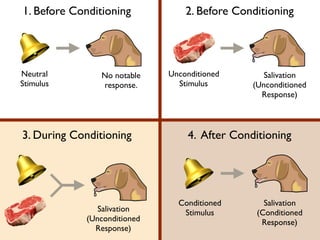
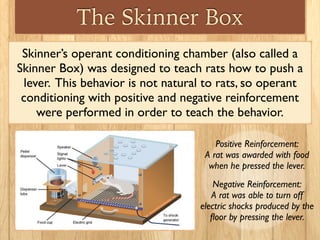
The document discusses two types of learning: classical conditioning and operant conditioning. Classical conditioning involves associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a response, as in Pavlov's dog experiment. Operant conditioning is learning through reinforcement or punishment of behaviors. Reinforcers increase behaviors and punishments decrease them. Examples are given of positive and negative reinforcement and punishment in operant conditioning.