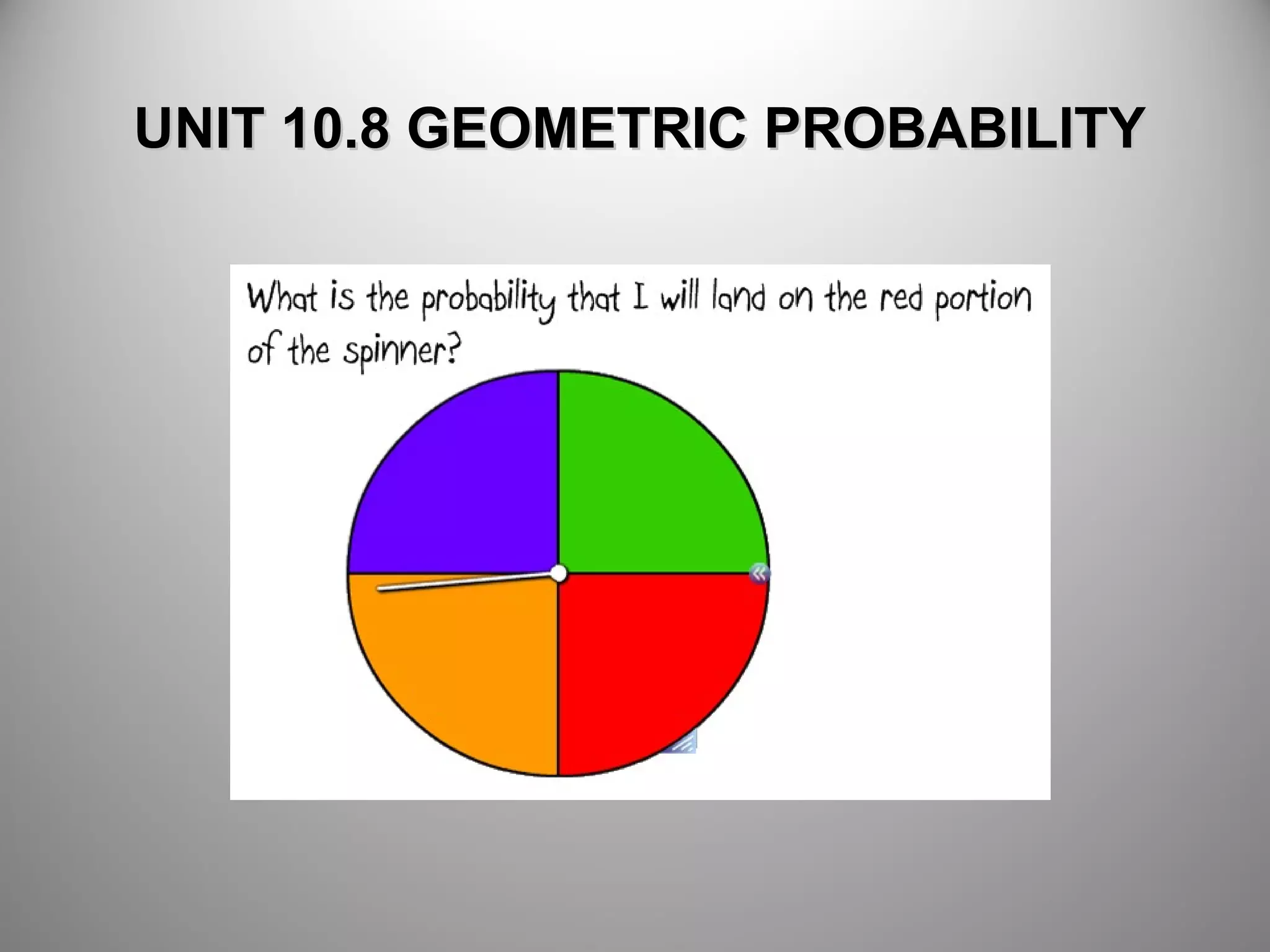
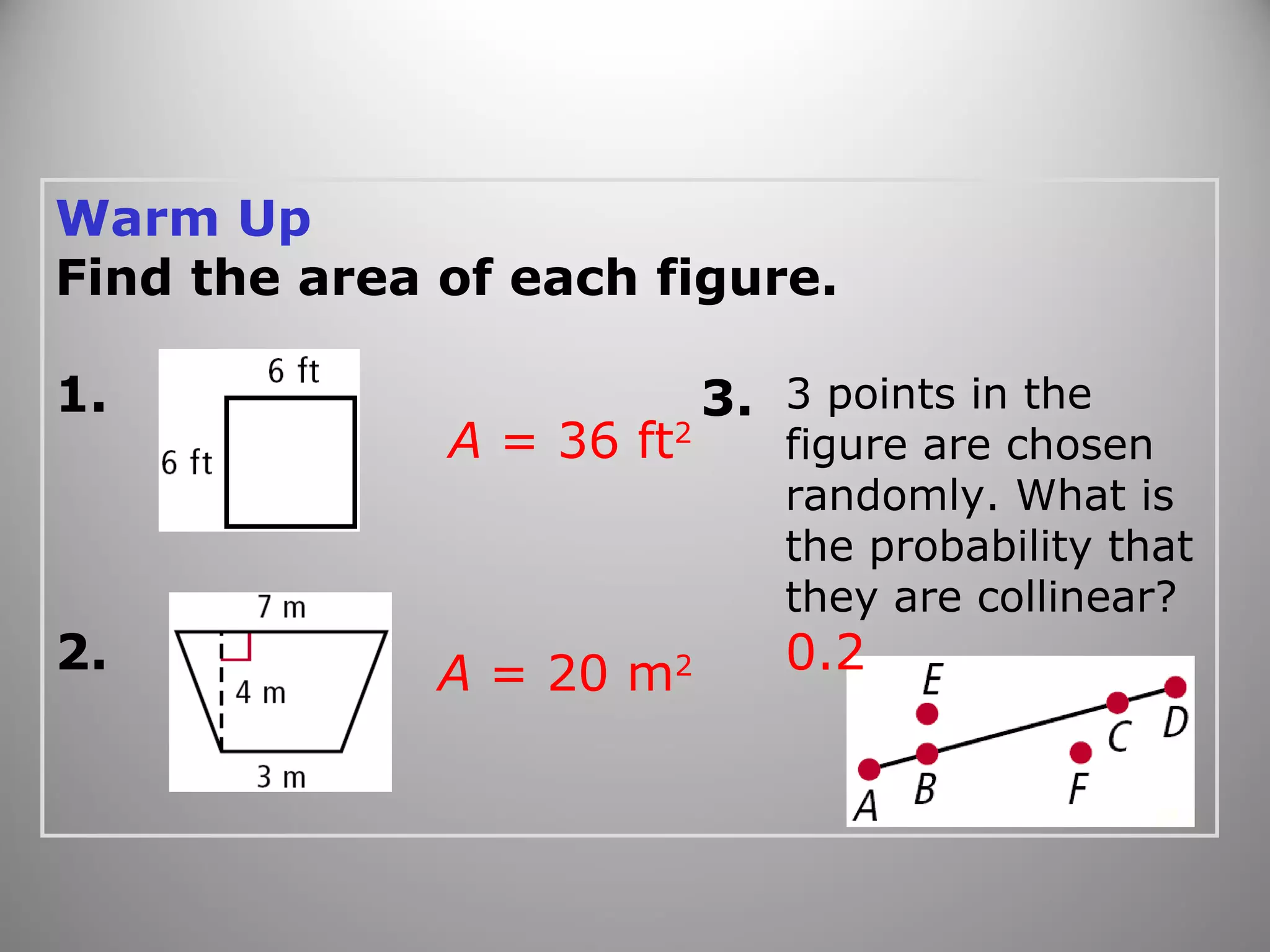
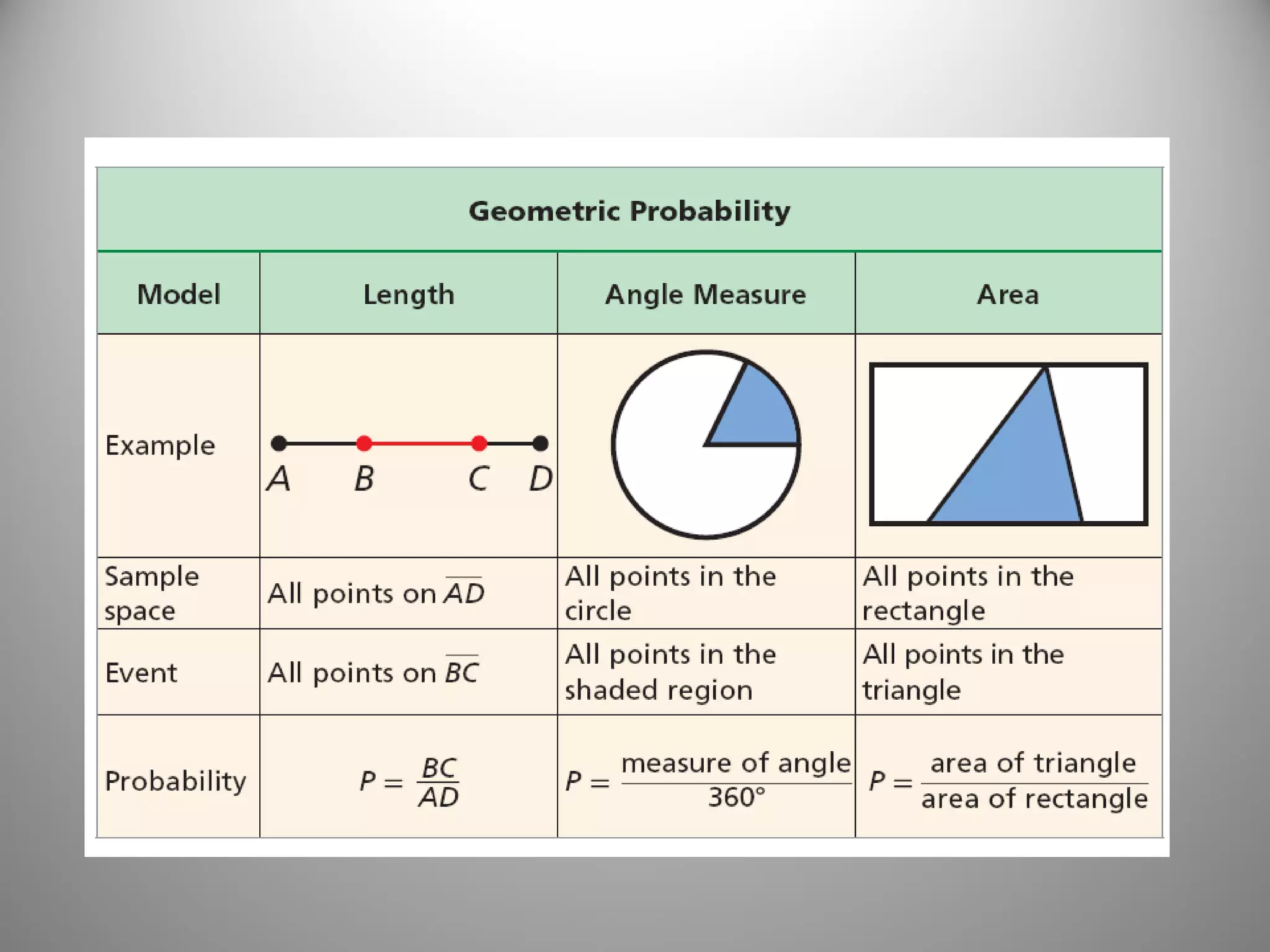
