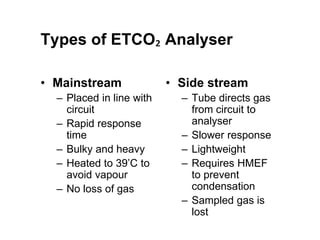
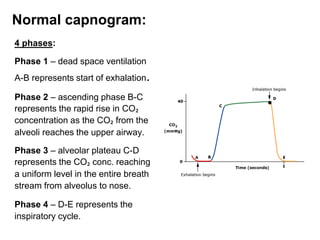
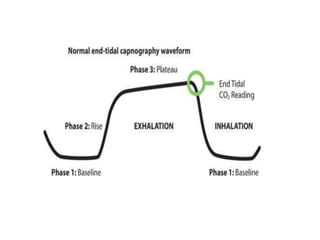
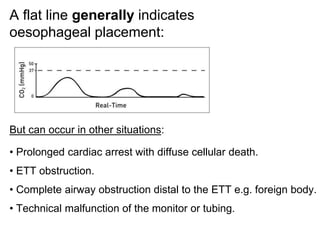
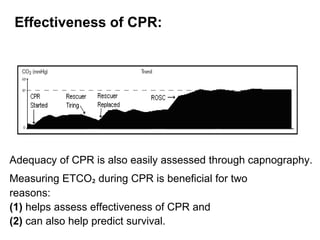
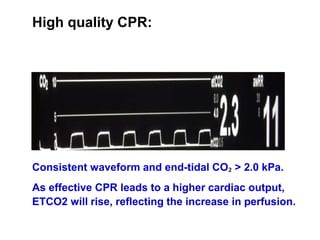
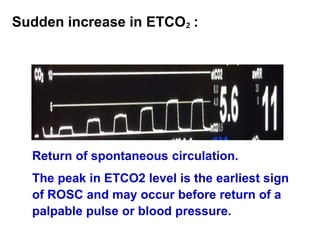
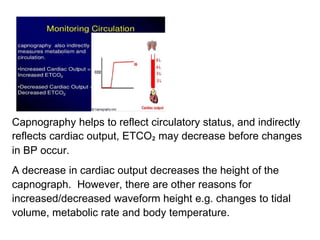
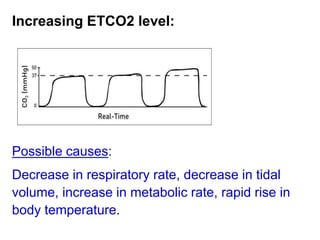
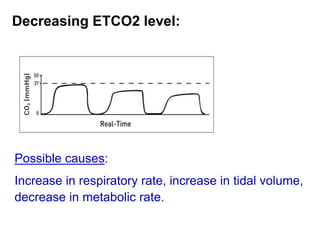
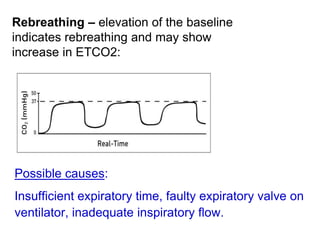
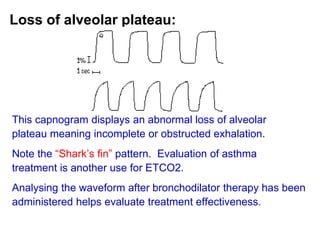
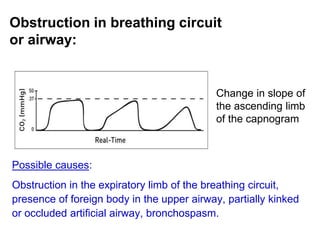
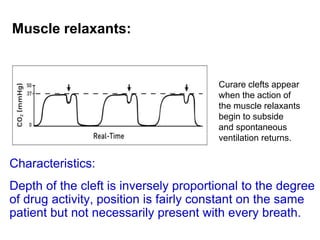
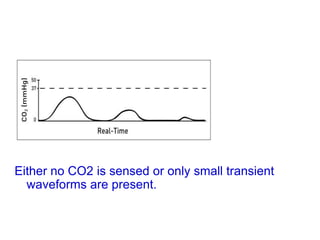
Capnography measures carbon dioxide levels during exhalation and can provide information about a patient's ventilation and circulation. It is useful for confirming proper endotracheal tube placement, assessing CPR effectiveness, detecting return of spontaneous circulation during cardiac arrest, and optimizing ventilation rates in patients with traumatic brain injury. Changes in the shape of the capnogram waveform or the end-tidal carbon dioxide level can indicate conditions like asthma exacerbations, endotracheal tube obstruction, or inadequate chest compressions.