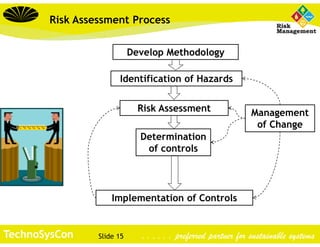
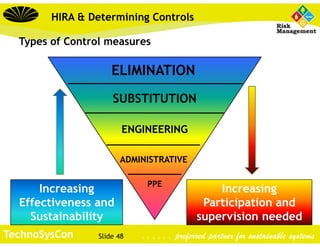
This document discusses hazard identification, risk assessment, and determining controls. It provides definitions of hazards and risk. It explains that hazard identification and risk assessment should involve identifying hazards, assessing risks, determining controls, implementing controls, and managing change. The document outlines a methodology for teams to identify hazards in their work areas by observing work conditions and tasks and using a risk matrix to rate risks and identify existing and needed controls. The overall aim is to provide a systematic approach to evaluating workplace hazards and risks.