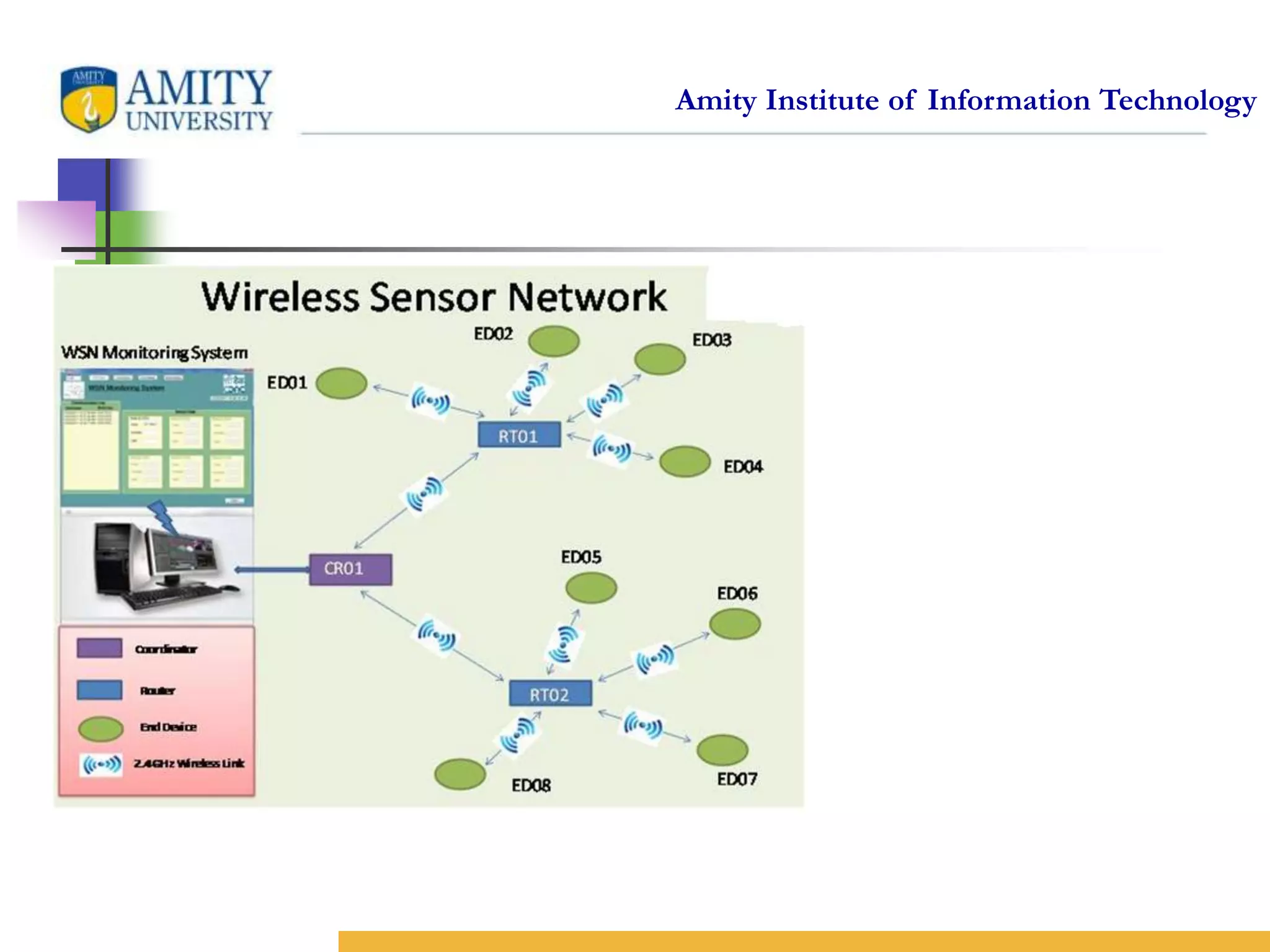
