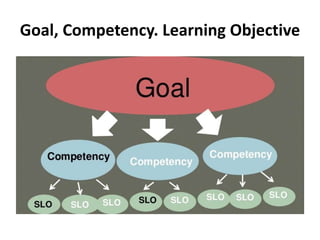
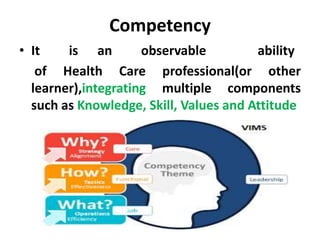
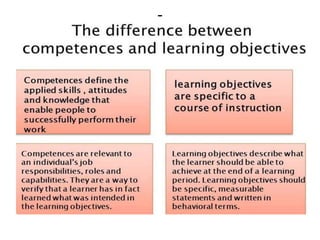
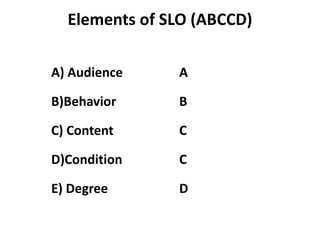
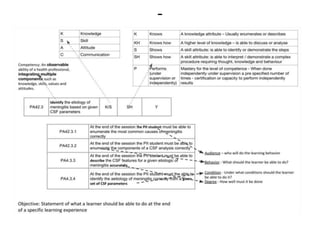
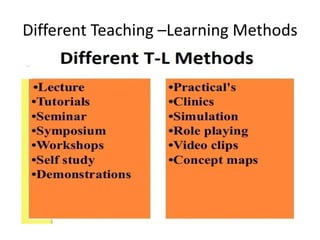
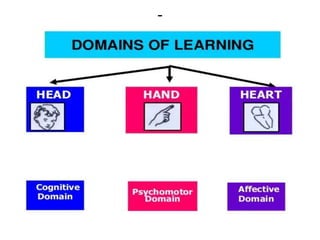
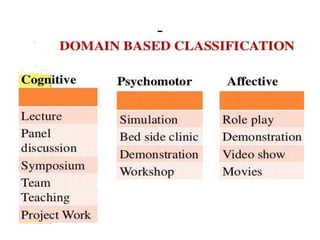
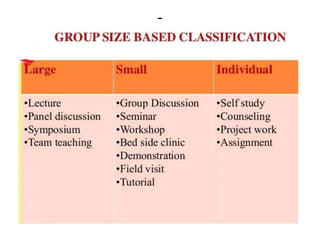
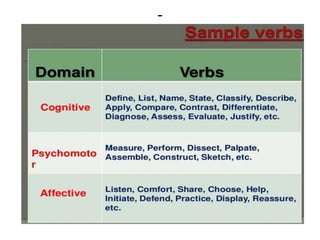
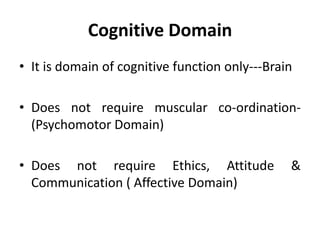
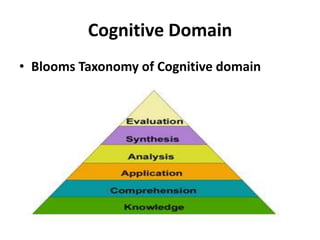
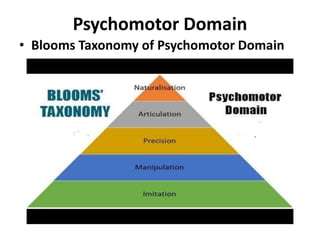
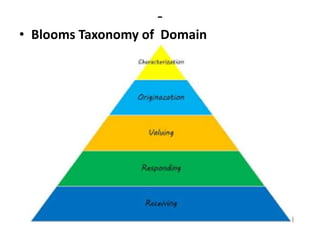
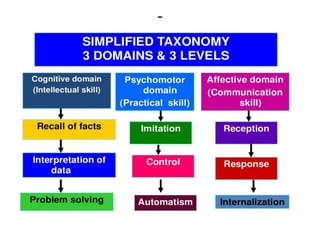
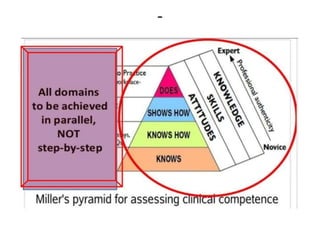
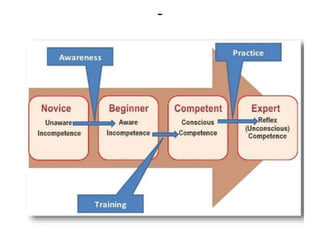
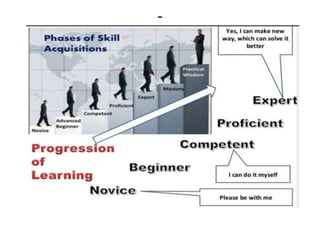
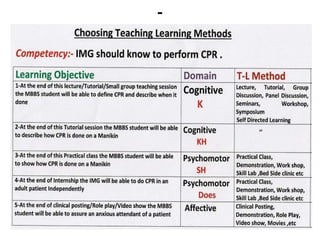
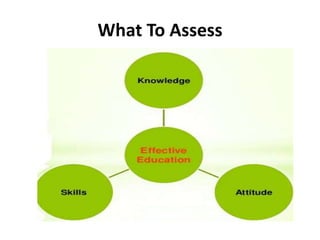
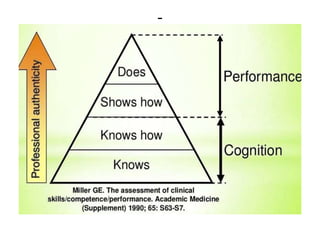
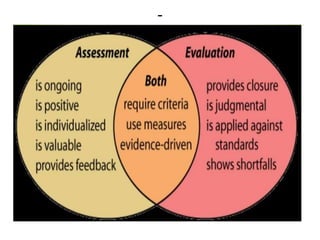
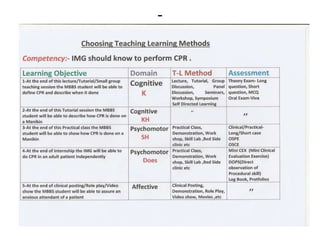
The document discusses the development of learning objectives from competencies in medical education, emphasizing the roles and competencies required of Indian medical graduates (IMGs). It outlines the definition and differentiation between competencies and learning objectives, providing examples and a structured approach to framing specific learning objectives (SLOs). Additionally, it highlights the importance of aligning teaching methods with competencies and learning objectives across cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains.