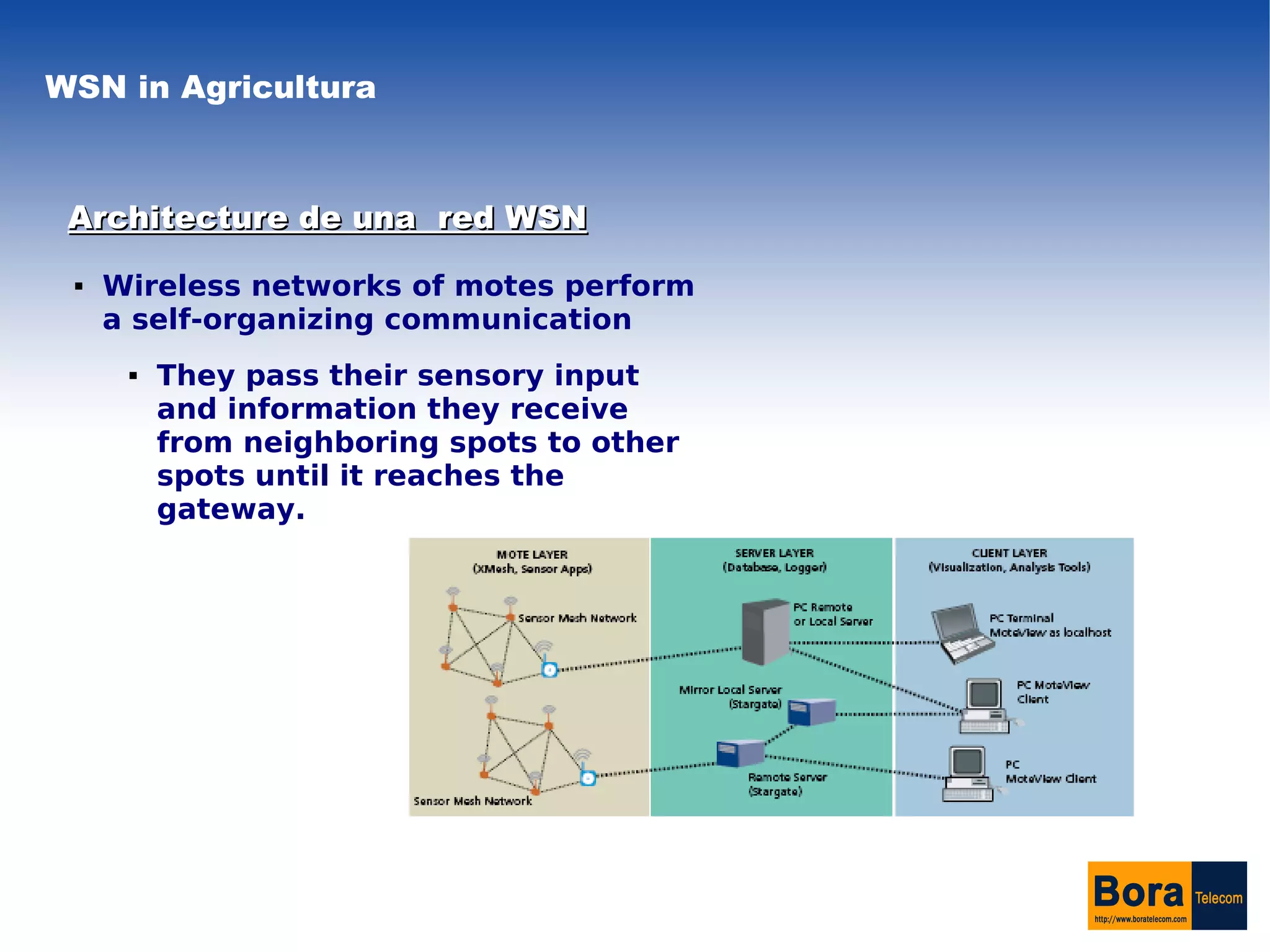
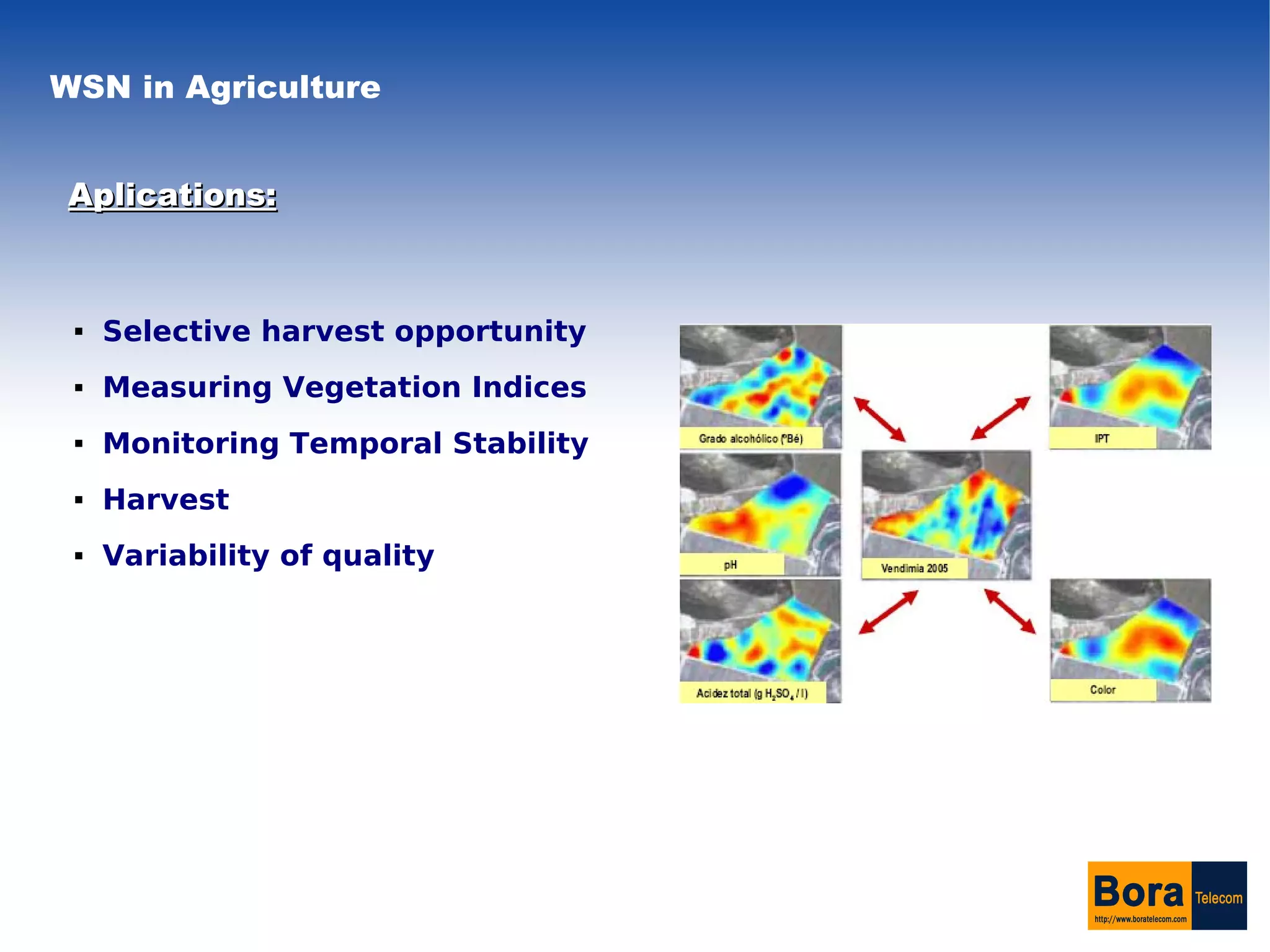
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) can be used in precision agriculture to monitor various parameters like temperature, humidity, and soil conditions. The network is made up of small sensor nodes called motes that self-organize to communicate sensory data to a gateway. This allows farmers to selectively harvest crops, monitor crop health over time, and view sensor measurements on a web application for historical analysis and geostatistical modeling. However, the technology faces limitations due to the small size and limited resources of the sensor nodes.