The document provides information on educating healthcare providers including guiding principles, provider roles, core competencies, and challenges.
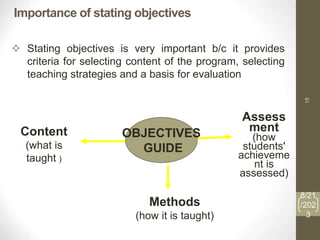
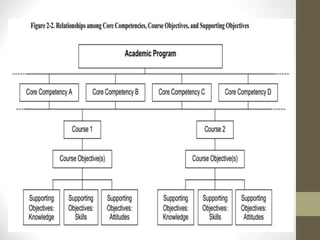
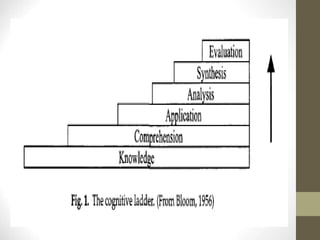
The guiding principles state that education of healthcare providers must address priority health needs within a society, identify relevant national policies and standards, and define the expected role of providers. Provider roles include caregiver, decision-maker, communicator, community leader, and manager. Core competencies encompass essential knowledge, skills, values and behaviors that are common to all students in an academic program. Challenges in educating providers include information overload, limited opportunities for skills practice, poor monitoring of student progress, and lack of incentives for teachers to improve.