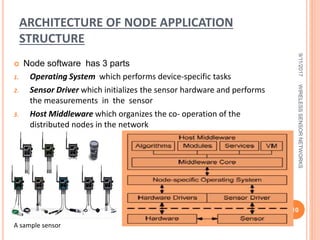
This document discusses wireless sensor networks (WSNs), including their types, characteristics, architecture, middleware, standards, applications, challenges and future scope. WSNs consist of spatially distributed autonomous sensors that monitor physical or environmental conditions. They have constraints in terms of cost, size, topology and power. The document outlines the components and software architecture of WSNs, and examines issues like energy efficiency. It also explores common applications in areas like healthcare, pollution monitoring and home automation, along with ongoing challenges in hardware, software and large-scale deployment.