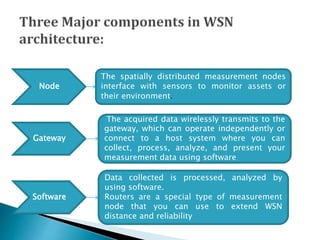
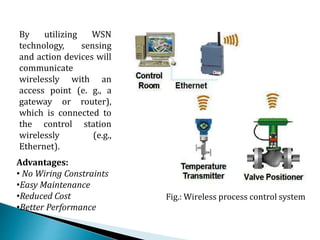
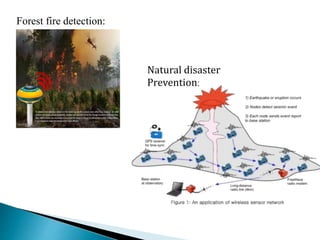
1. Wireless sensor networks consist of distributed sensor nodes that communicate wirelessly to monitor physical or environmental conditions, such as temperature, sound, or pollution levels.
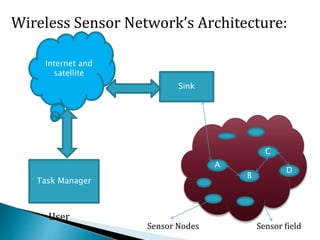
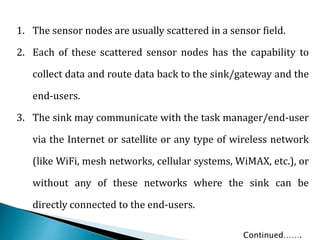
2. The sensor nodes gather and route data back to a central sink/gateway node where the information can be analyzed.
3. Communication protocols and algorithms are required for efficient multi-hop routing of data between sensor nodes and the sink node.