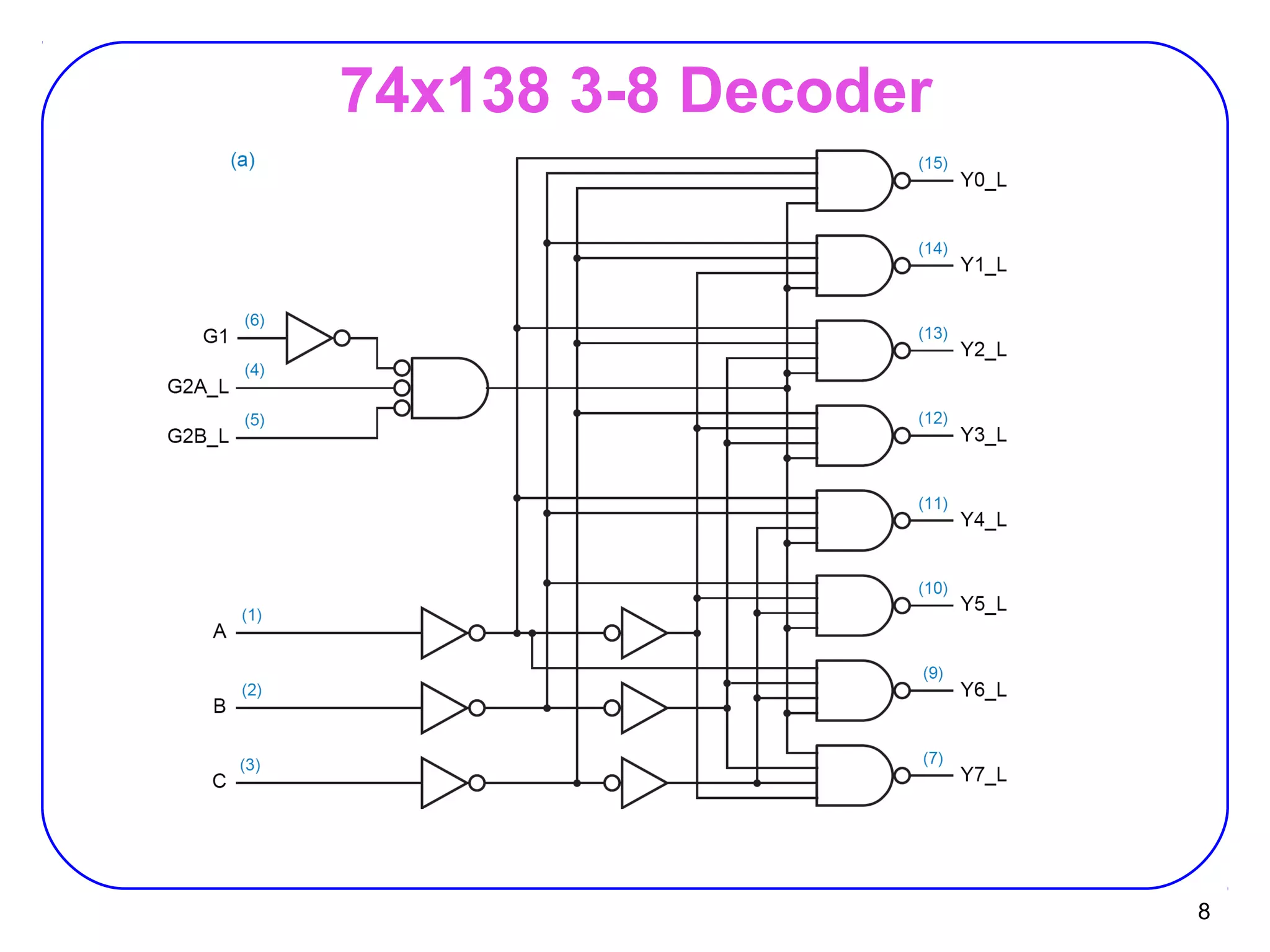
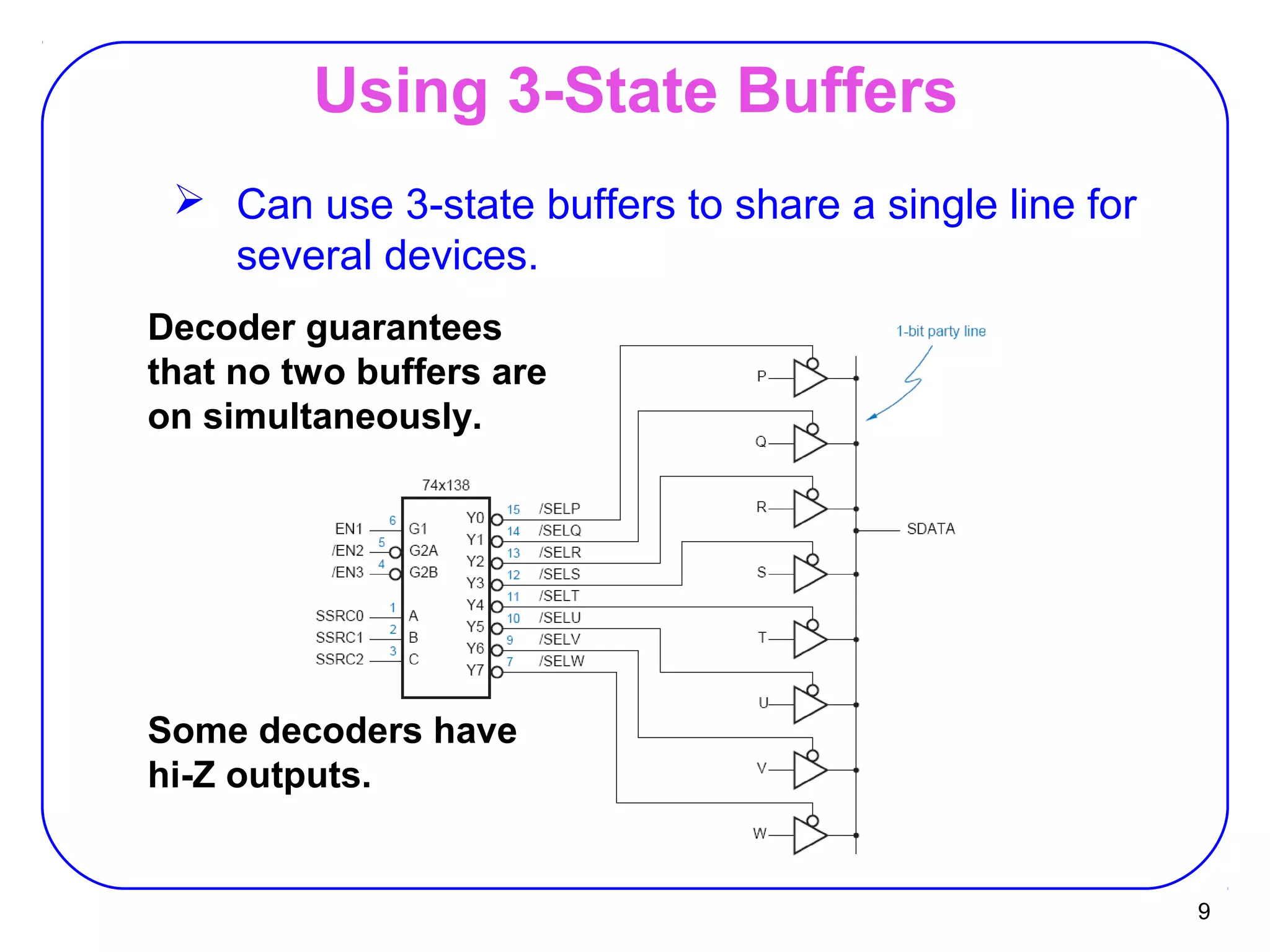
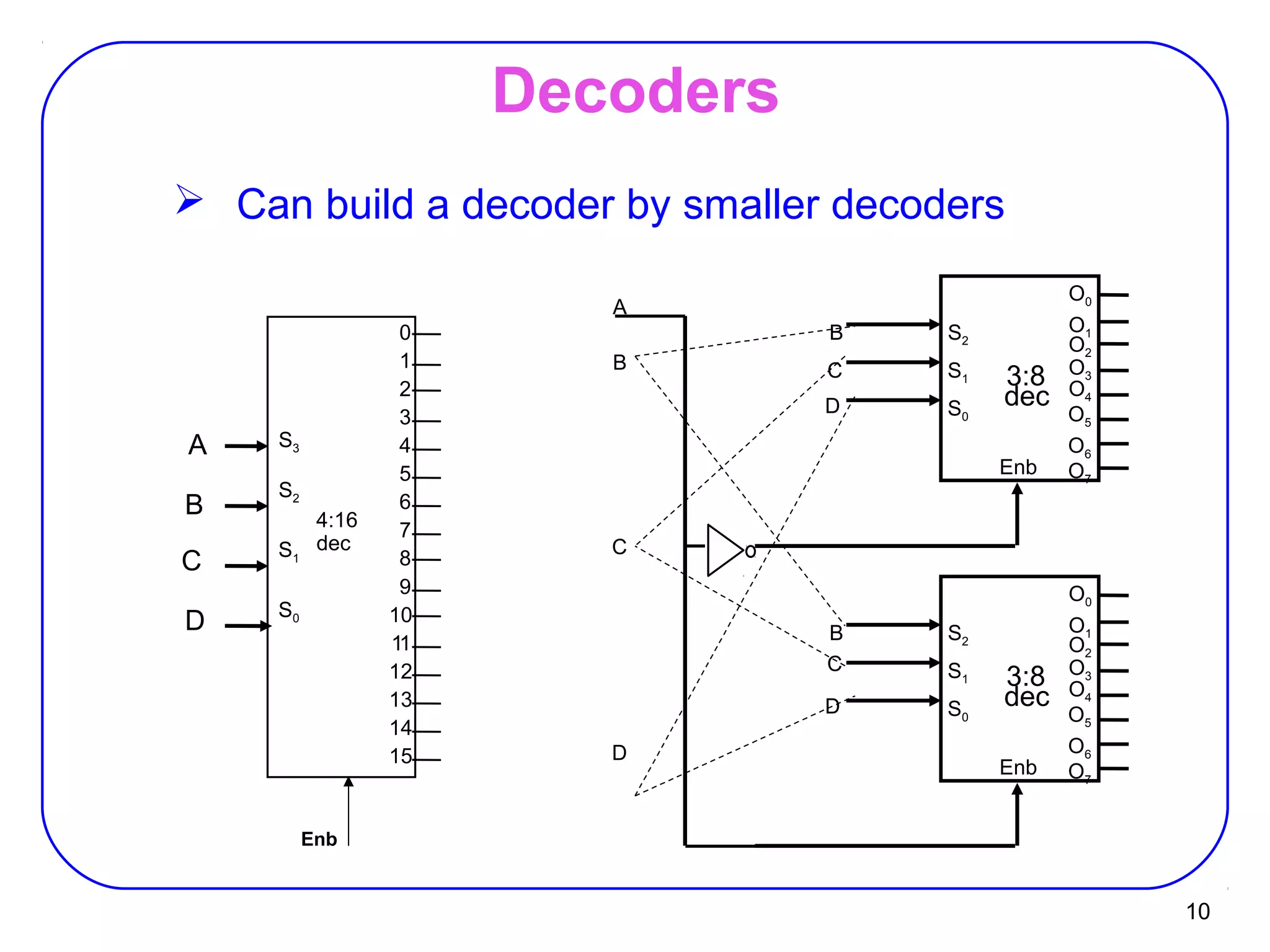
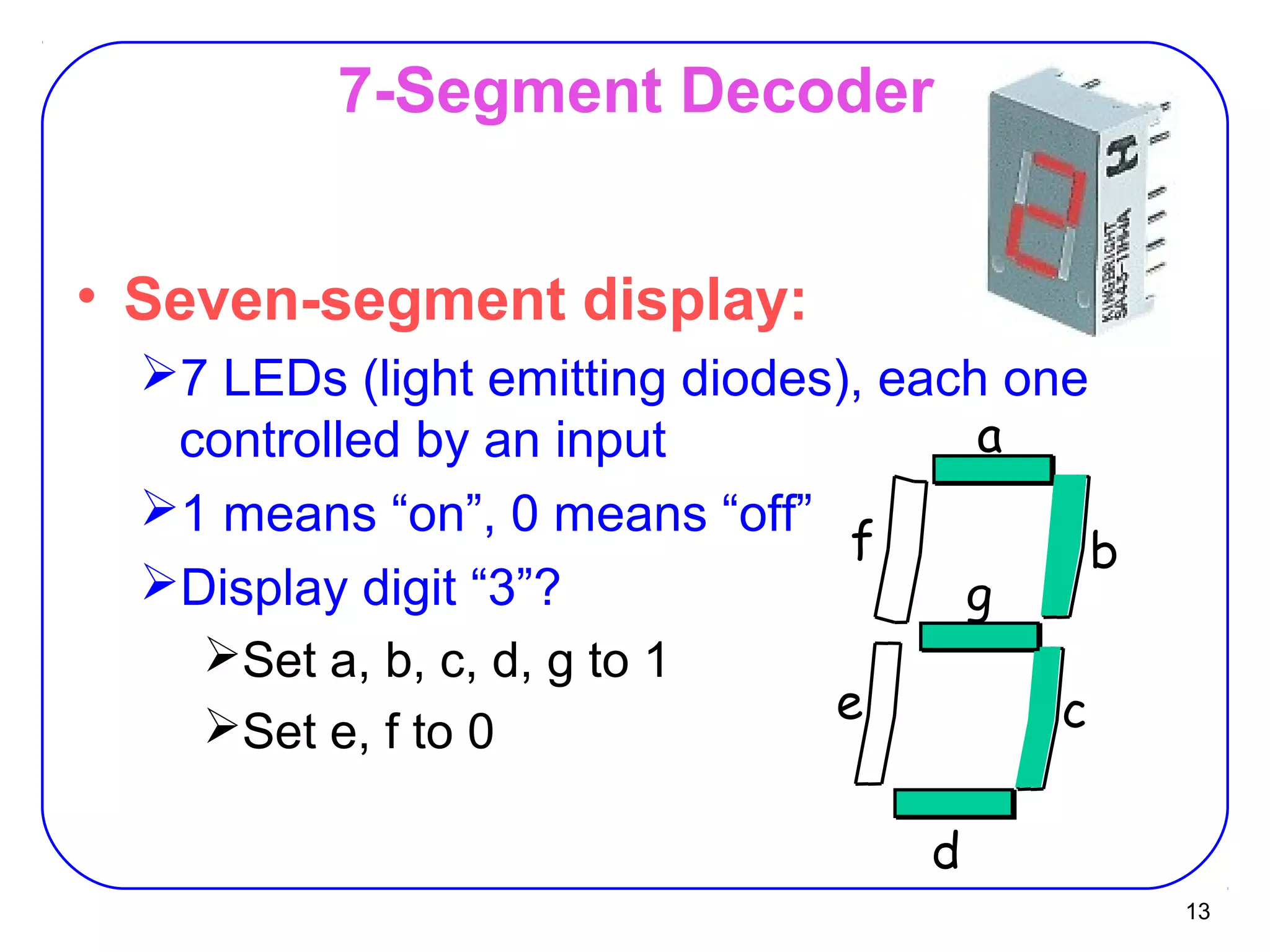