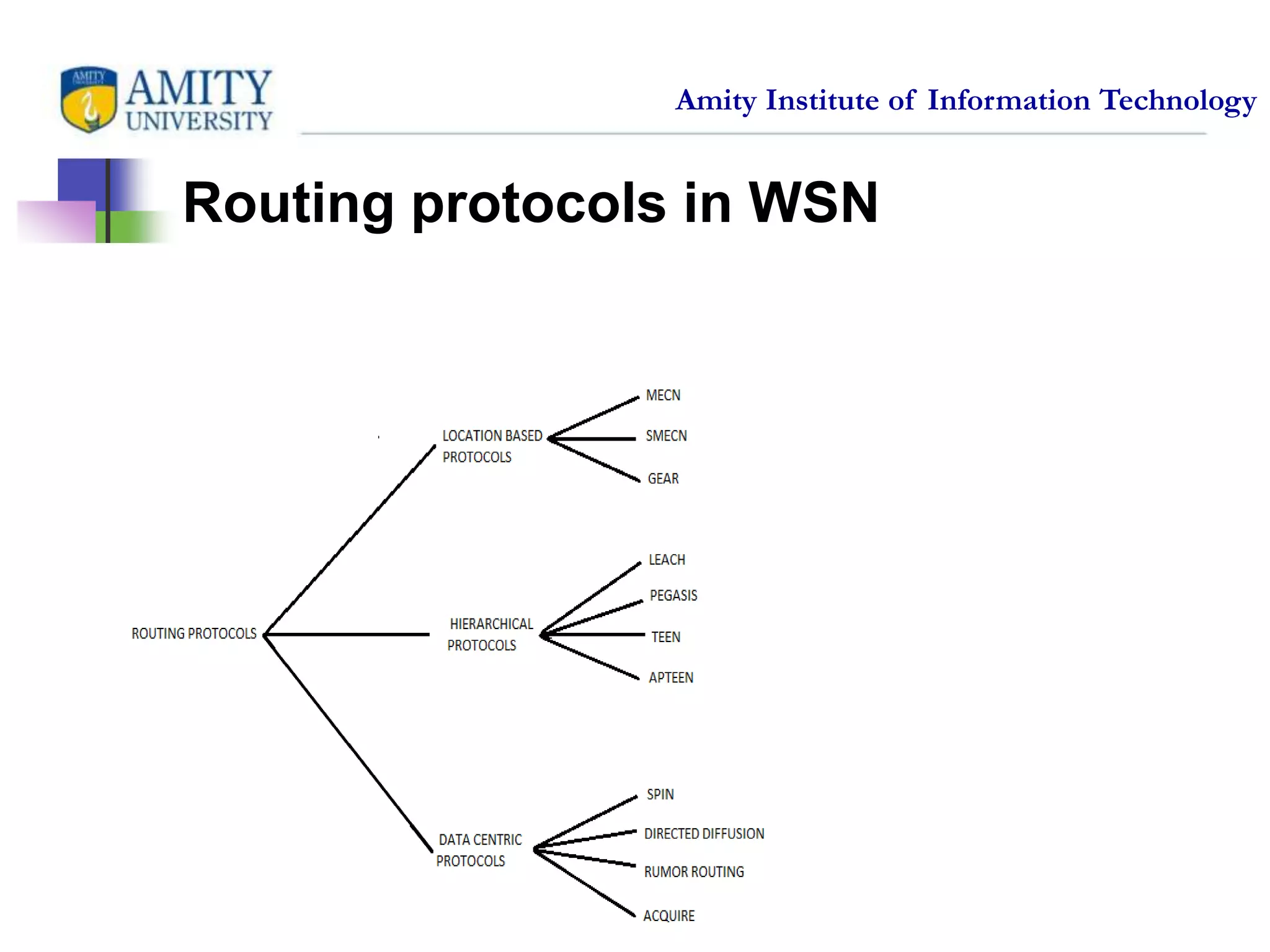
