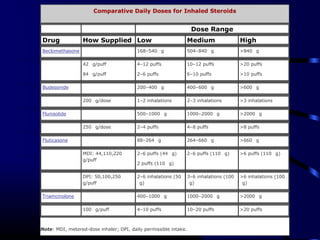
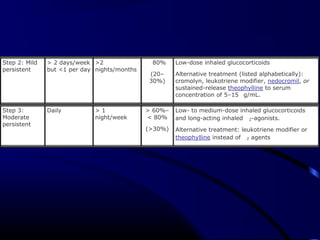
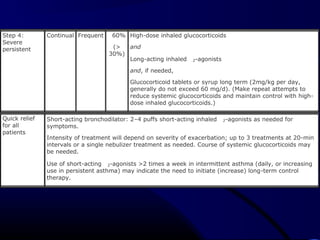
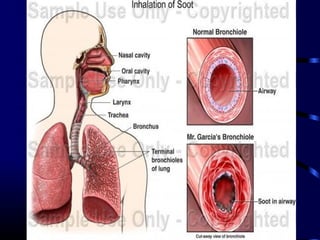
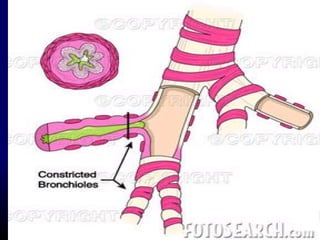
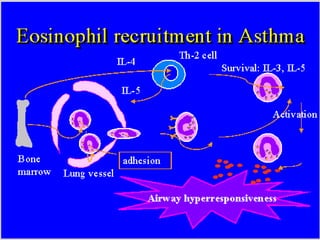
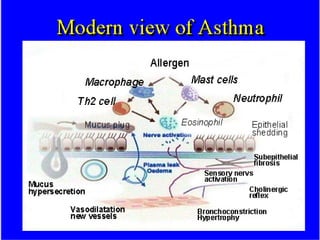
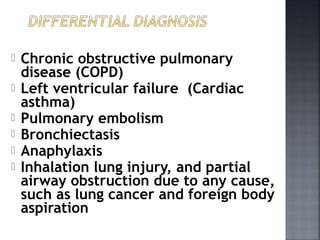
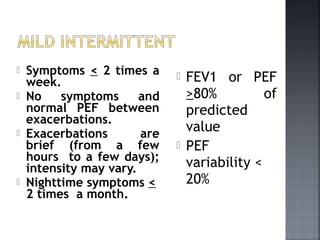
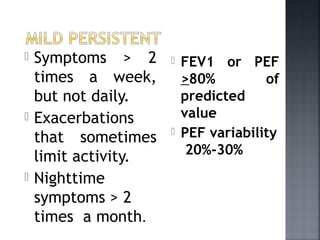
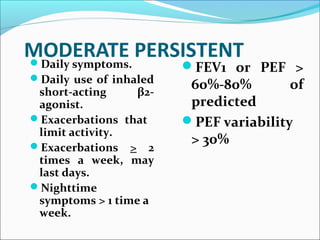
This document provides information on bronchial asthma, including its definition, epidemiology, etiology, provoking factors, pathology, symptoms, physical exam findings, laboratory/diagnostic findings, classification by severity, and treatment approaches. Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease characterized by reversible airway obstruction and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. It has a prevalence of 5-15% worldwide and is caused by genetic and environmental factors like allergens. Symptoms include wheezing, chest tightness, cough, and dyspnea. Treatment involves controllers like inhaled corticosteroids and relievers like short-acting bronchodilators.





































![Cromolyn and Nedocromil
Cromolyn MDI 1 mg/puff 2–4 puffs tid-qid
Nebulizer 20 mg/ampule 1 ampule tid-qid
Nedocromil MDI 1.75 mg/puff 2–4 puffs bid-qid
Leukotriene modifiers
Montelukast 4- or 5-mg chewable tablet, 10-mg
tablet
10 mg qhs
Zafirlukast 10- or 20-mg tablet 40 mg daily (20-mg tablet bid)
Zileuton 300- or 600-mg tablet 2400 mg daily (given tablets qid)
Methylxanthines [Serum monitoring is important (serum concentration of 5–15 g/mL at steady state)].
Theophylline Liquids, sustained-release tablets,
and capsules
Starting dose 10 mg/kg per day up to 300 mg max;
usual max, 800 mg/d
MDI, metered-dose inhaler; DPI, daily permissible intake](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-170713085913/85/Bronchial-Asthma-47-320.jpg)