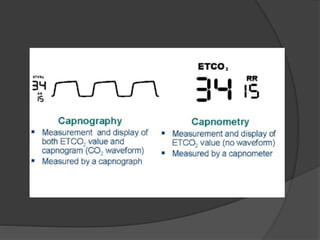
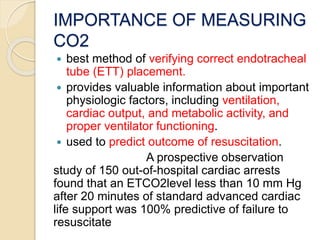
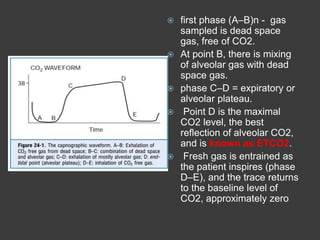
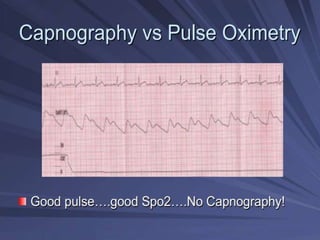
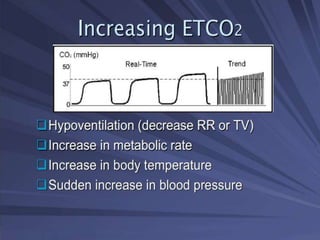
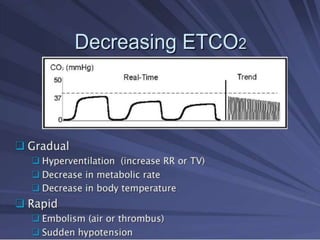
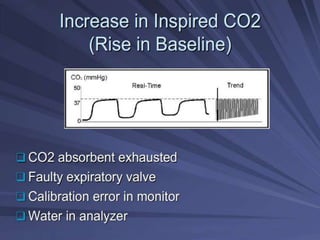
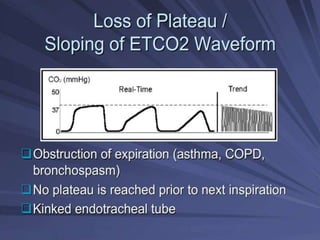
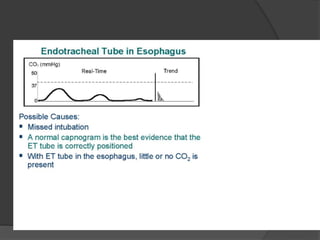
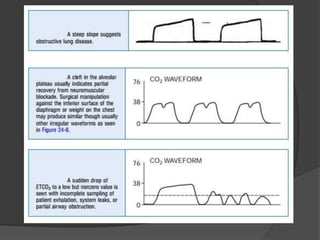
Capnography is superior to capnometry as it provides a graphical display of expired carbon dioxide (CO2) levels over time, allowing analysis of the capnographic waveform. Measuring end-tidal CO2 (ETCO2) using capnography is the best non-invasive method to verify correct endotracheal tube placement and provides valuable information about ventilation, cardiac output, and metabolism. ETCO2 levels normally approximate arterial CO2 (PaCO2) but the correlation decreases with abnormalities that increase the ventilation-perfusion mismatch. Key features of the capnographic waveform include the baseline, rise and contour of the CO2 curve which can provide diagnostic clues about various clinical conditions.