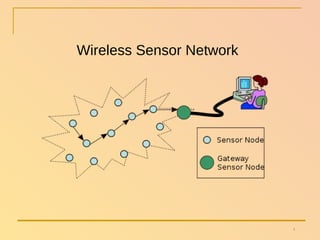
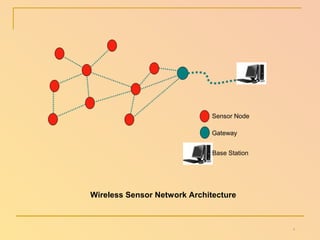
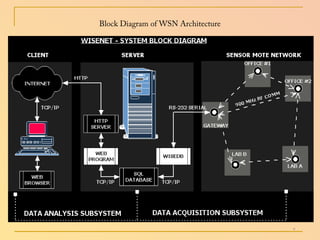
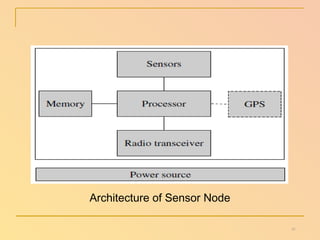
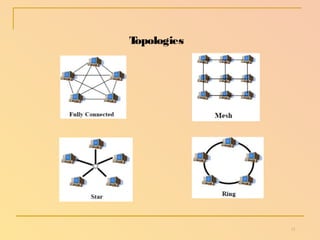
The document summarizes a seminar presentation on wireless sensor networks. It discusses the architecture of WSNs, including sensor nodes, gateways, base stations, and networking topologies. It also covers the advantages and disadvantages of WSNs, their applications in fields like environmental monitoring and medical monitoring, and their future potential to bridge the physical and digital worlds.