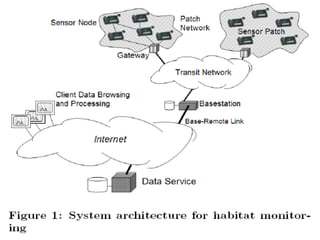
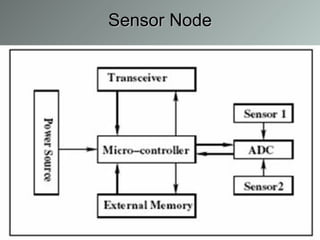
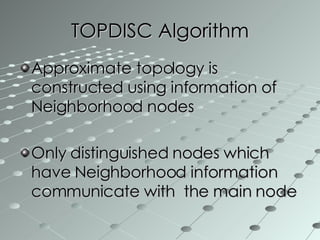
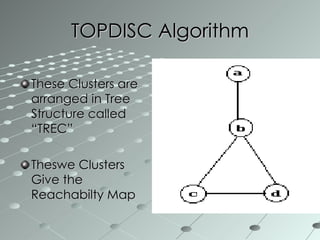
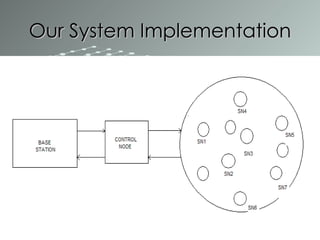
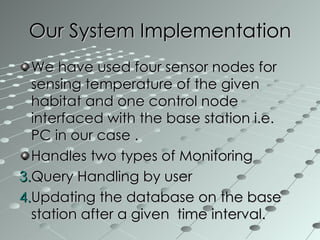
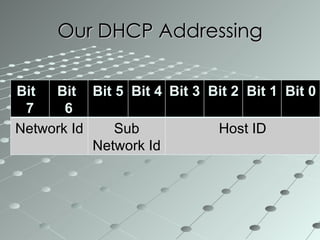
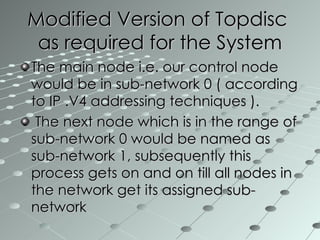
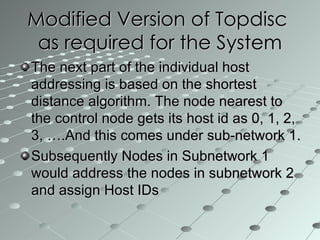
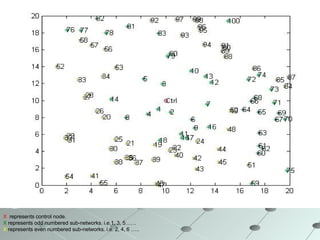
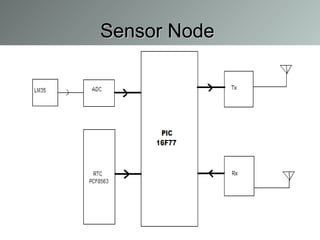
This document summarizes a wireless sensor network system implemented by the authors. The system uses 4 sensor nodes to sense temperature and a control node interfaced with a base station PC. It implements a modified version of the TOPDISC topology discovery algorithm using DHCP for dynamic addressing. The routing algorithm uses a mixture of spanning tree and N-link state protocols. Future enhancements include implementing fail safes and fully configuring the wireless sensor network system.