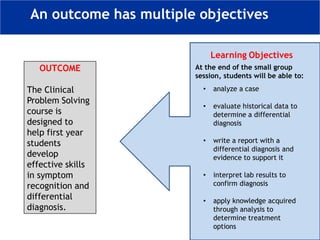
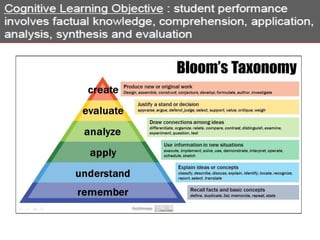
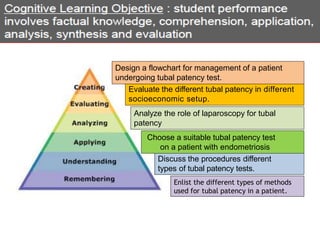
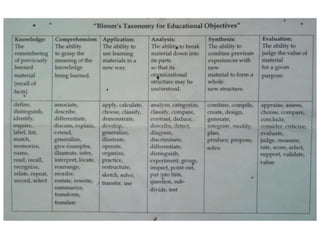
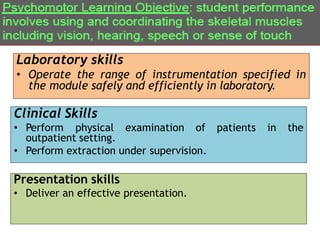
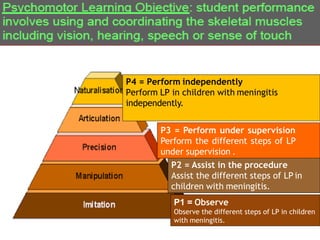
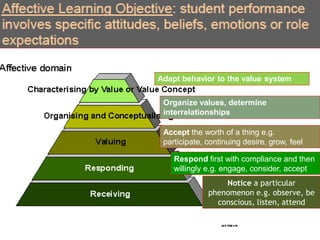
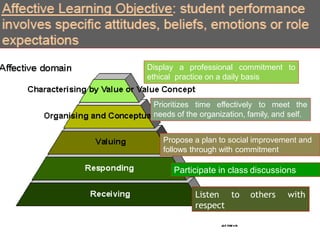
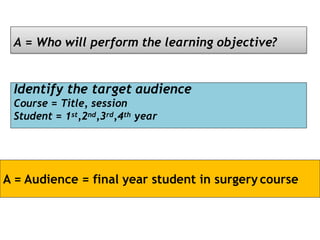
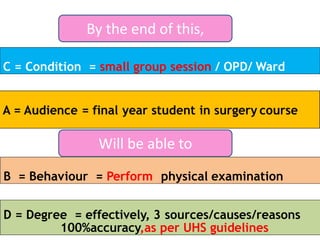
The document outlines a workshop focused on writing effective learning objectives. Participants will differentiate between learning outcomes and objectives, understand the importance of appropriate verbs, and learn the ABCD technique for formulating objectives. The content includes definitions of learning, the characteristics of meaningful objectives, and examples related to medical education.