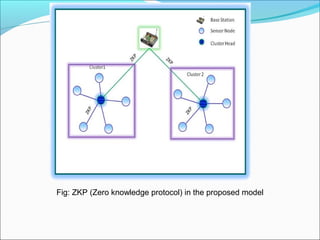
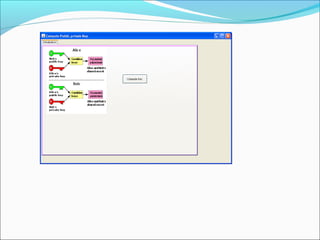
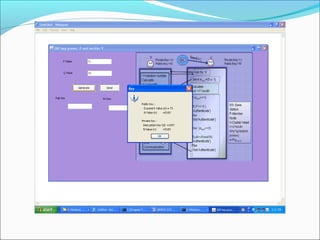
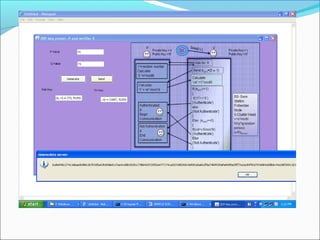
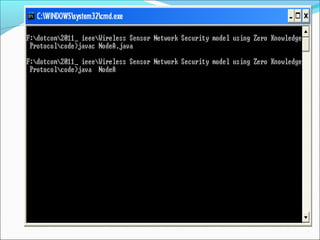
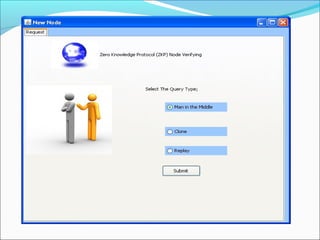
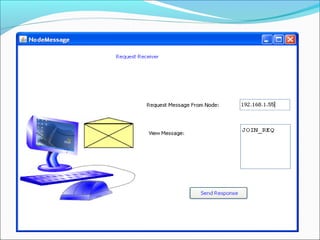
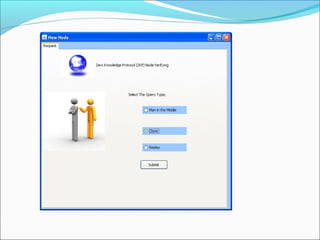
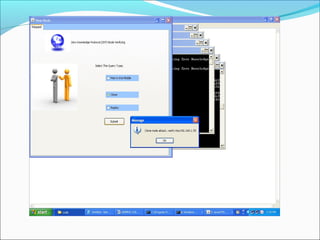
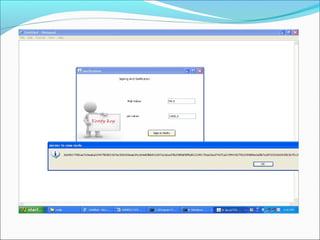
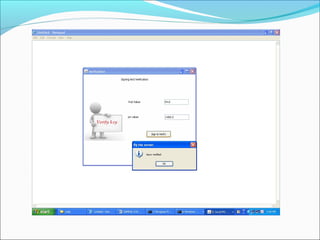
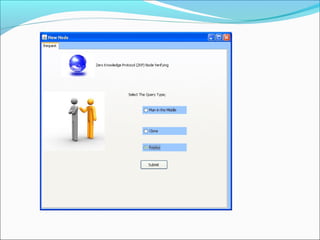
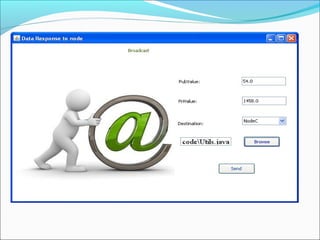
This document proposes a security model for wireless sensor networks that addresses cloning attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and replay attacks. It divides sensor nodes into base stations, cluster heads, and member nodes. Each node knows its cluster head, and base stations store information on all nodes. The model uses a "social fingerprint" based on neighboring nodes and zero knowledge protocols to detect cloned nodes and verify sender authenticity without transmitting sensitive information. Screenshots demonstrate implementation and the model is analyzed for various attack scenarios, performance, and cryptographic strength.