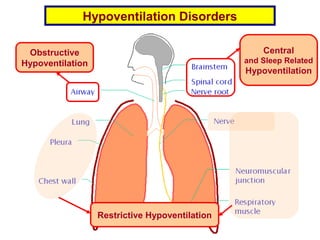
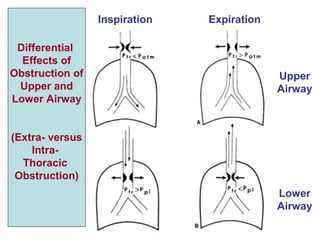
This document discusses various hypoventilation disorders including obstructive and restrictive types. It covers topics like upper vs lower airway obstruction, patterns of hypoventilation, obstructive lung diseases like asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It also discusses tests to evaluate lung function and restrictive vs obstructive patterns. Central sleep apnea and exercise induced bronchoconstriction are also summarized.