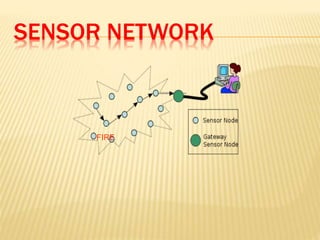
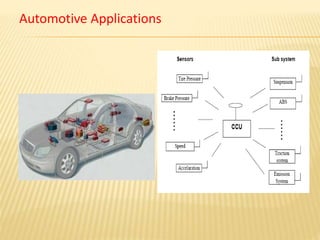
Wireless sensor networks consist of distributed autonomous sensors that monitor physical or environmental conditions. Sensor nodes gather data and transmit it to a central location. Wireless sensor networks have applications in fields like military surveillance, environmental monitoring, healthcare, home automation, and traffic control. The design of wireless sensor networks is influenced by factors like fault tolerance, scalability, hardware constraints, topology, and power consumption.