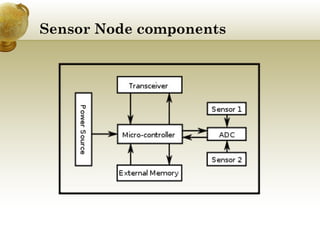
The document discusses wireless sensor networks (WSN) and their applications. It defines a WSN as a collection of sensor nodes that communicate wirelessly and self-organize after deployment. Sensor nodes collect data at regular intervals, convert it to electrical signals, and send it to a base station. The document outlines the components of sensor nodes and describes how WSNs are used for applications like forest fire detection, air/water pollution monitoring, landslide detection, and military surveillance. It also discusses the TinyOS operating system commonly used for WSNs and its features for efficiently utilizing energy in sensor nodes.