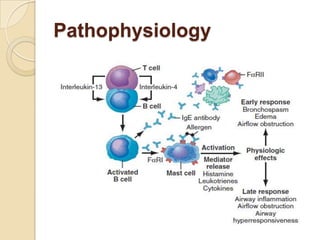
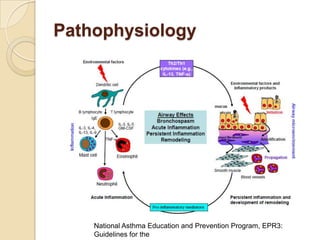
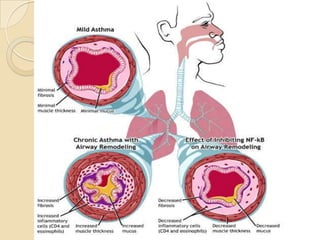
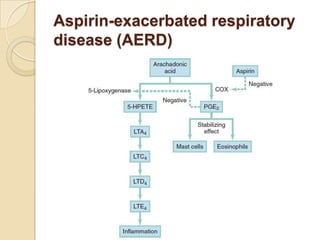
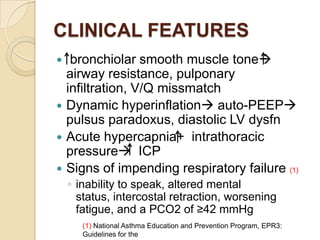
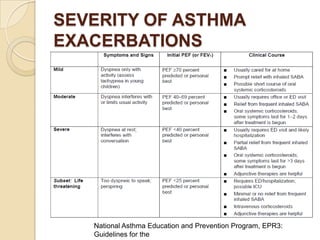
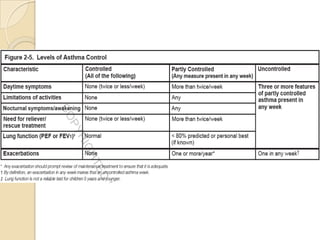
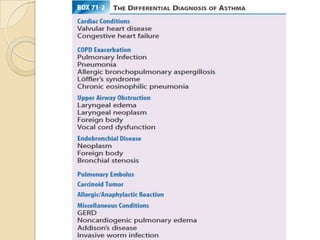
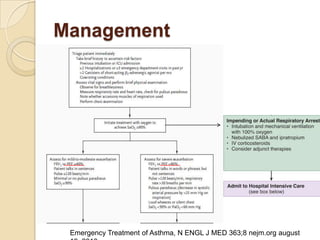
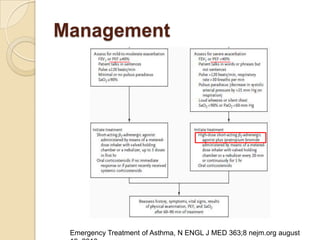
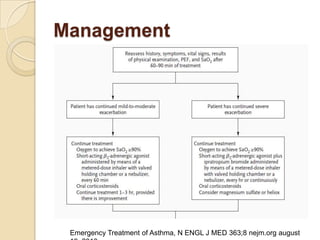
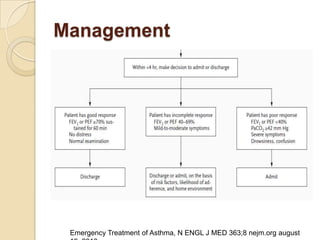
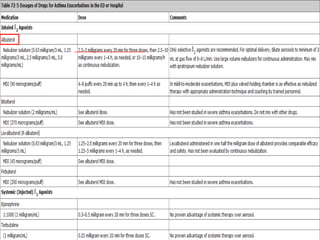
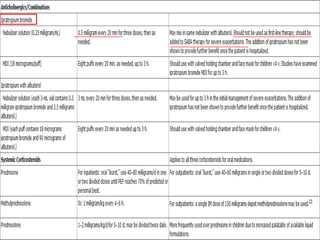
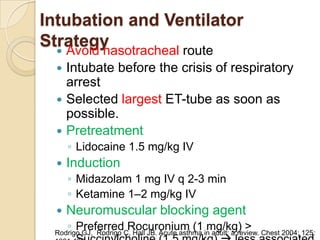
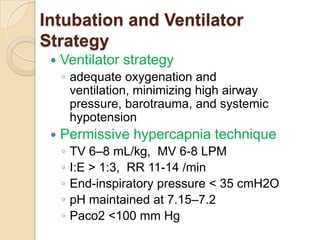
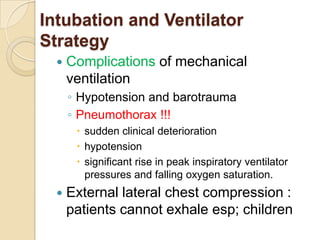
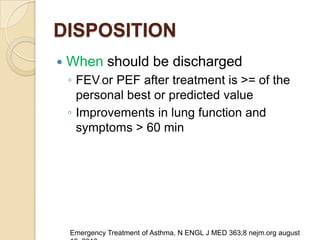
Acute asthma exacerbations are characterized by bronchospasm and airway inflammation. Key goals in treatment are rapid reversal of airflow obstruction through repetitive administration of inhaled short-acting beta-2 agonists and ensuring adequate oxygenation. Systemic corticosteroids improve resolution of obstruction and reduce relapse rates. Inhaled corticosteroids are also beneficial when combined with short-acting beta-2 agonists. Anticholinergic agents and intravenous beta-2 agonists may be considered for severe exacerbations unresponsive to other therapies.