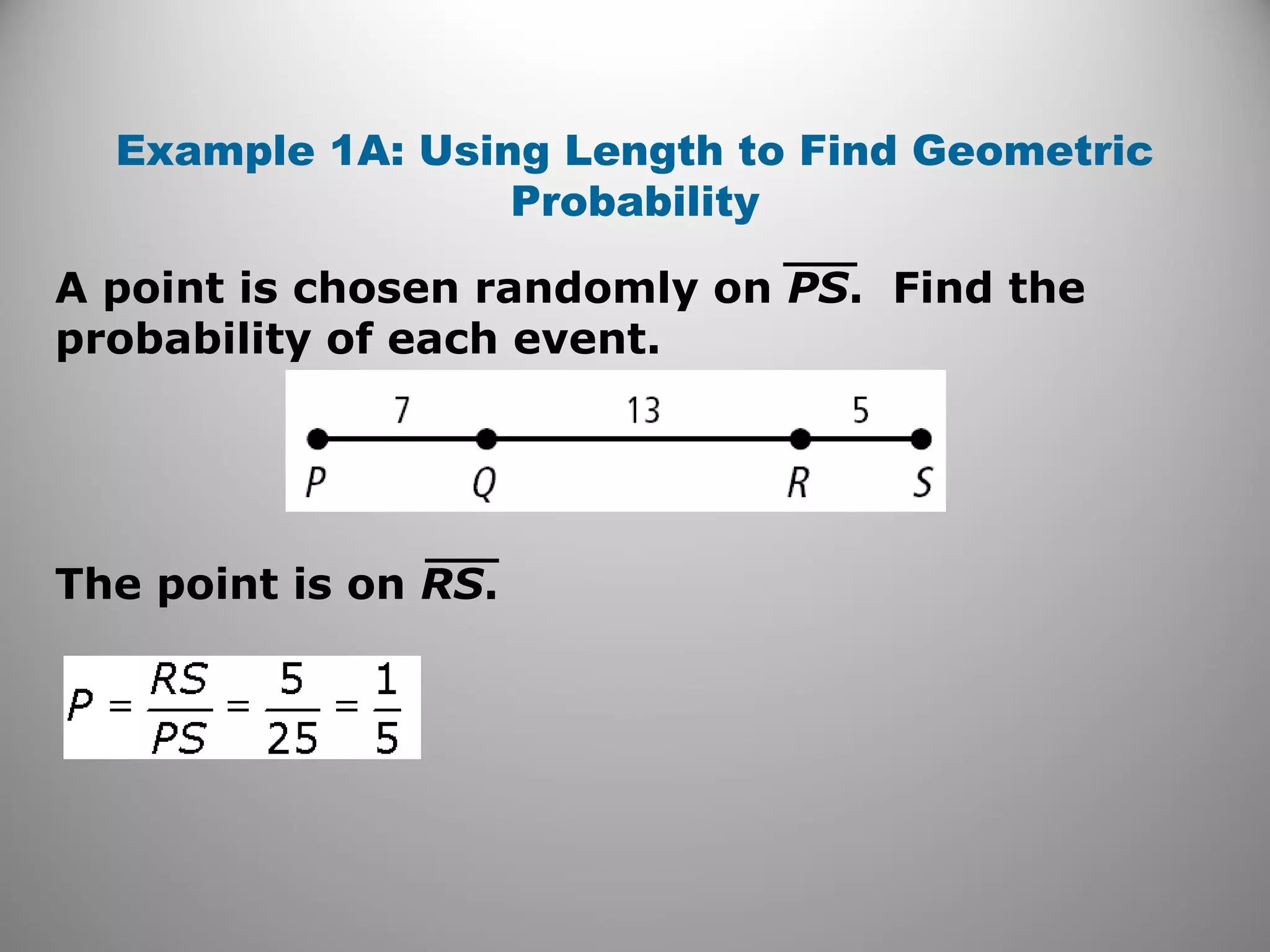
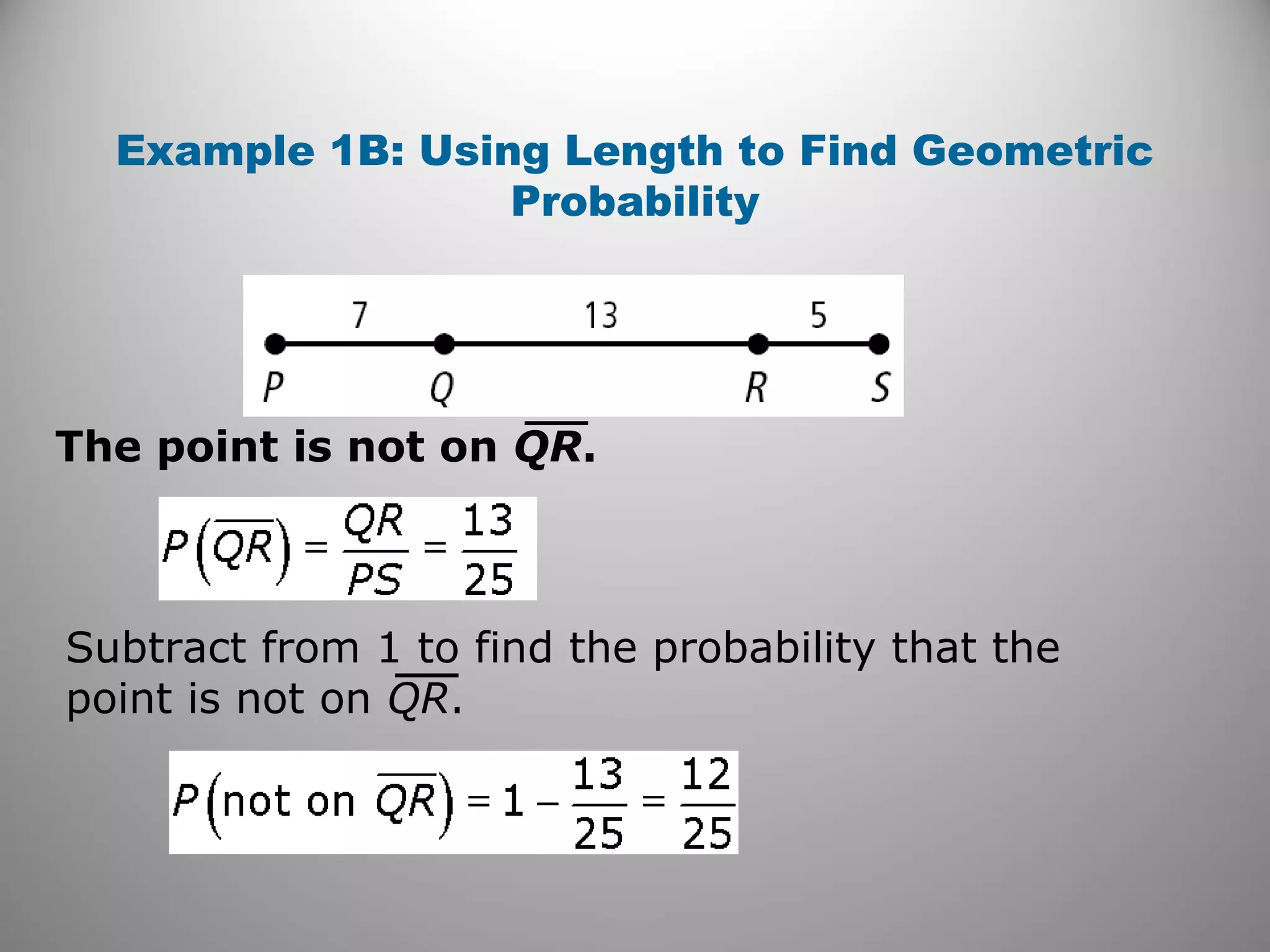
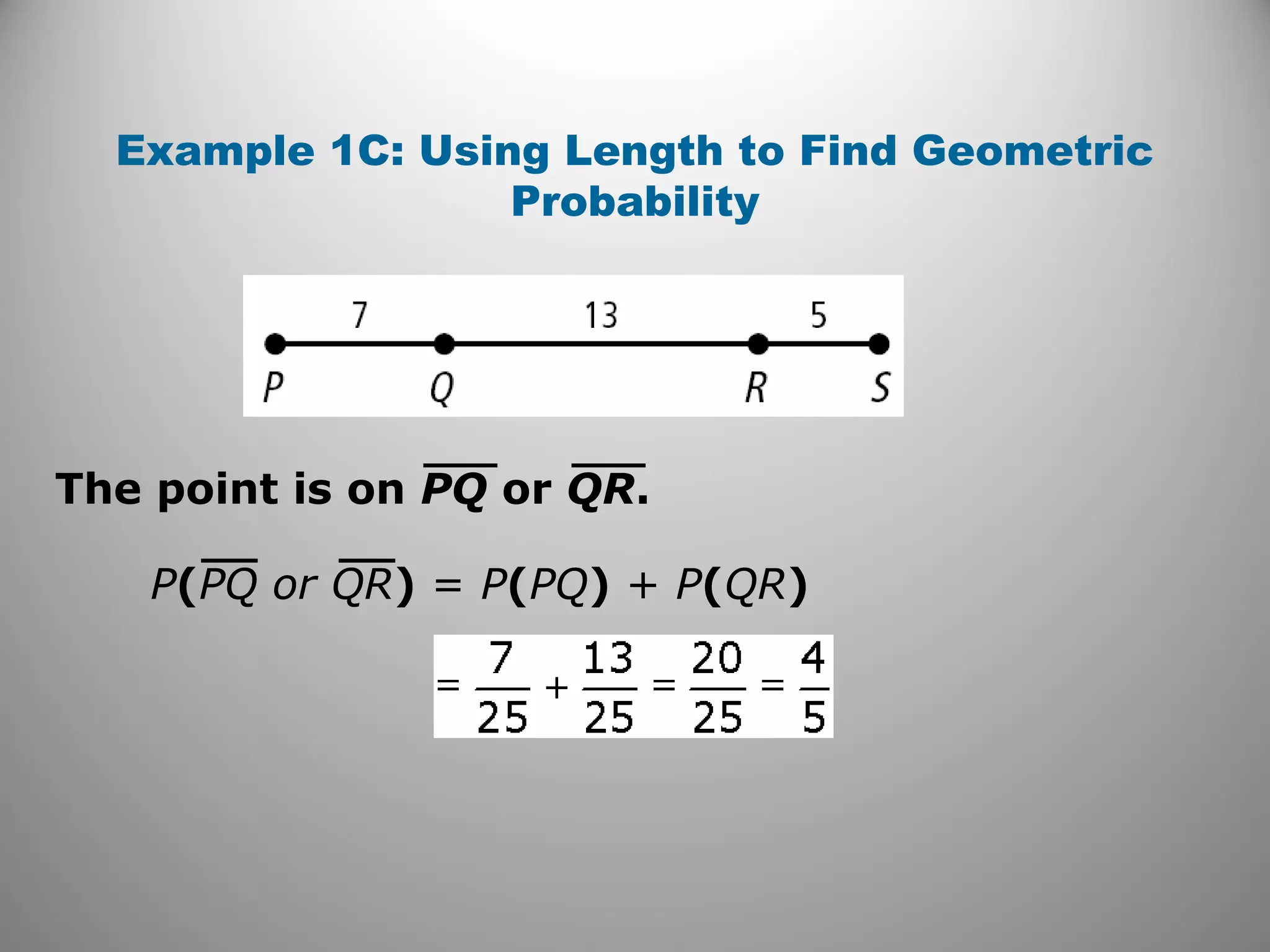
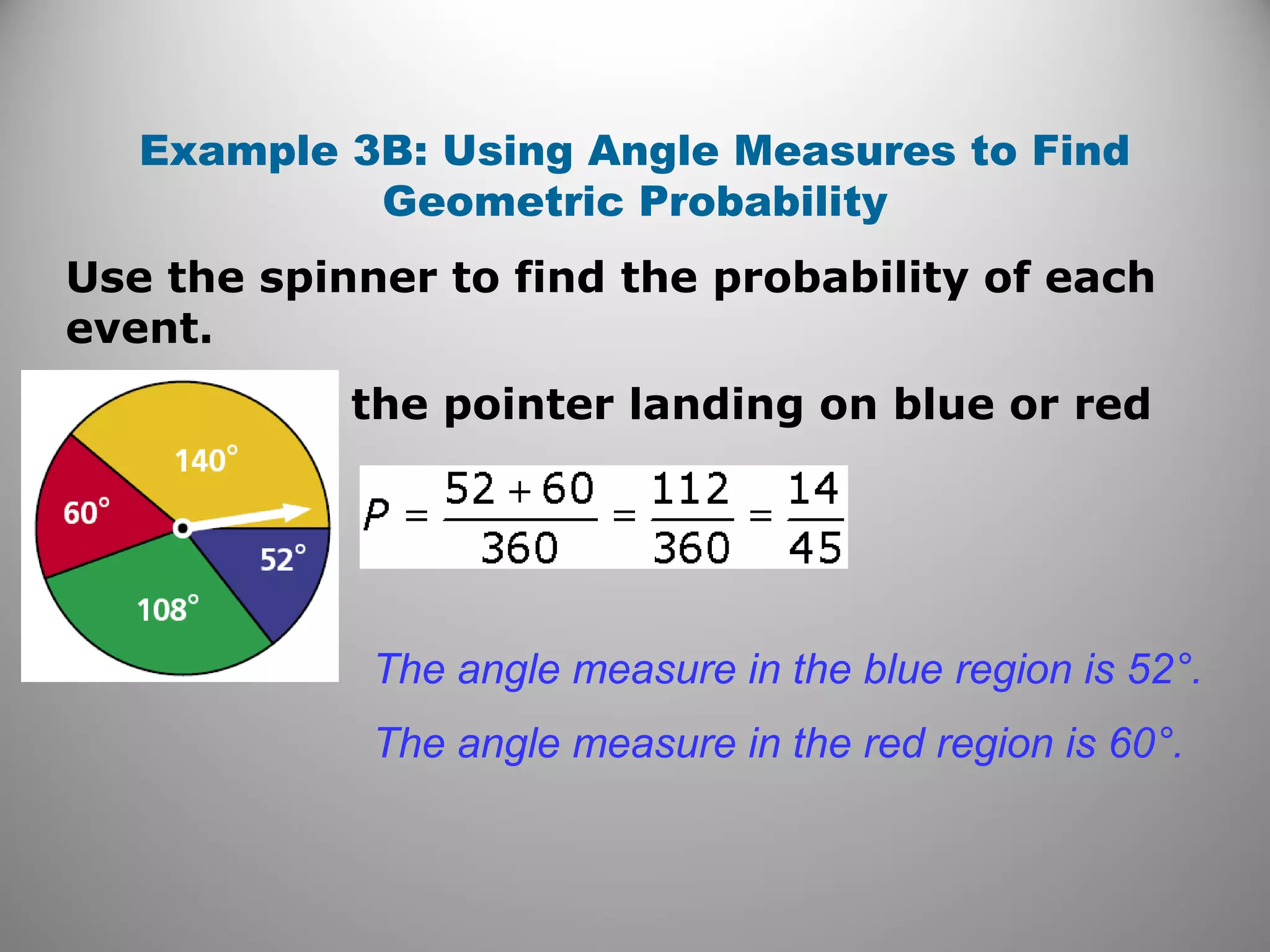
