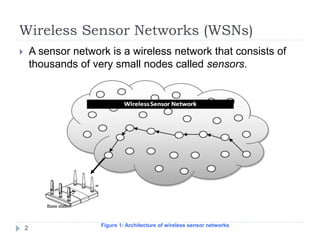
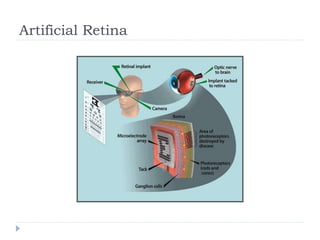
Wireless sensor networks consist of thousands of small sensor nodes that work together to monitor physical conditions like temperature, sound, pollution levels etc. Sensors have limited power, memory, and computing capabilities. They communicate wirelessly and can be deployed in large numbers in environments that are hard for humans to access. Applications of wireless sensor networks include environmental/habitat monitoring, precision agriculture, infrastructure protection, healthcare, smart homes and more. Key challenges in designing wireless sensor networks include energy efficiency, distributed processing, scalability, and operating in harsh environments with unreliable individual sensor nodes.