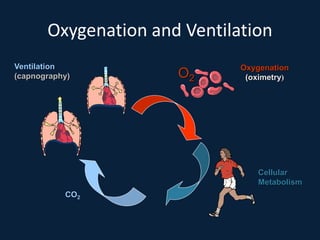
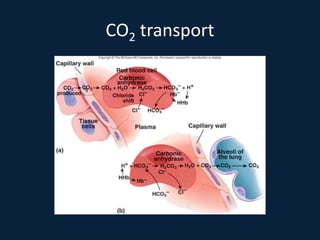
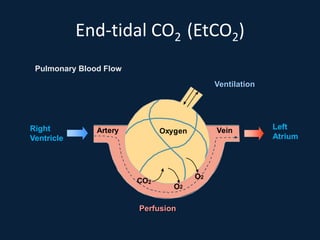
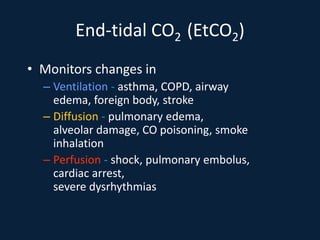
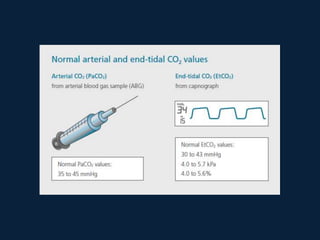
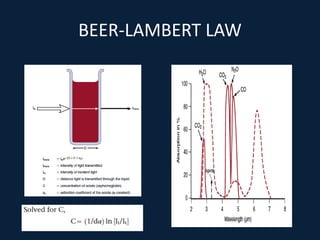
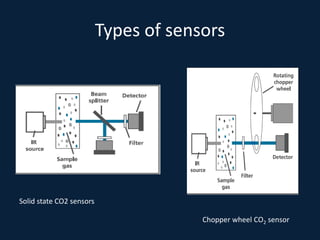
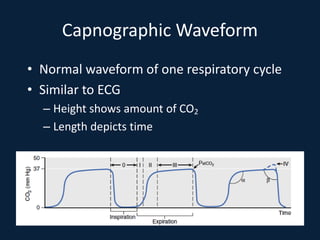
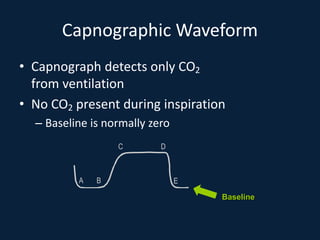
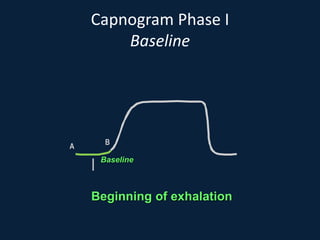
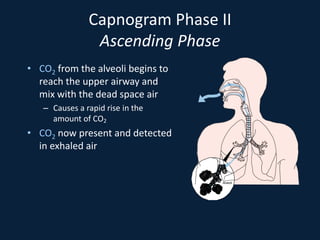
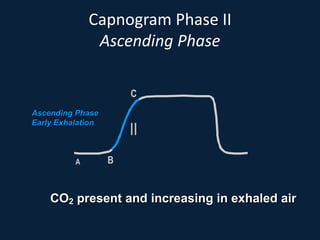
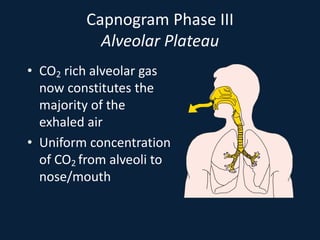
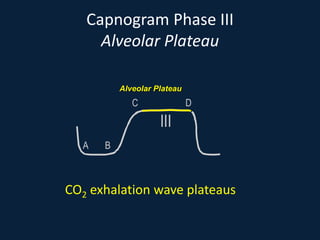
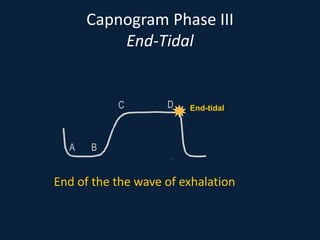
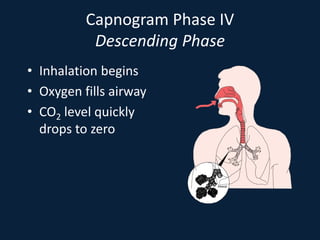
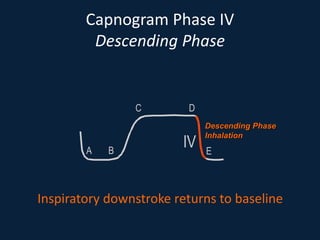
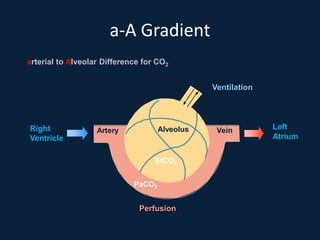
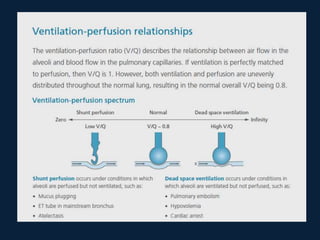