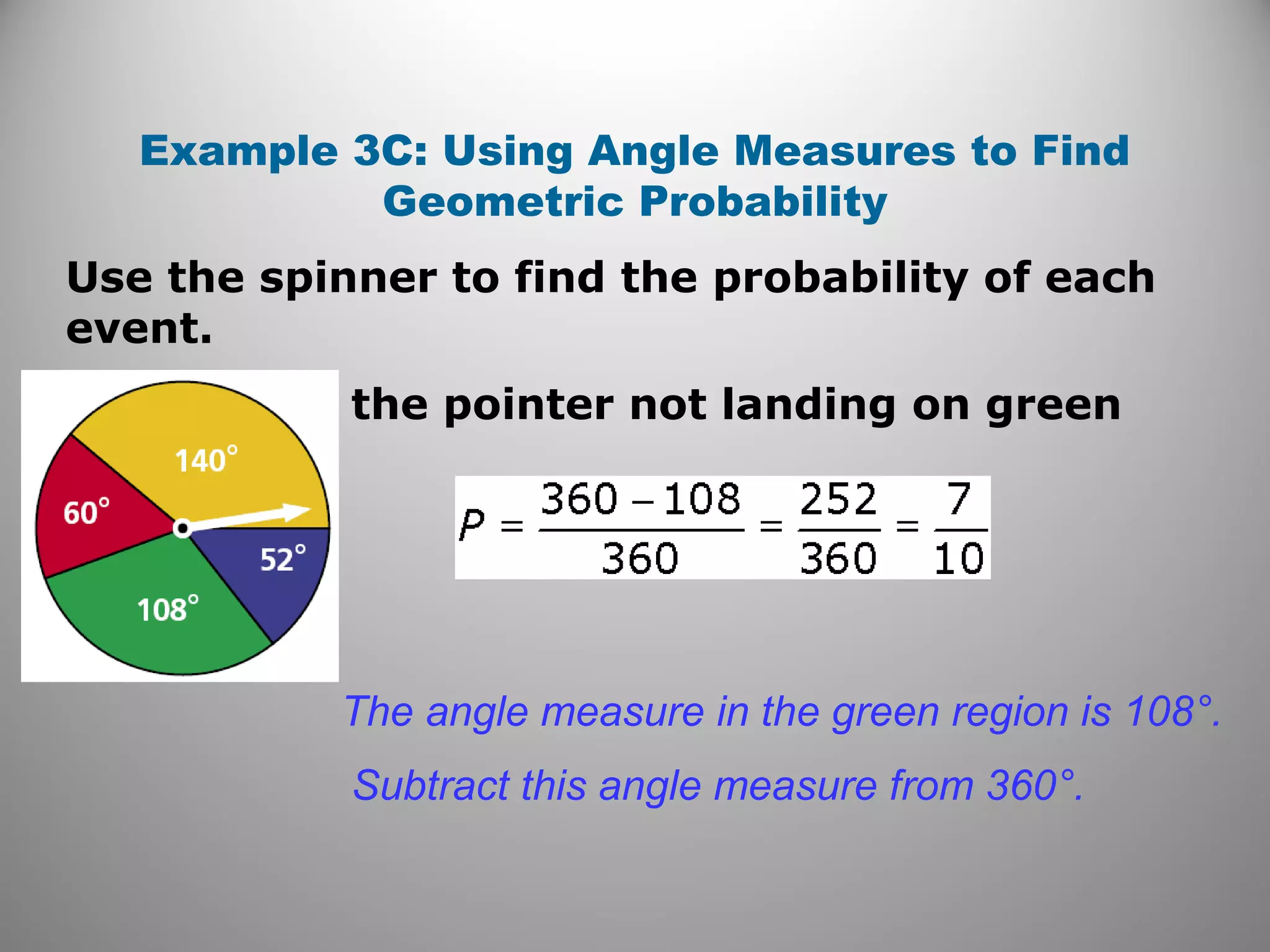
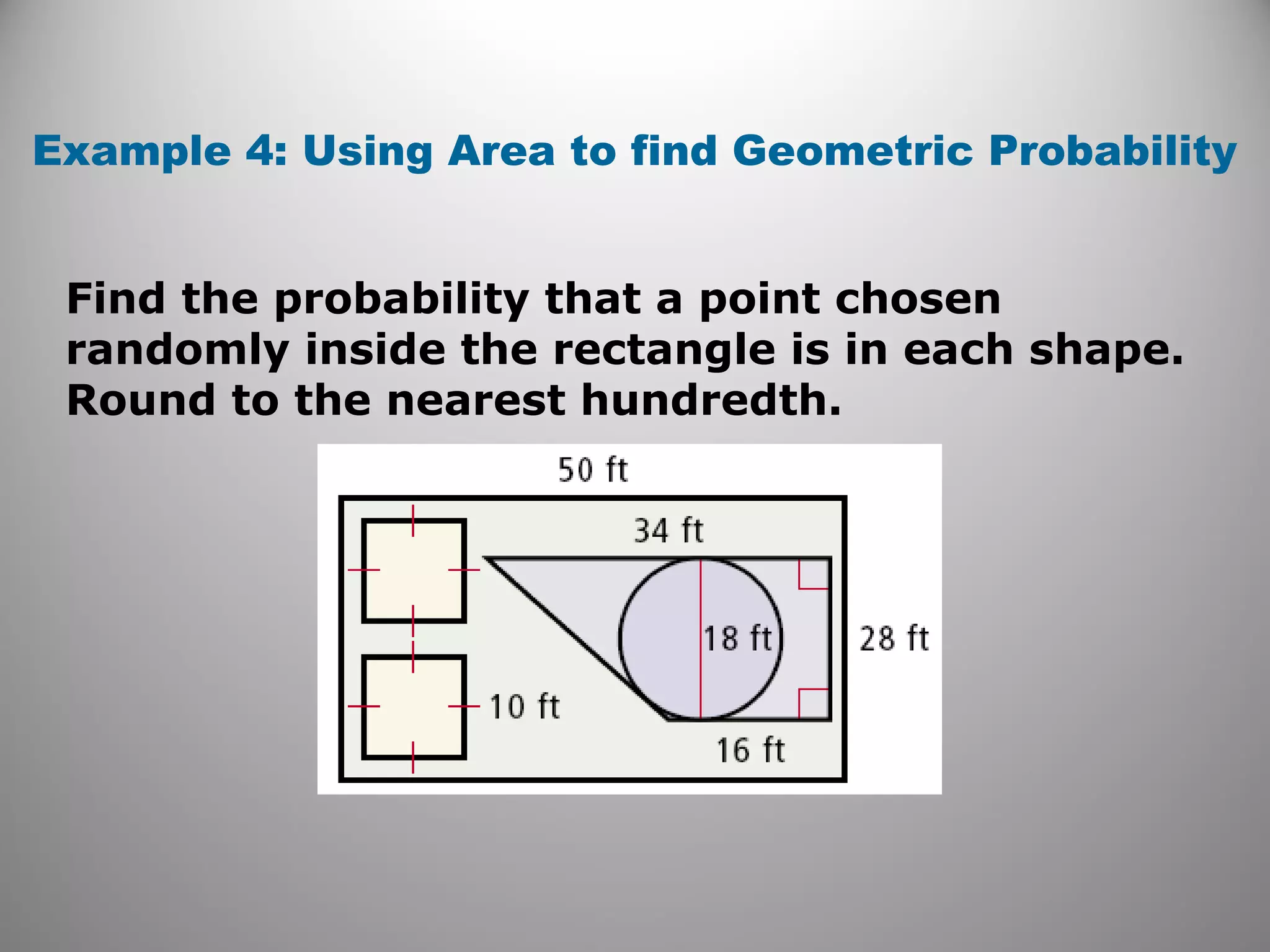
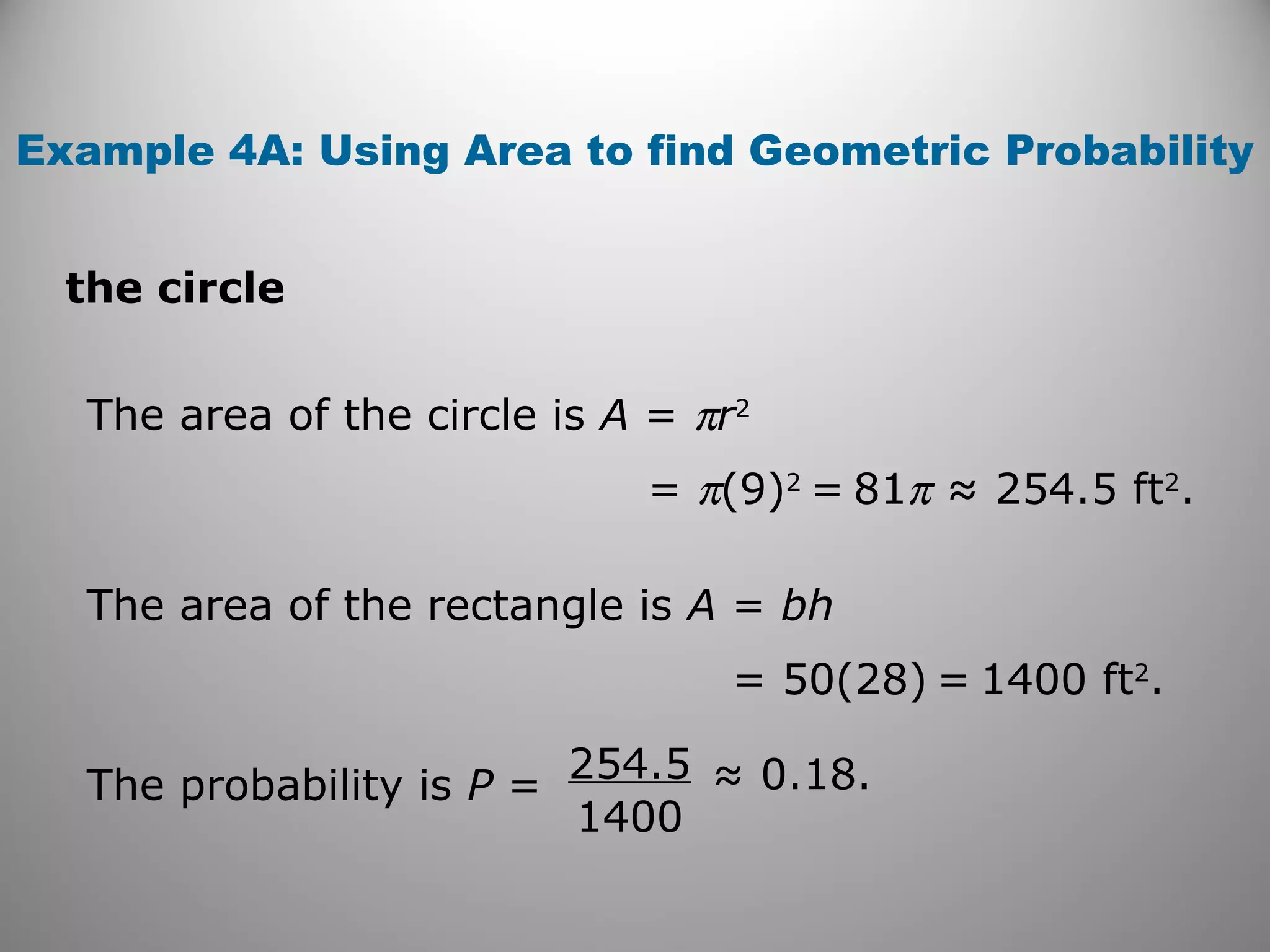