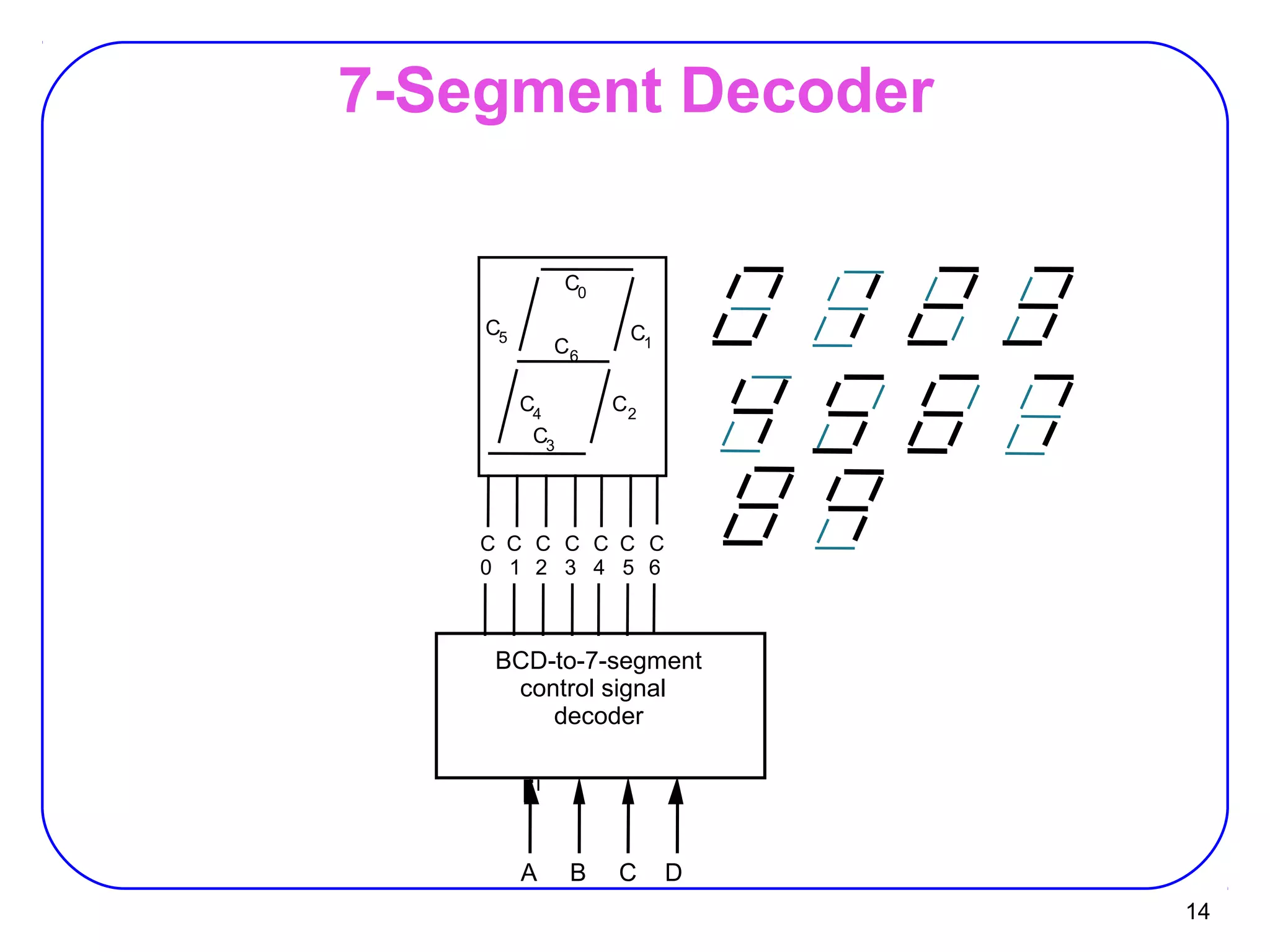
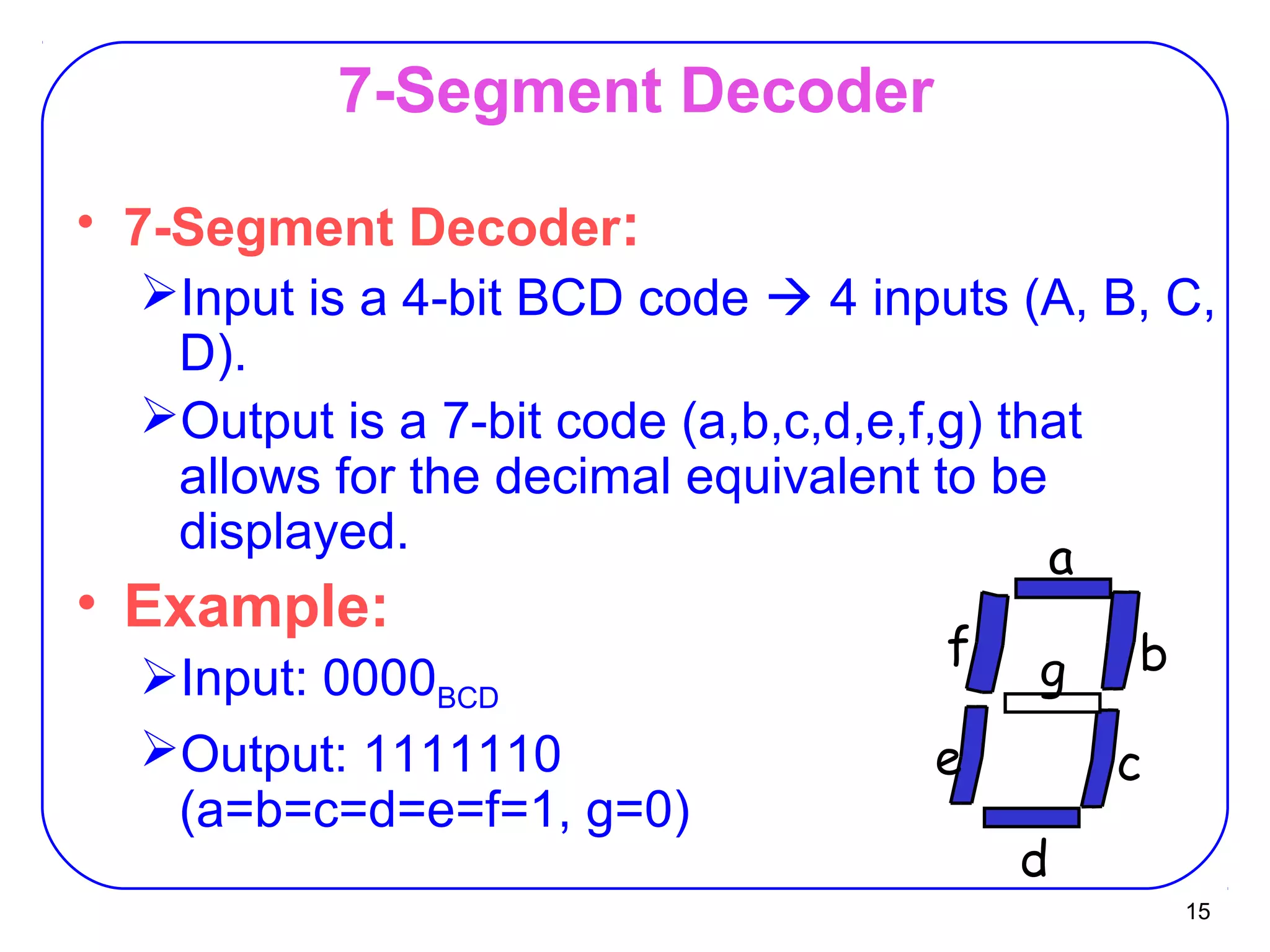
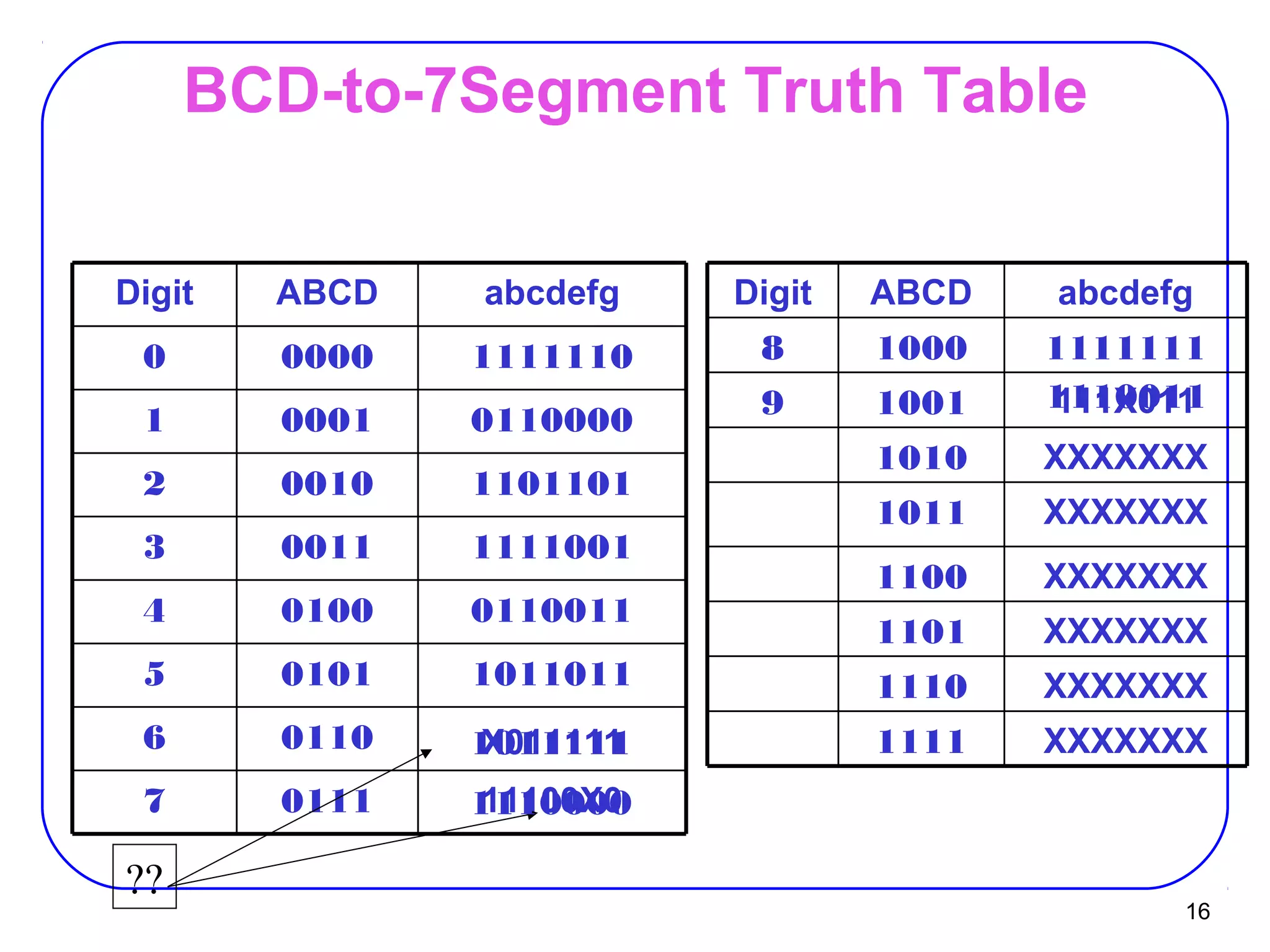
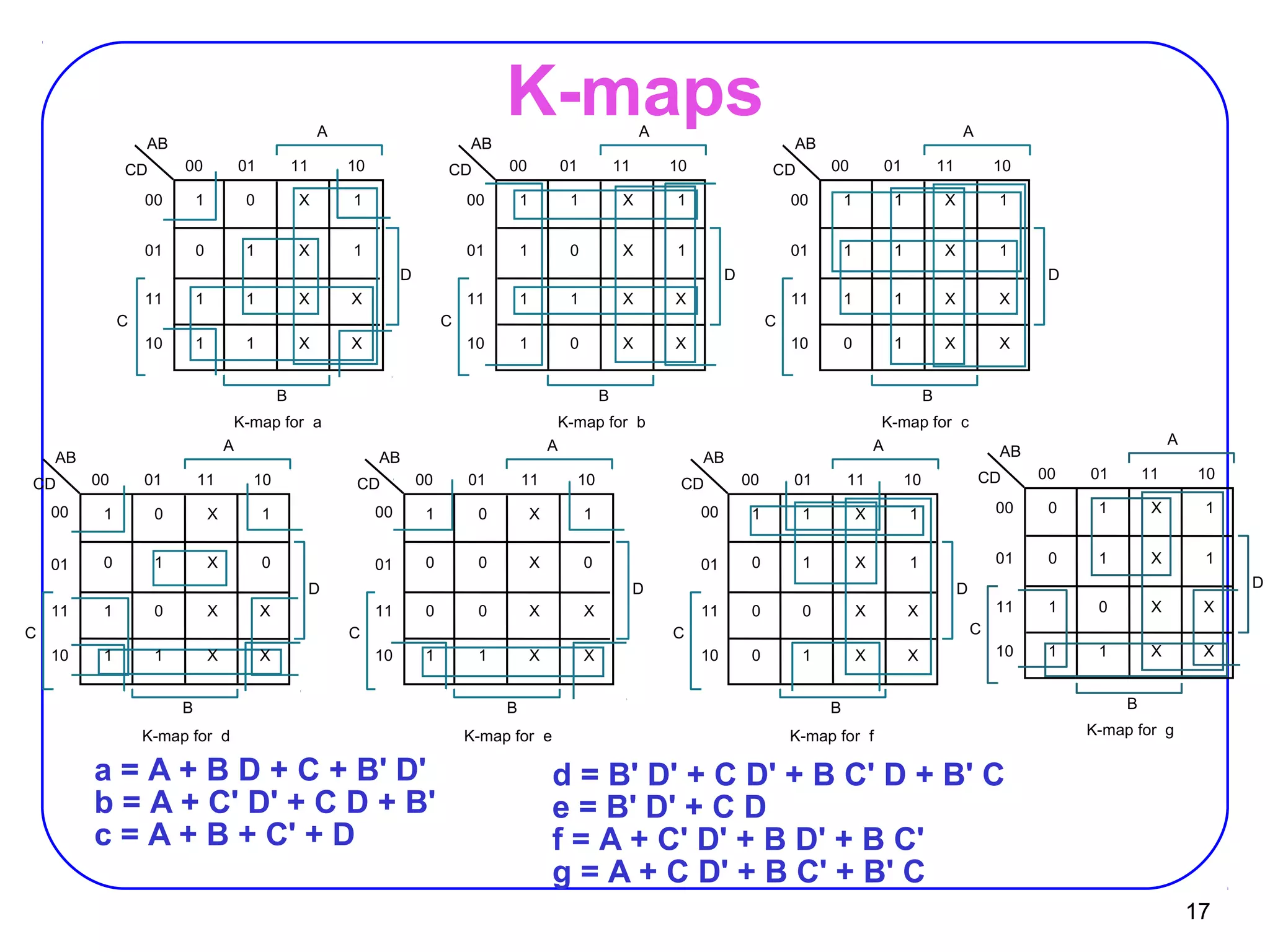
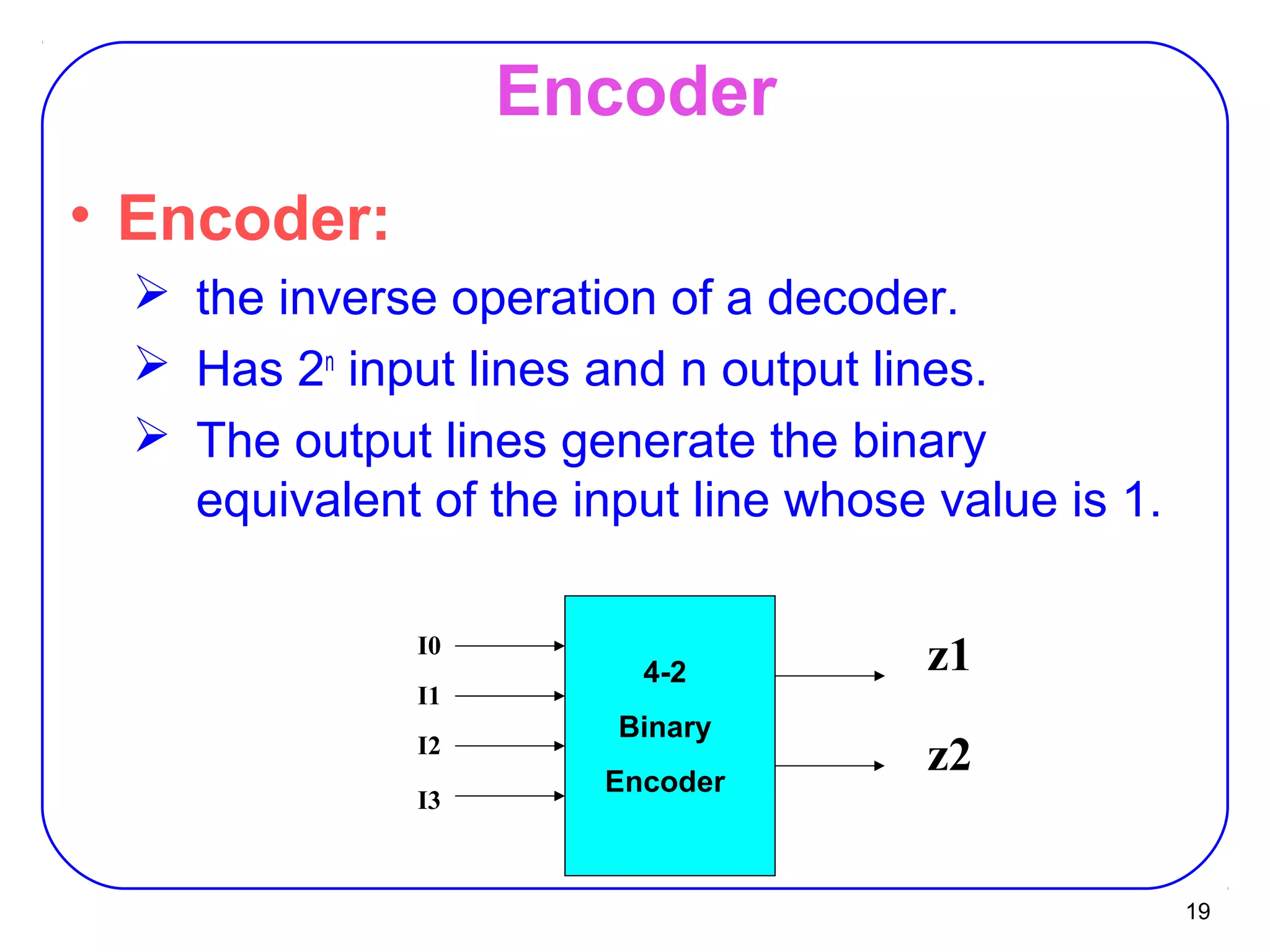
