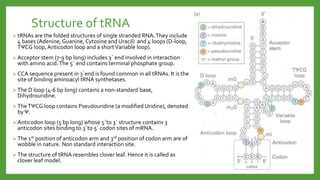
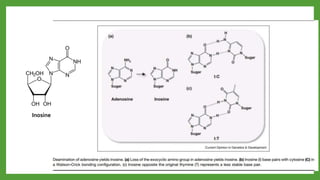
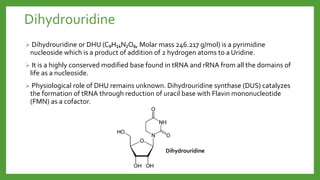
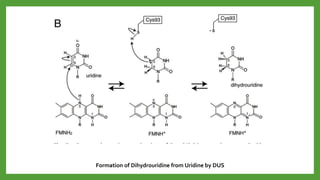
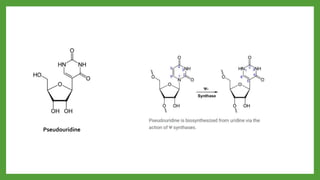
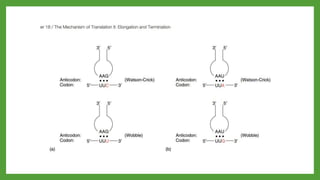
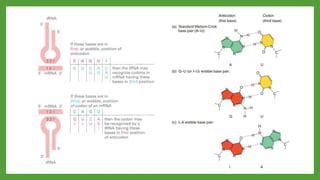
The document discusses codon-anticodon interactions and the wobble hypothesis. It explains that tRNAs have anticodons that interact with mRNA codons to add the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. The wobble hypothesis proposes that the third position of codons and first position of anticodons allow some variability, or "wobbling", in base pairing through interactions with inosine and other modified bases. This wobbling allows a single tRNA to bind to multiple codons, resolving the redundancy in the genetic code and allowing fewer tRNAs than codons.