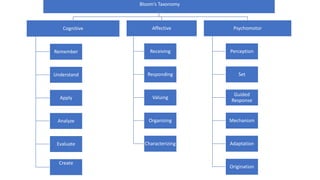
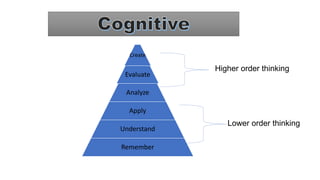
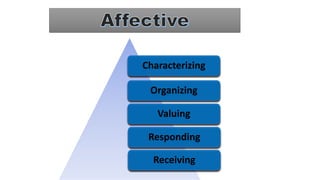
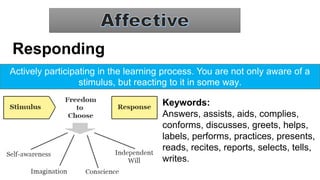
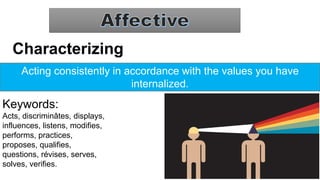
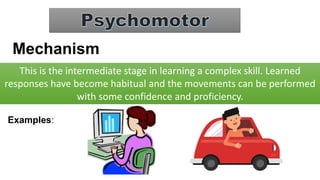
The document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, a classification framework for educational objectives in three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. It details learning outcomes and behaviors associated with each level of cognitive skill, such as remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating, as well as emotional and physical skill development. Additionally, it provides examples and characteristics of each level, emphasizing their importance in teaching and learning.