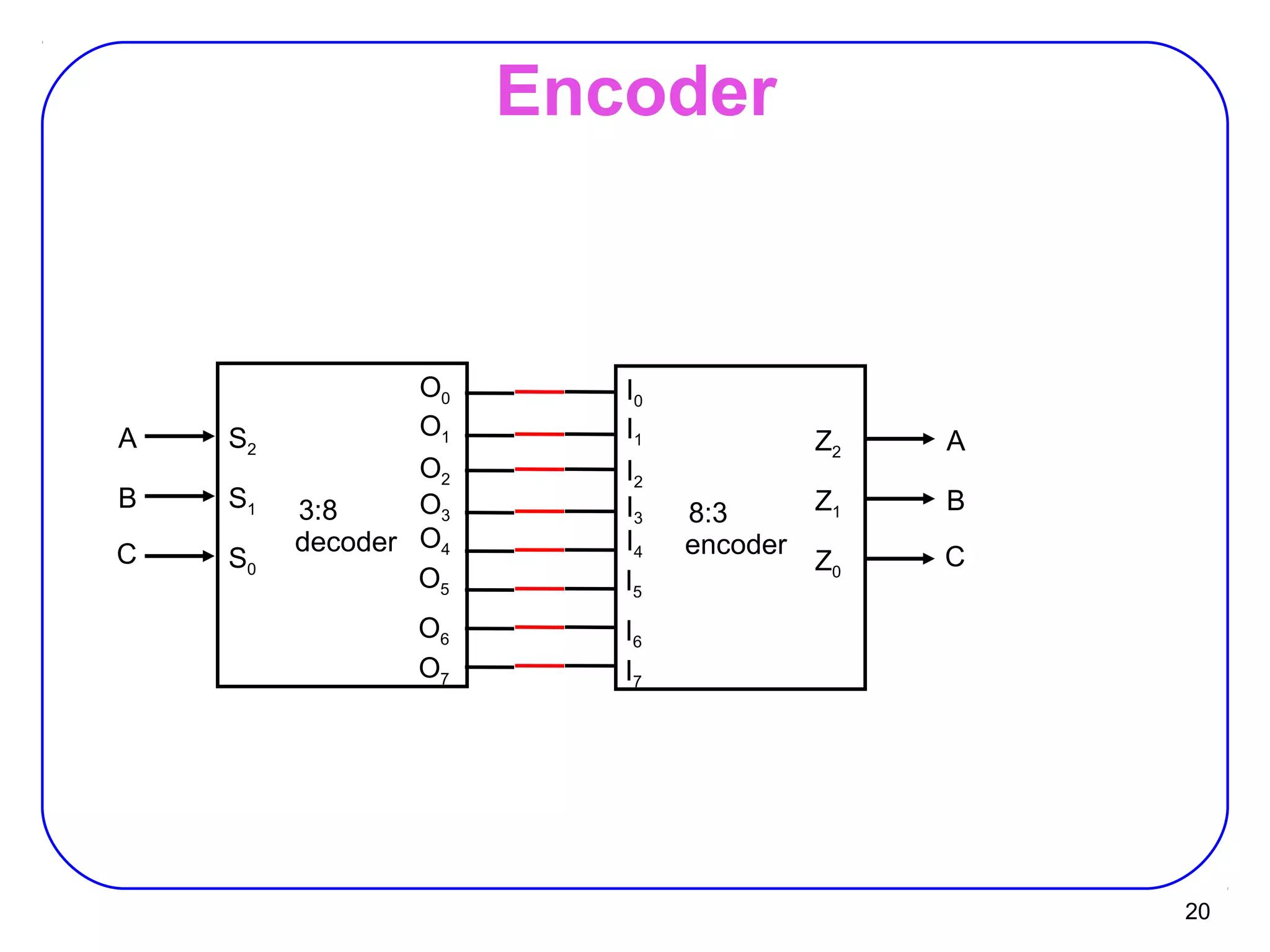
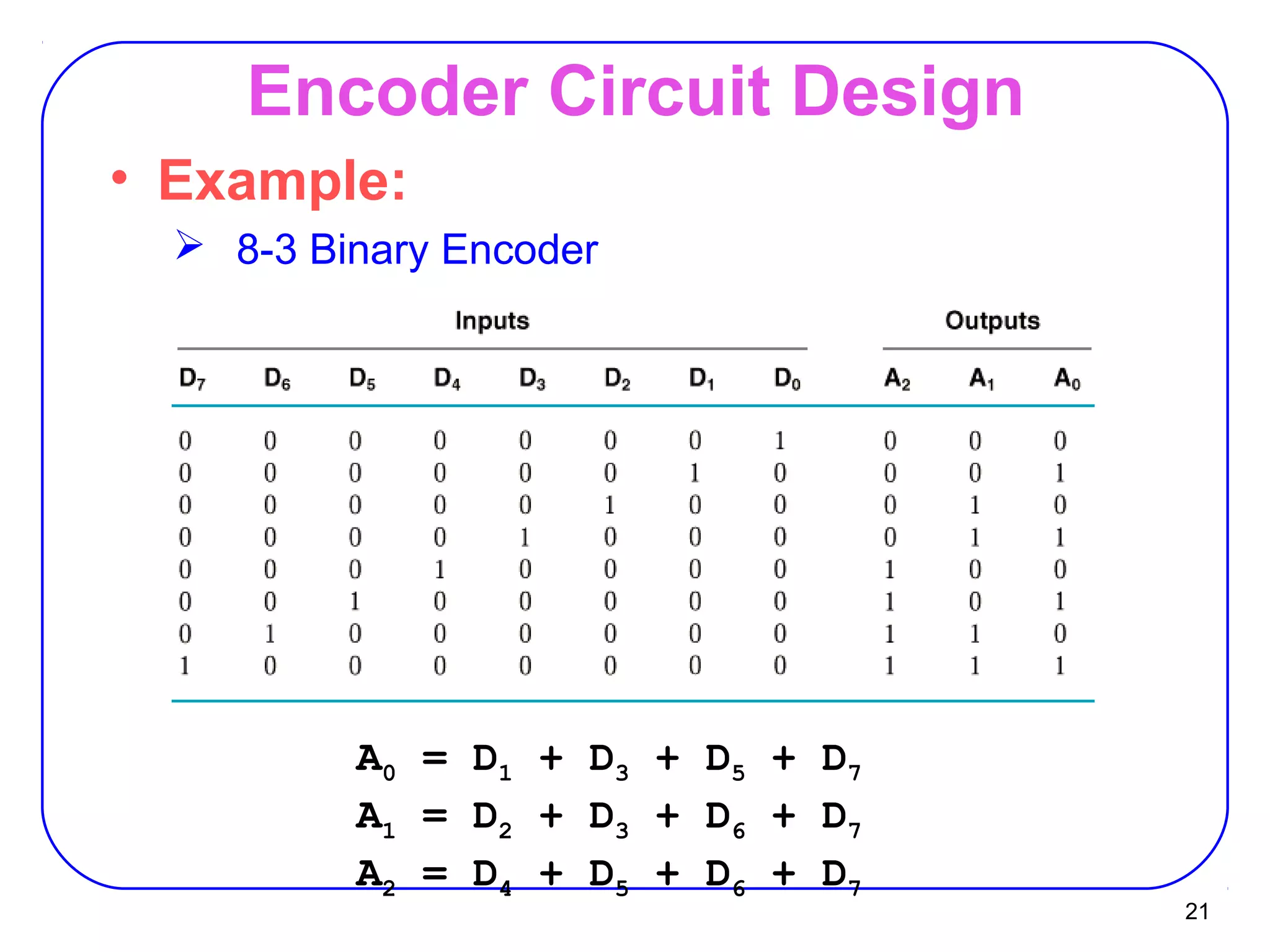
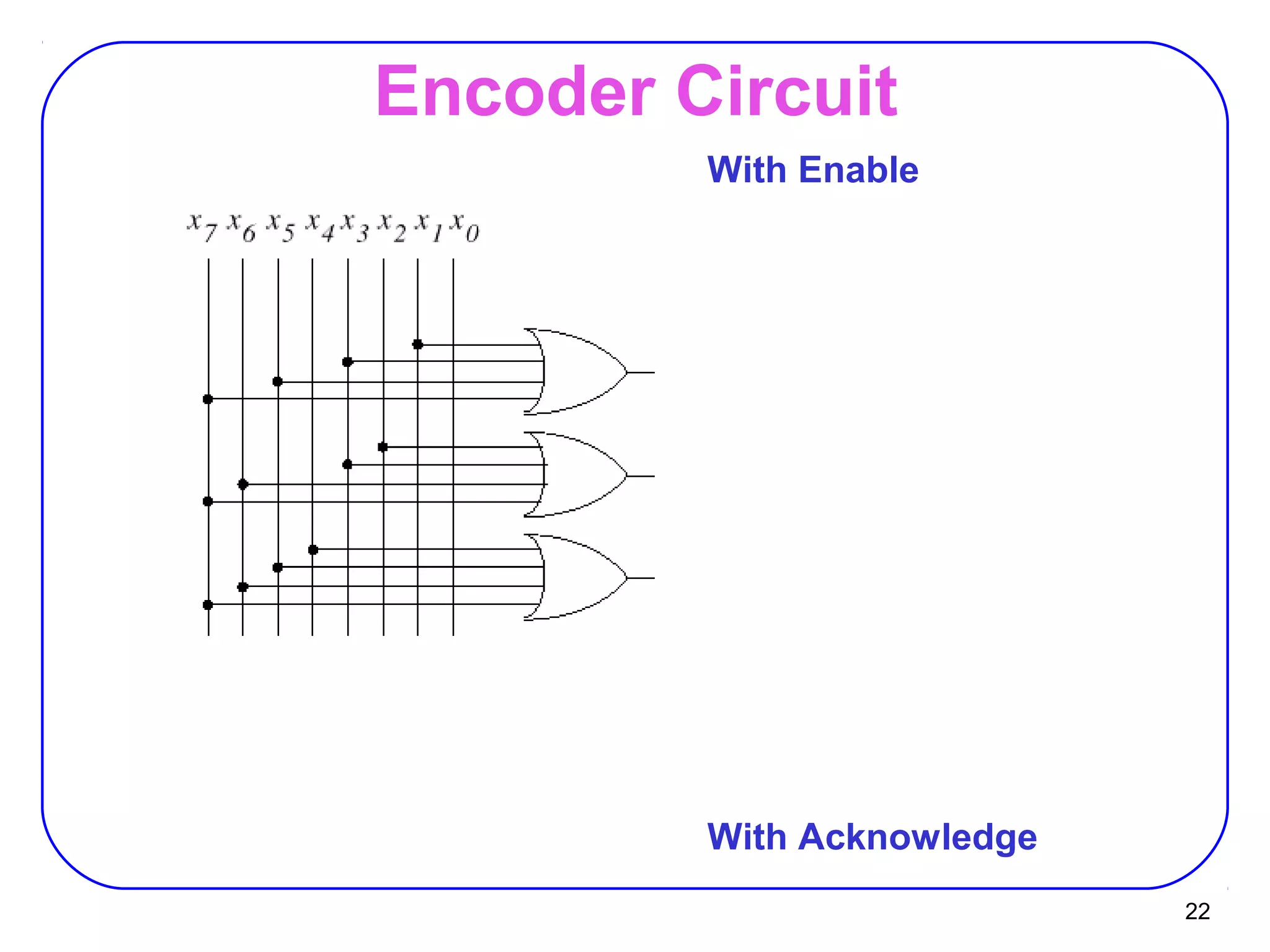
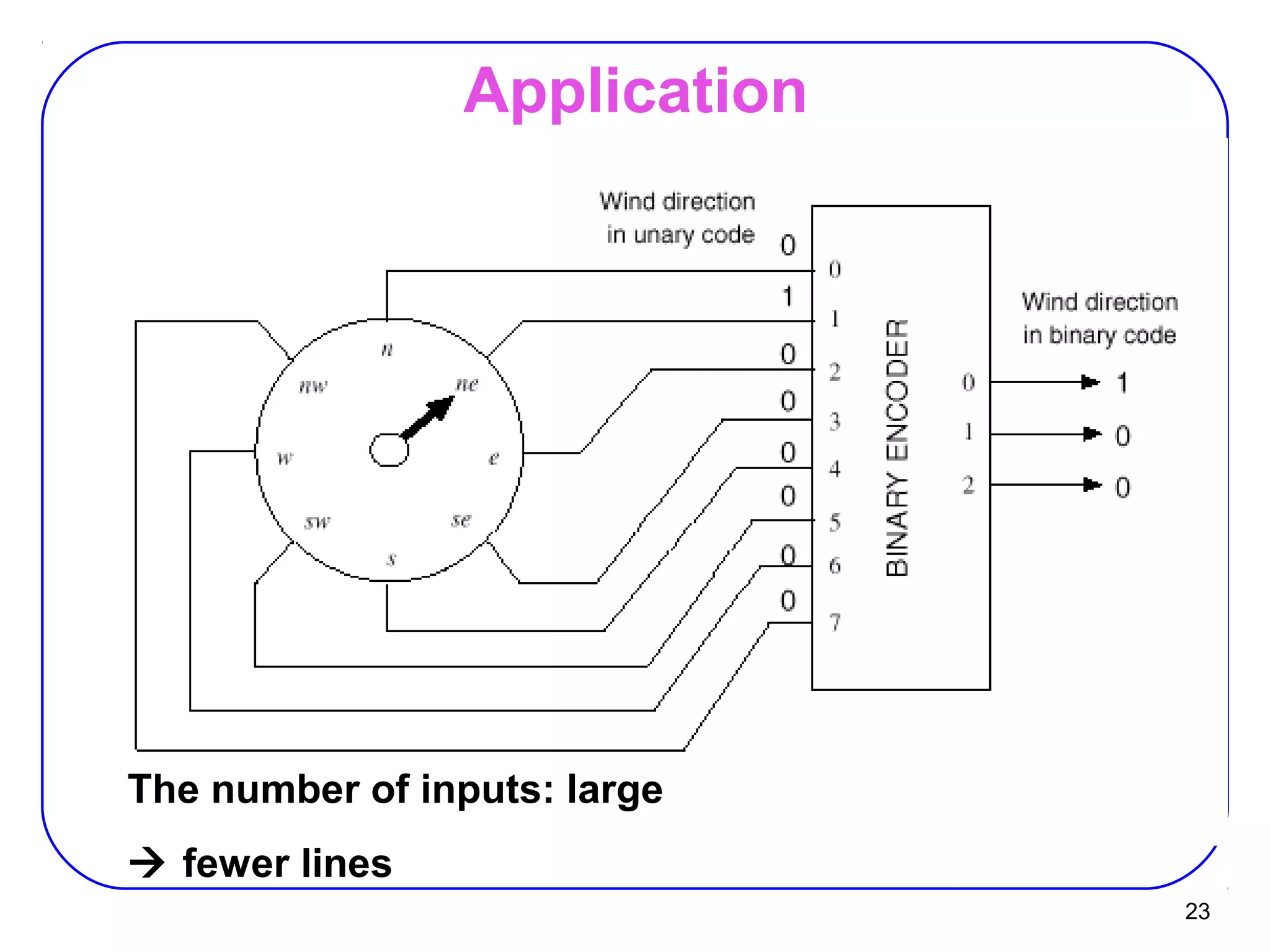