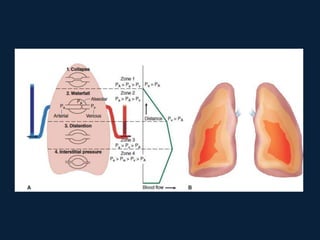
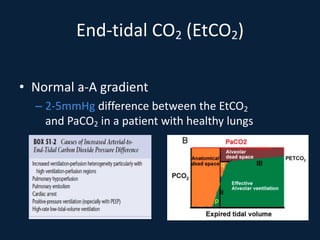
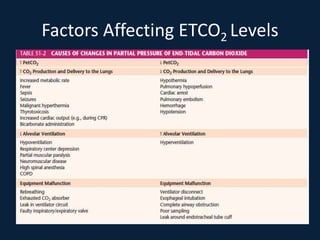
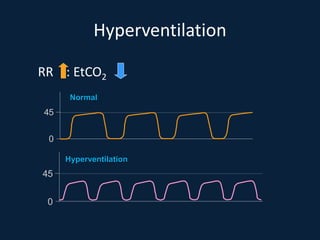
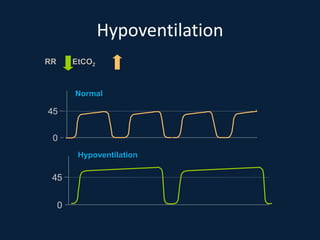
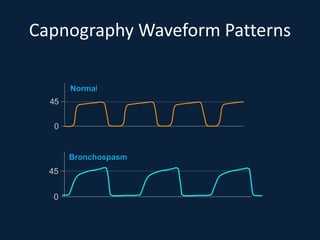
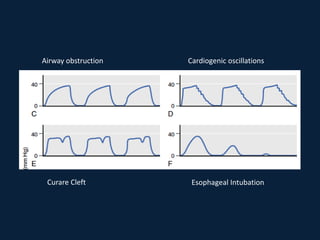
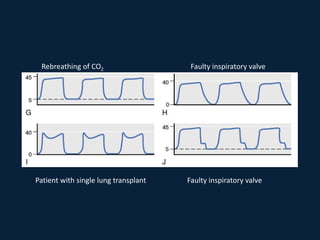
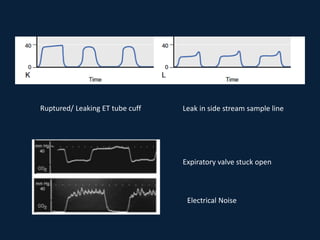
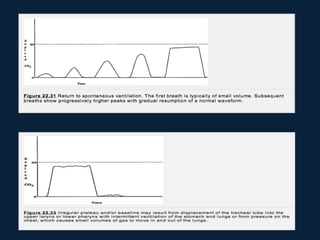
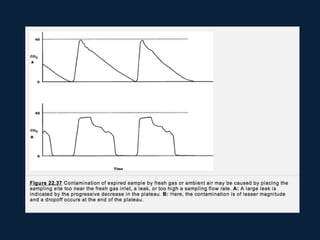
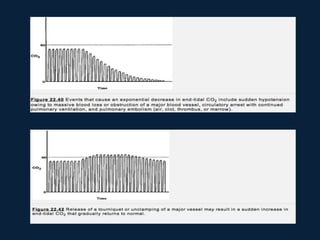
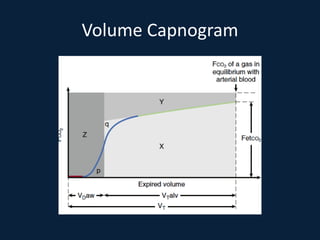
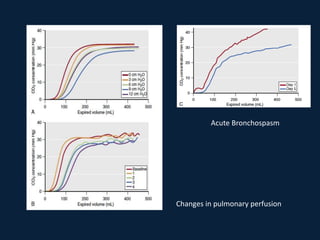
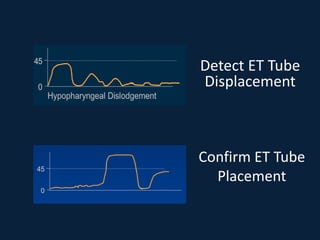
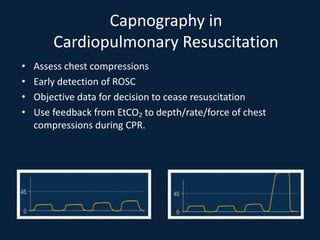
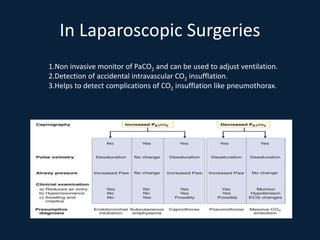
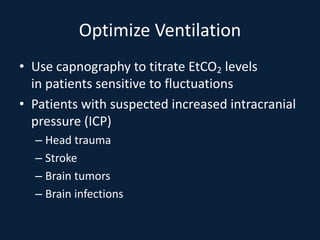
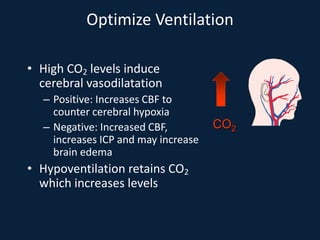