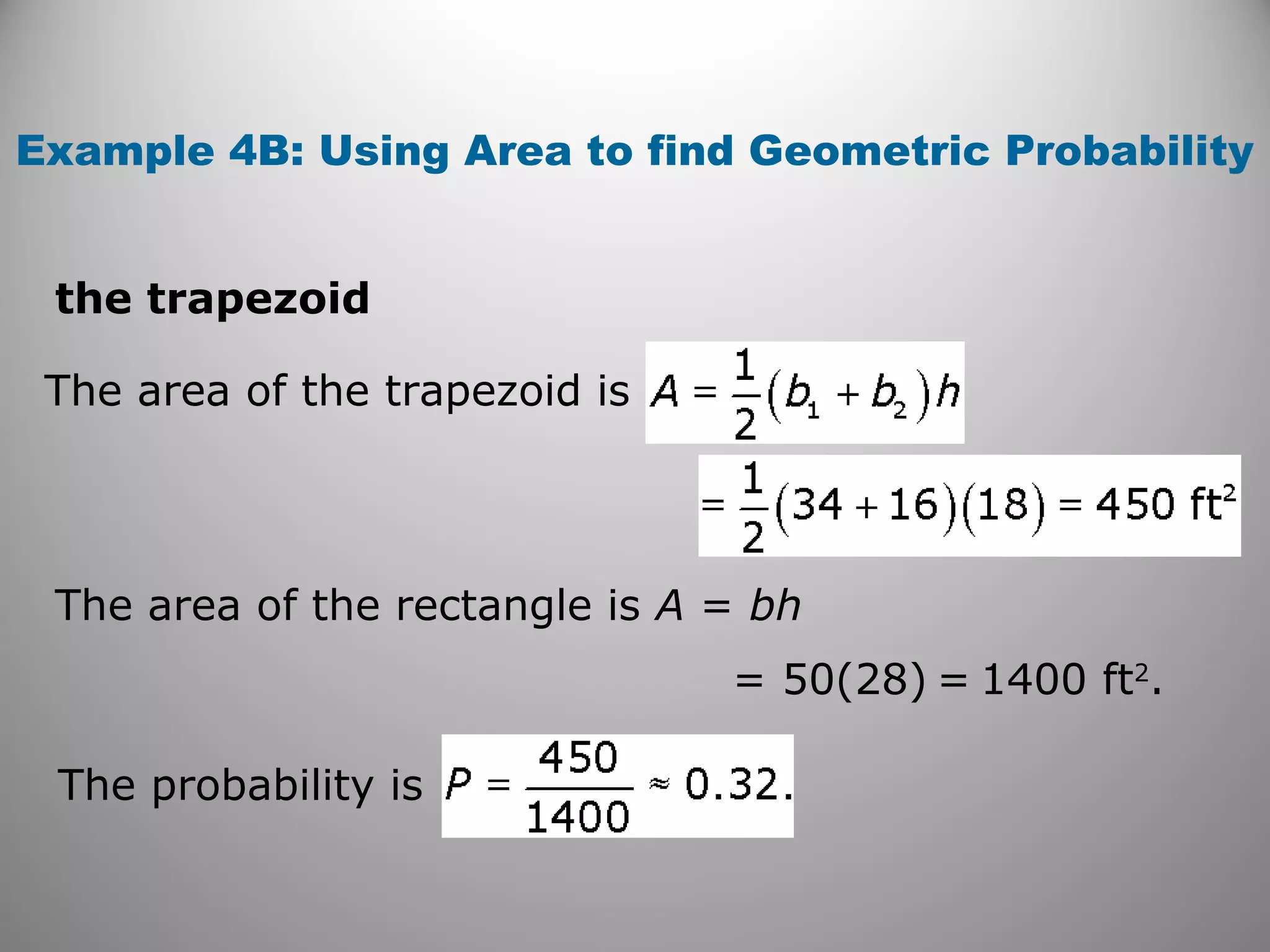
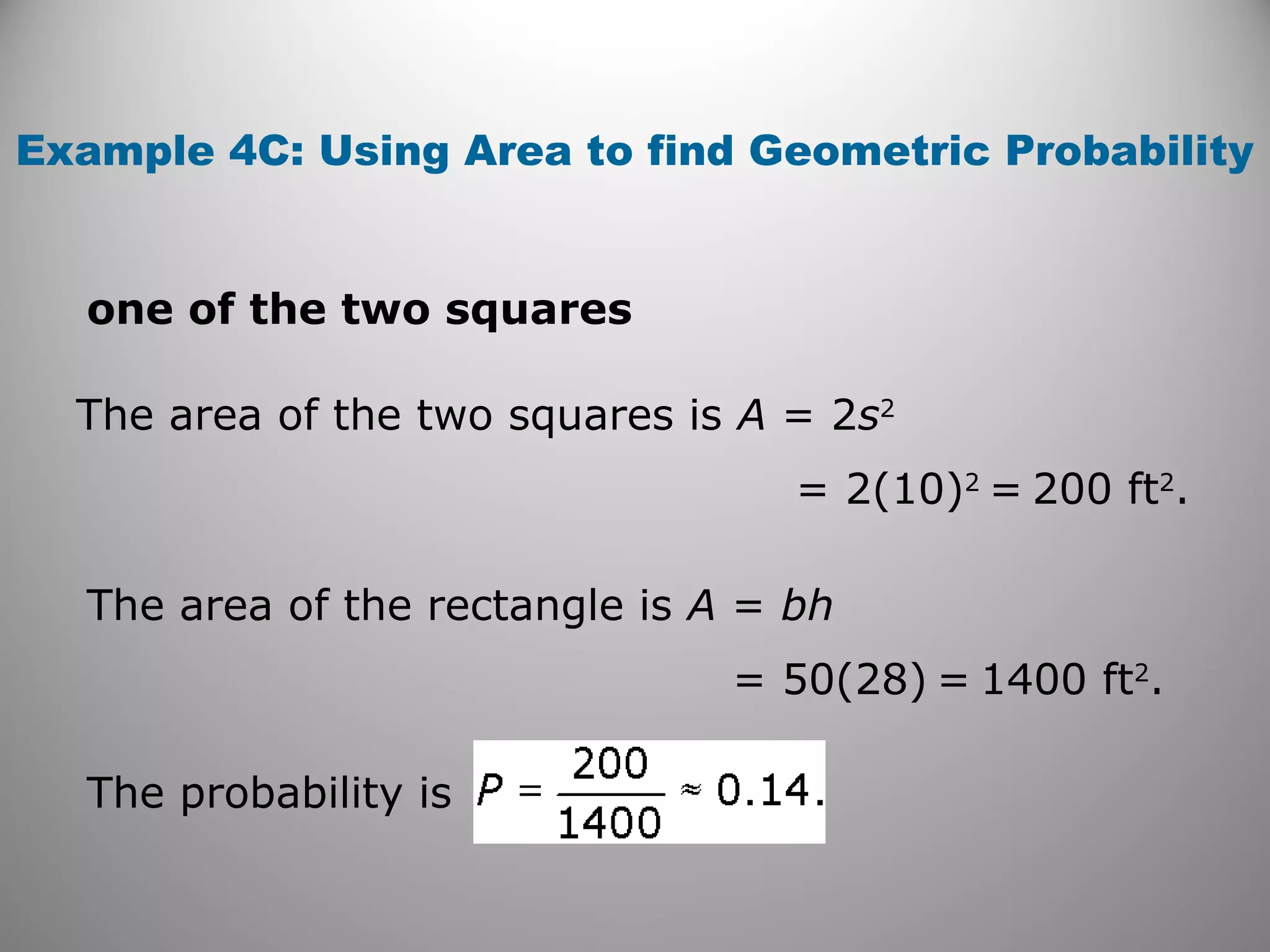
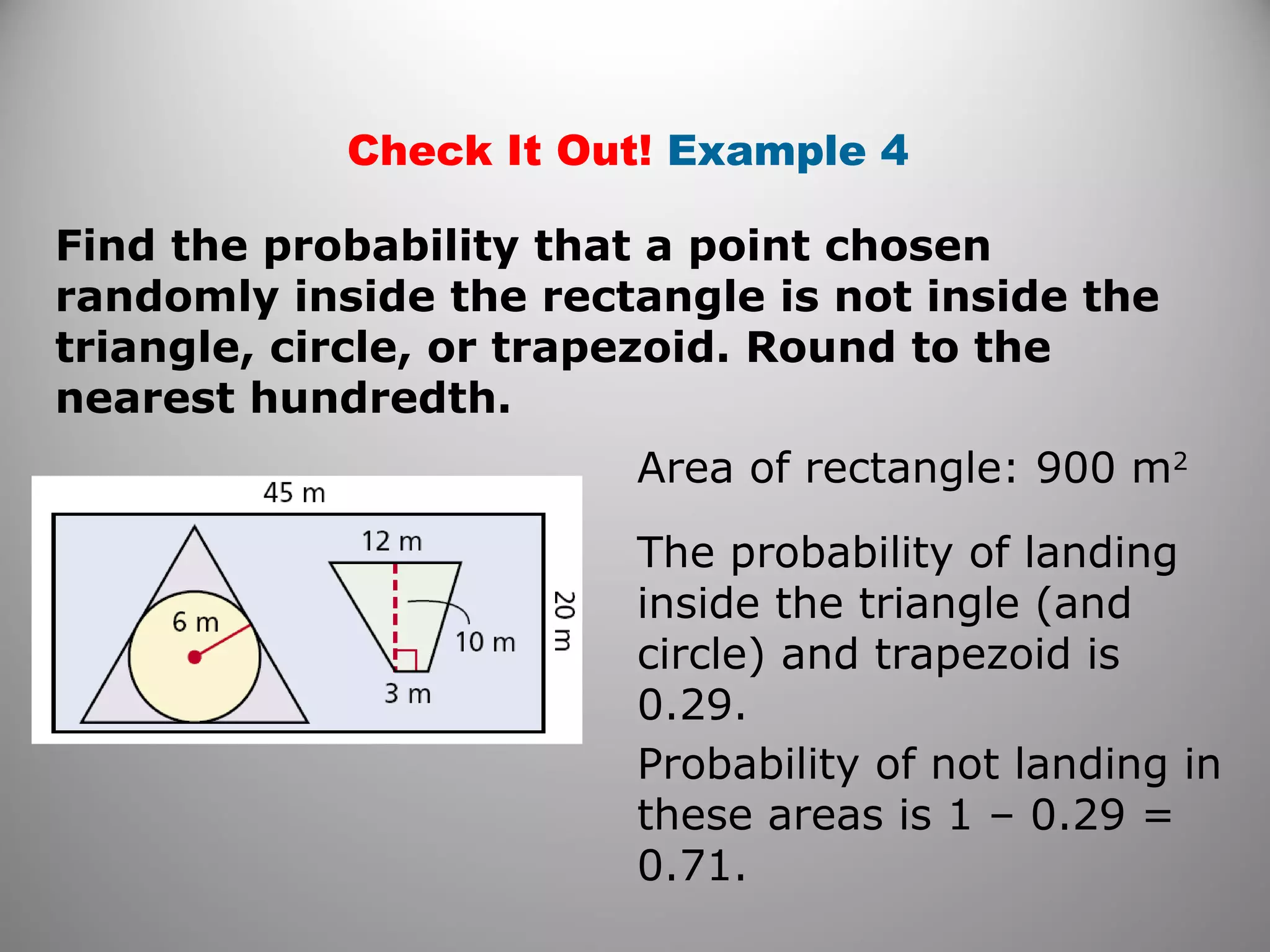
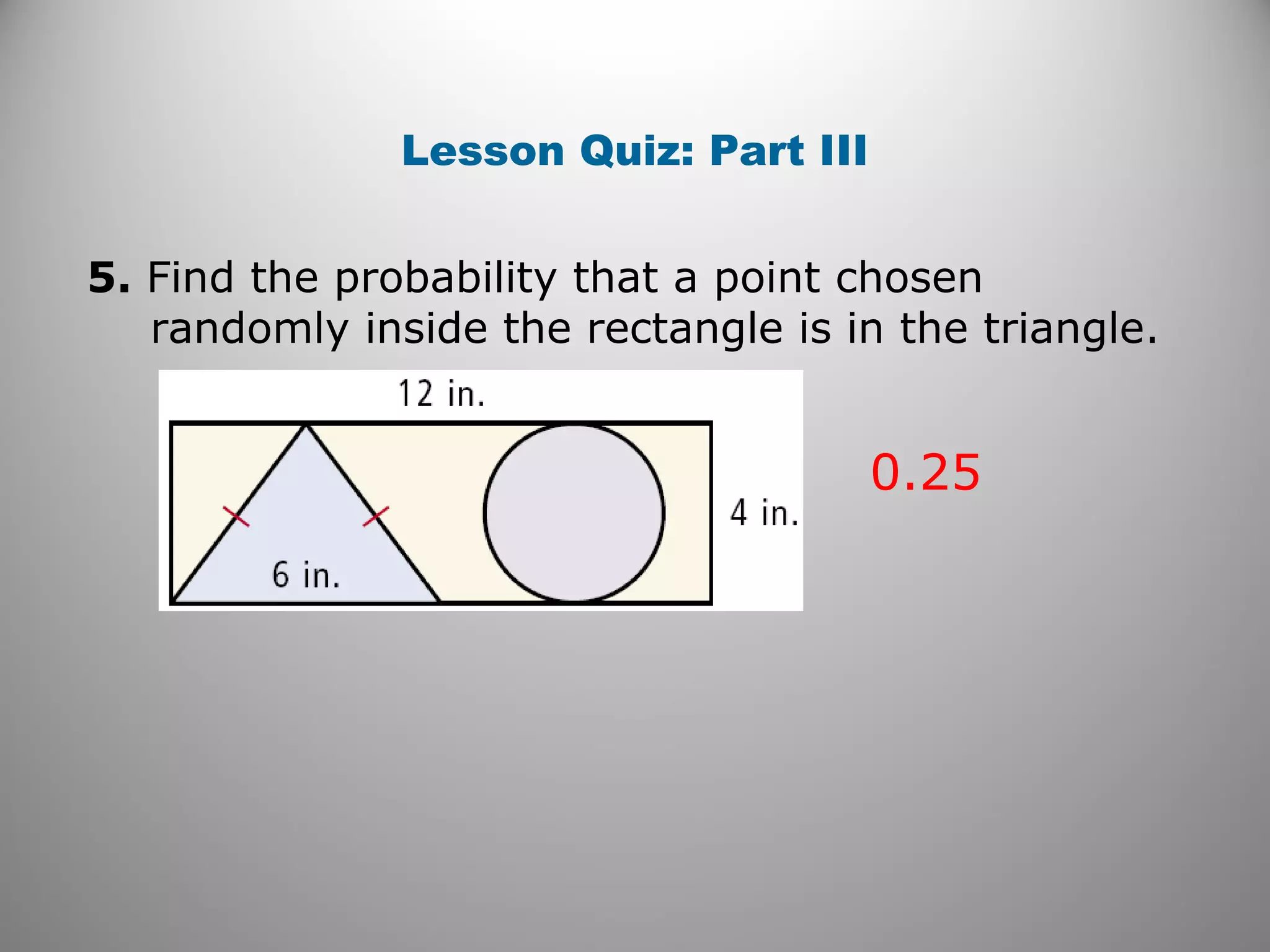
This document provides an overview of geometric probability and examples of calculating probabilities based on ratios of geometric measures like length, area, and angle measures. Geometric probability is used when an experiment has an infinite number of possible outcomes. Examples include finding the probability of a randomly selected point falling in a particular region of a line segment, shape, or spinner based on the relevant lengths, areas, or angle measures. The document also provides practice problems and solutions for calculating geometric probabilities.