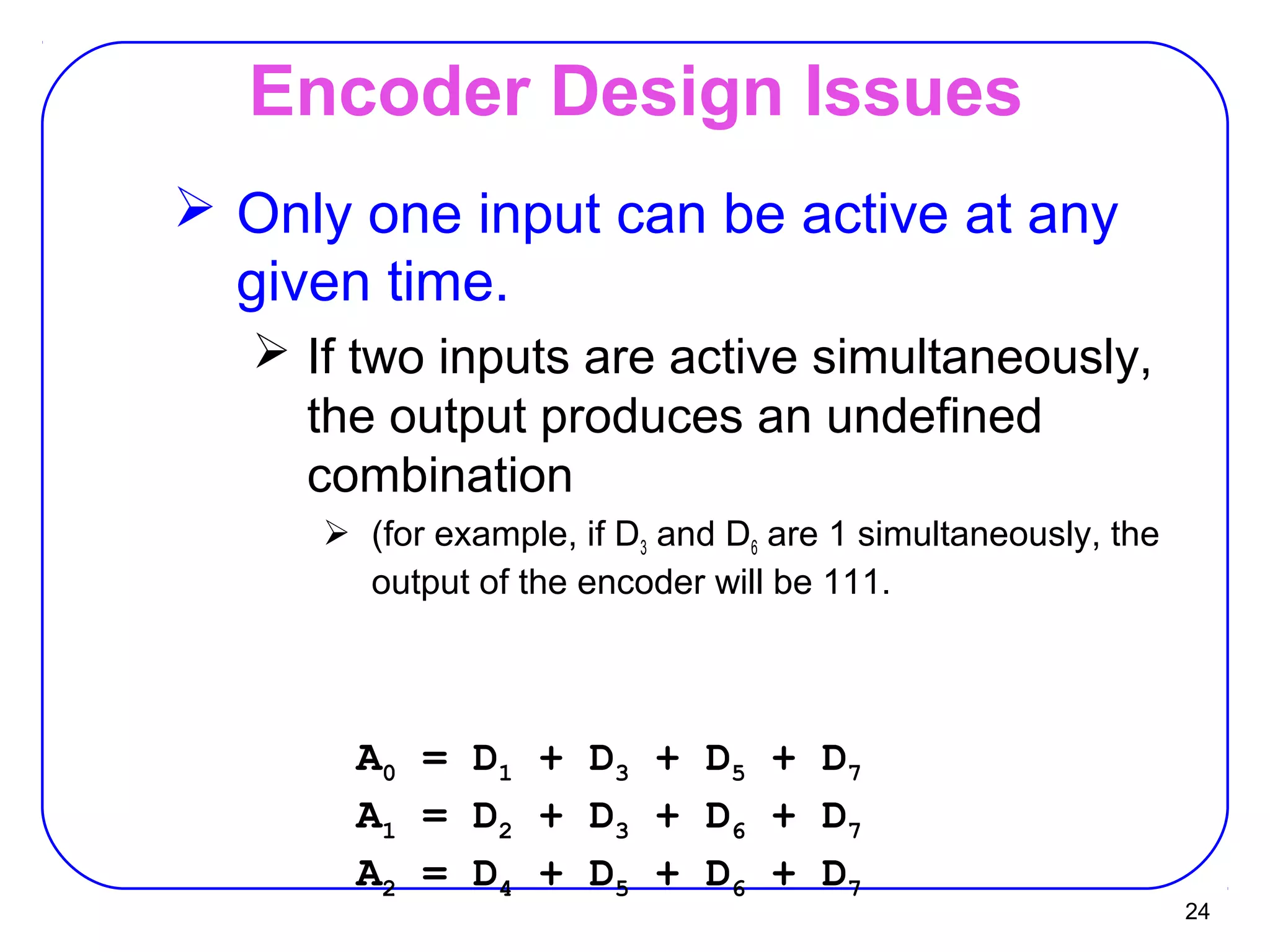
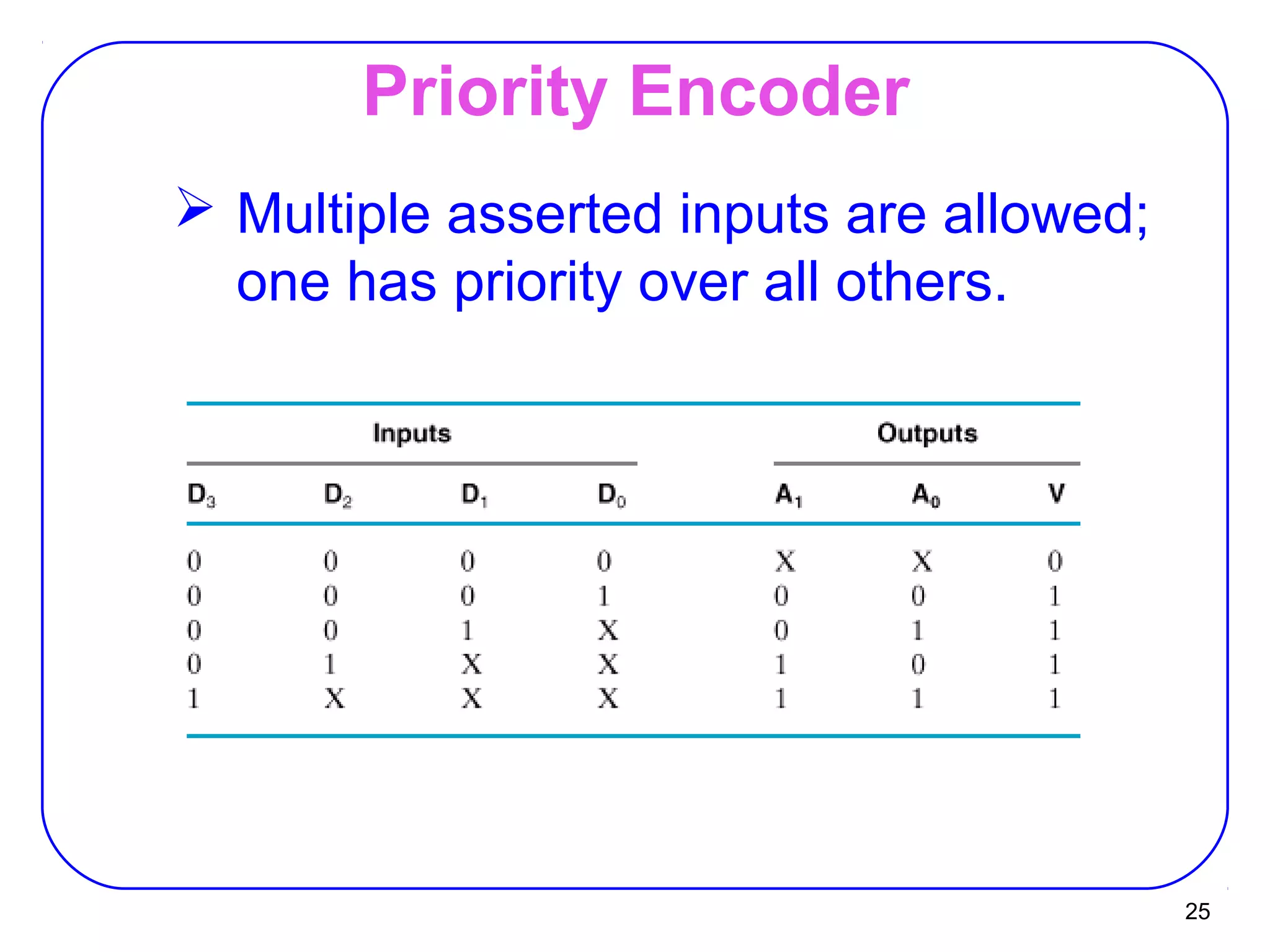
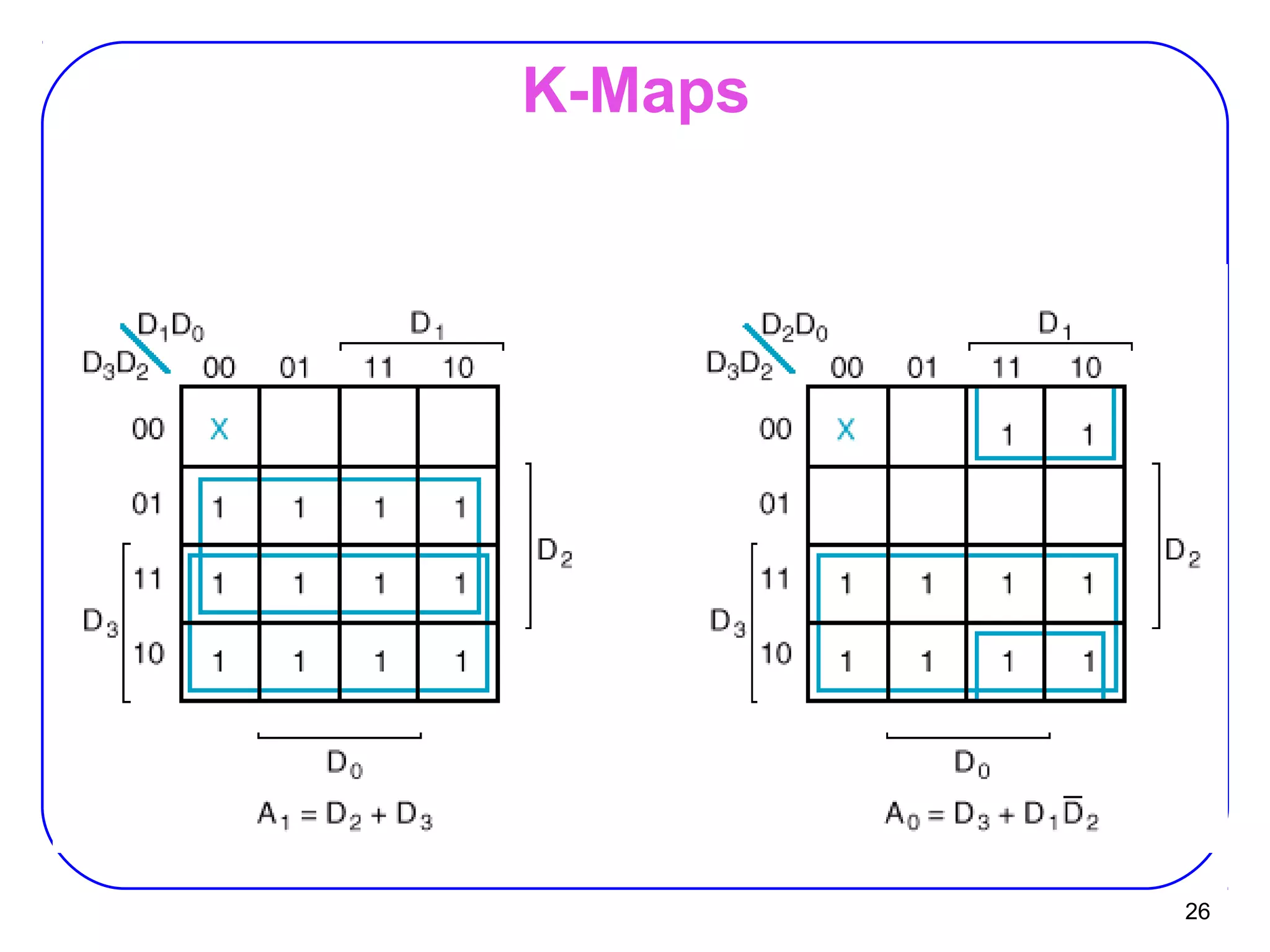
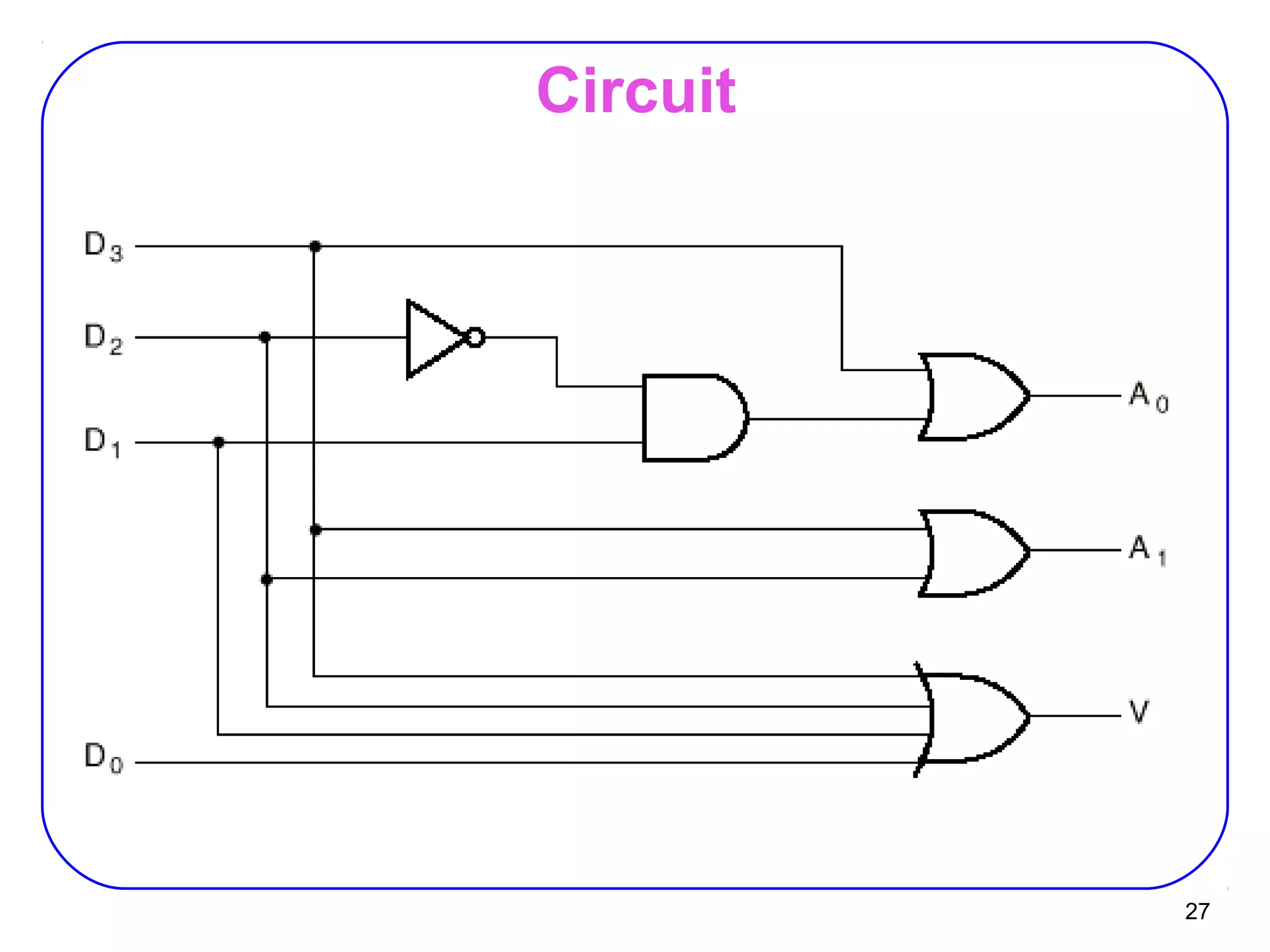
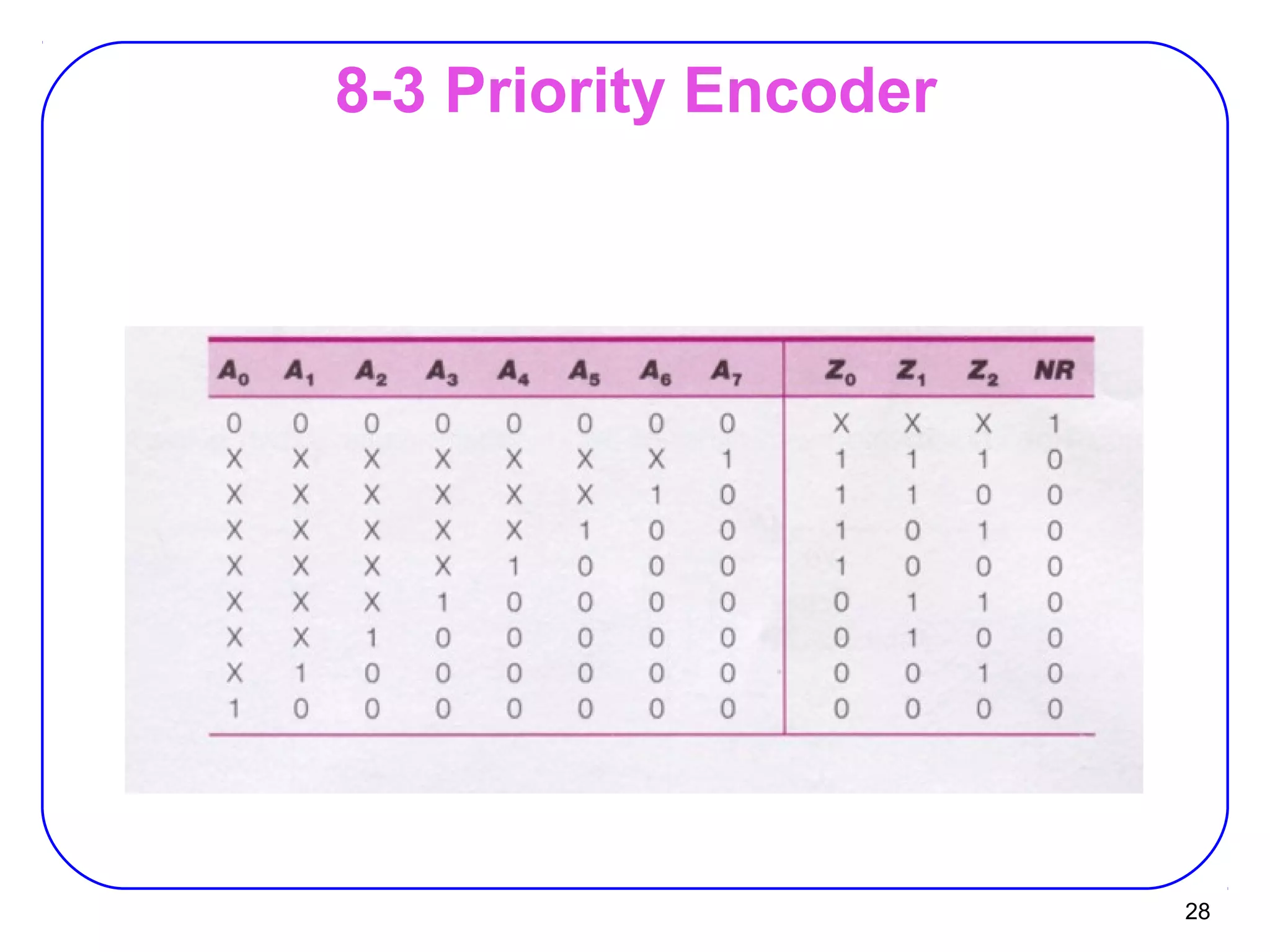
