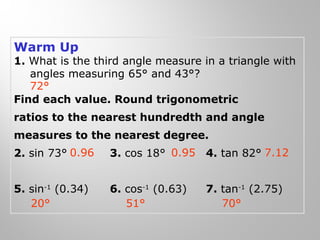
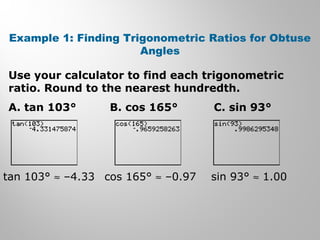
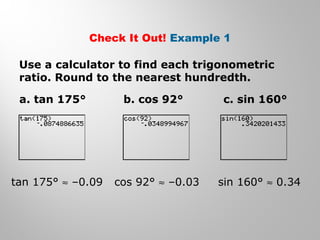
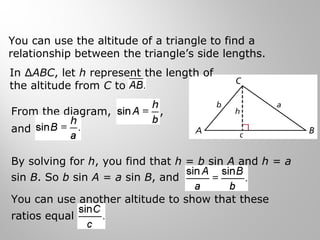
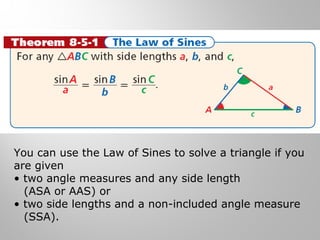
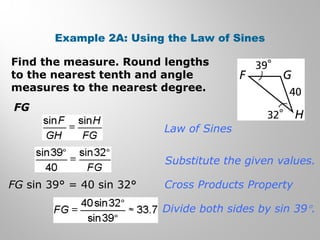
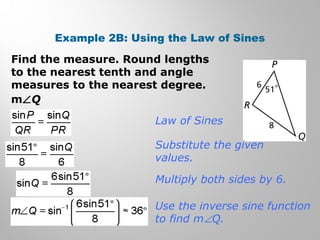
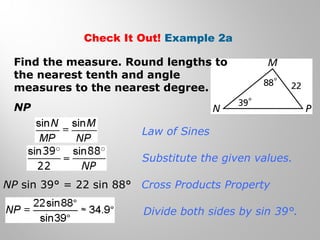
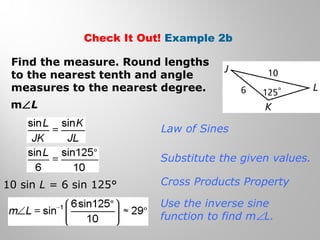
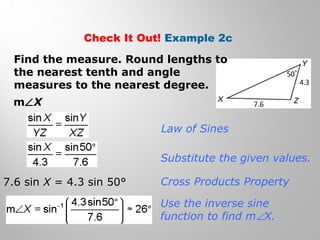
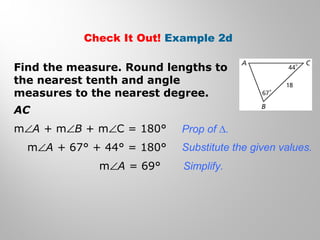
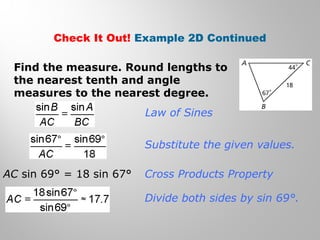
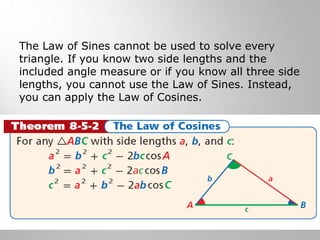
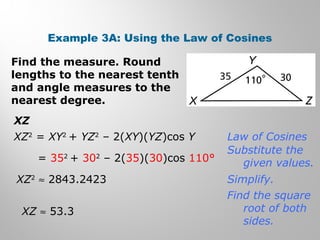
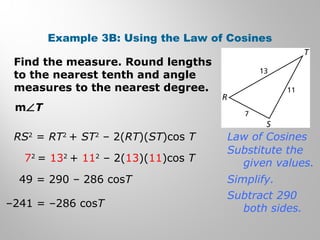
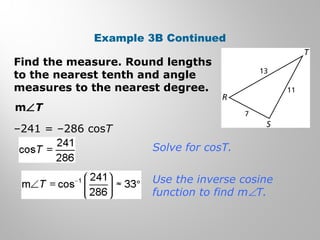
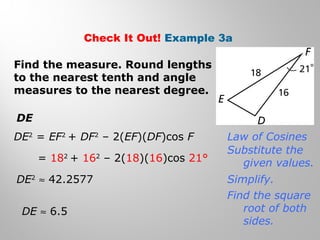
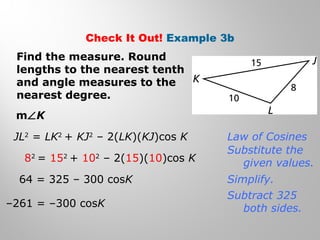
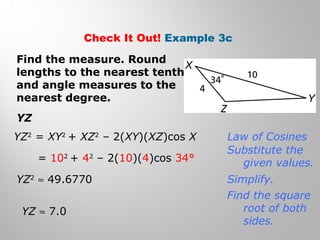
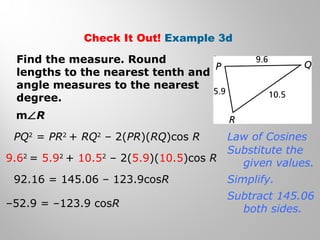
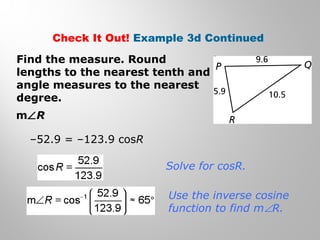
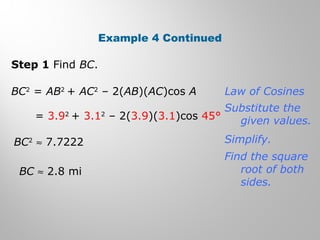
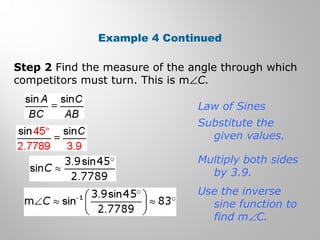
This document provides examples and explanations for using the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines to solve triangles. It begins with examples of finding trigonometric ratios for angles up to 180 degrees. It then shows how to use the Law of Sines to find missing side lengths or angle measures when given two angles and a side, or two sides and a non-included angle. The Law of Cosines is demonstrated for finding a missing side or angle when given two sides and the included angle, or all three sides. Multiple practice problems are provided to help understand applying these laws.