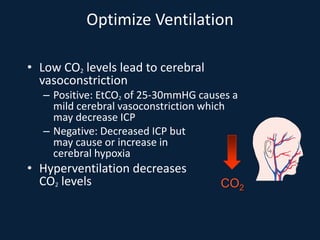
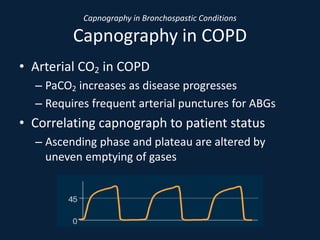
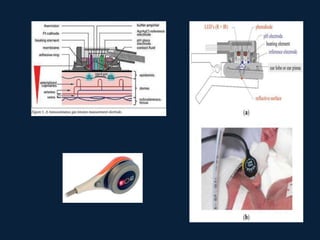
This document discusses end tidal carbon dioxide analysis and monitoring through capnography and capnometry. It begins by defining capnography and capnometry and describing the physiology of carbon dioxide transport and how end tidal carbon dioxide reflects ventilation, diffusion, and perfusion in the lungs. It then covers the principles behind capnography, different sensor types, sidestream vs mainstream monitoring. The document details the phases of the capnography waveform and factors that can affect end tidal carbon dioxide levels. It concludes by outlining various clinical applications of capnography and transcutaneous carbon dioxide monitoring.