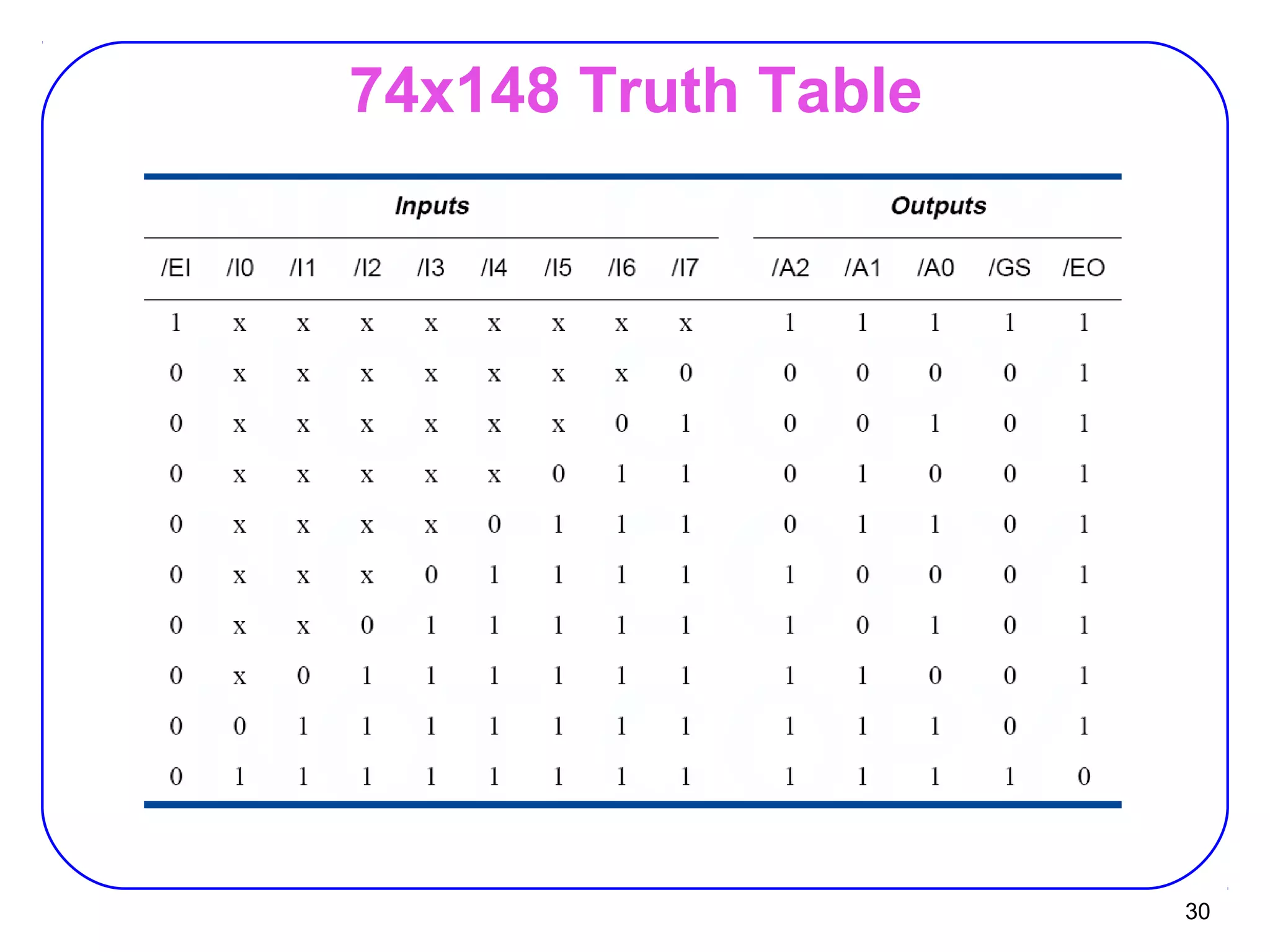
The document describes decoders and encoders. It begins by explaining what a decoder is, providing examples of 2-to-4 and 3-to-8 decoders. It then discusses how decoders can be used to implement general logic and combinational circuits using decoders and OR gates. The document proceeds to describe specific decoder chips like the 74x139 and 74x138 decoders. It also discusses using 3-state buffers with decoders and building decoders from smaller decoders. The document then shifts to discussing encoders, 7-segment decoders, truth tables, and K-maps in the design of decoders and encoders. It concludes by discussing priority encoders and the 74x148 priority encoder chip.