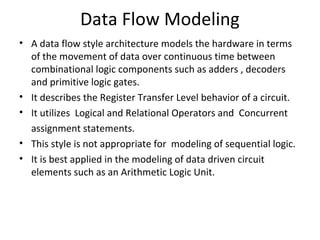
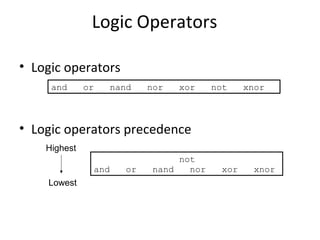
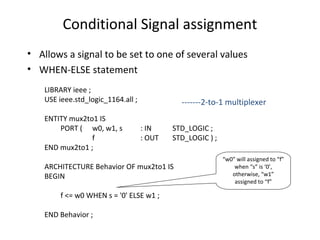
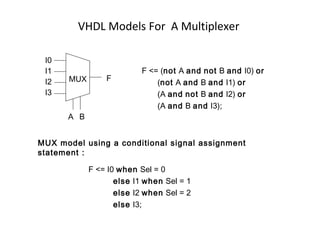
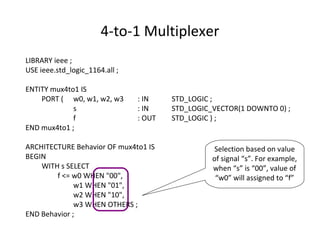
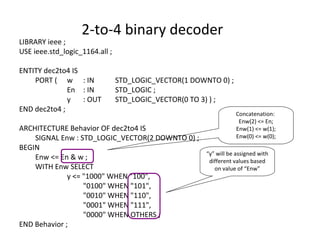
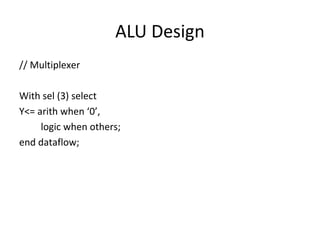
The document describes data flow modeling in VHDL. It discusses how data flow style architecture models hardware in terms of the movement of data over continuous time between combinational logic components. It also describes how concurrent signal assignment statements can be used to model simple combinational logic. Examples provided include half adder, full adder, comparator, multiplexer, decoder, and arithmetic logic unit designs modeled using data flow style and concurrent signal assignments.