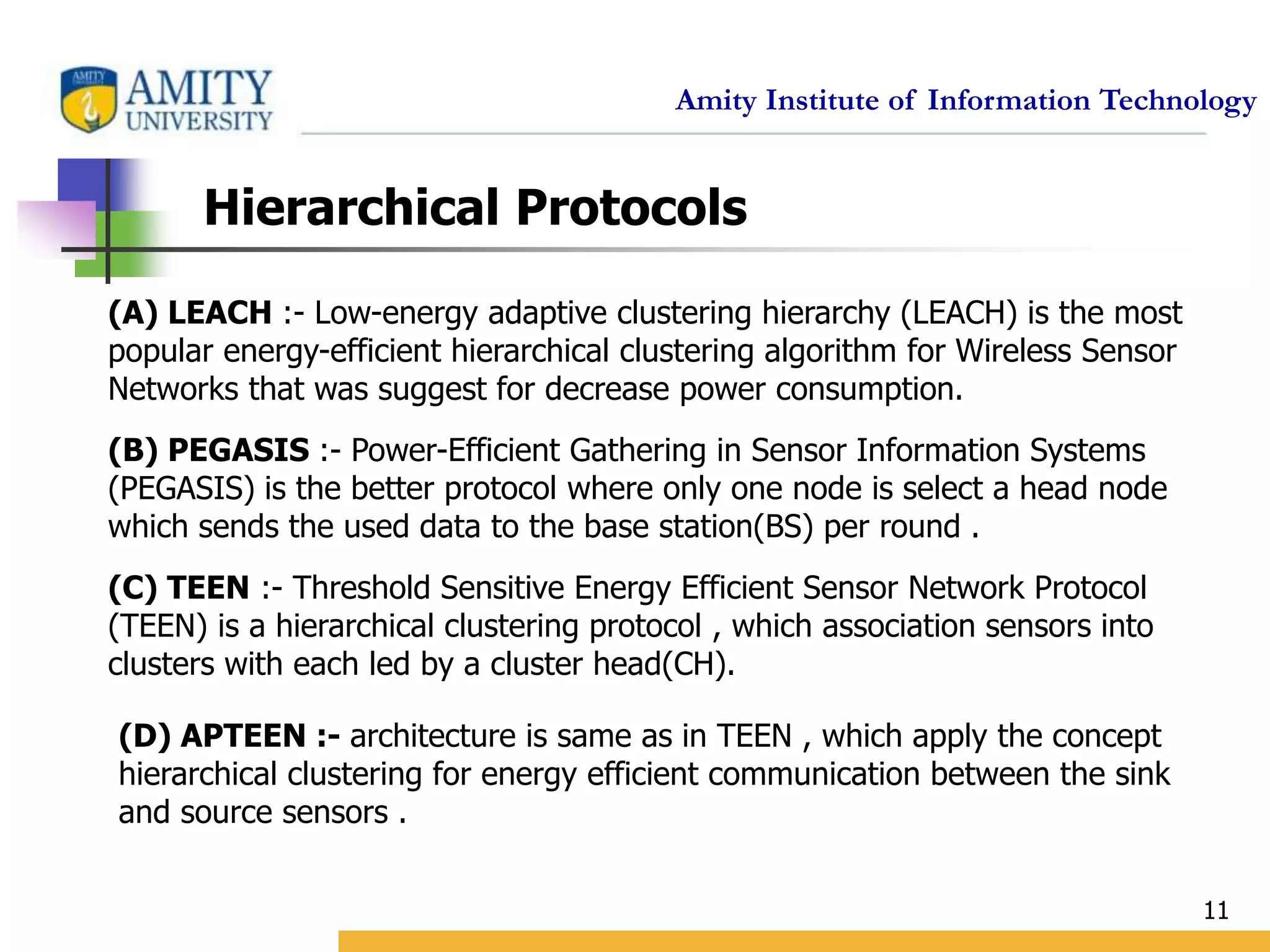
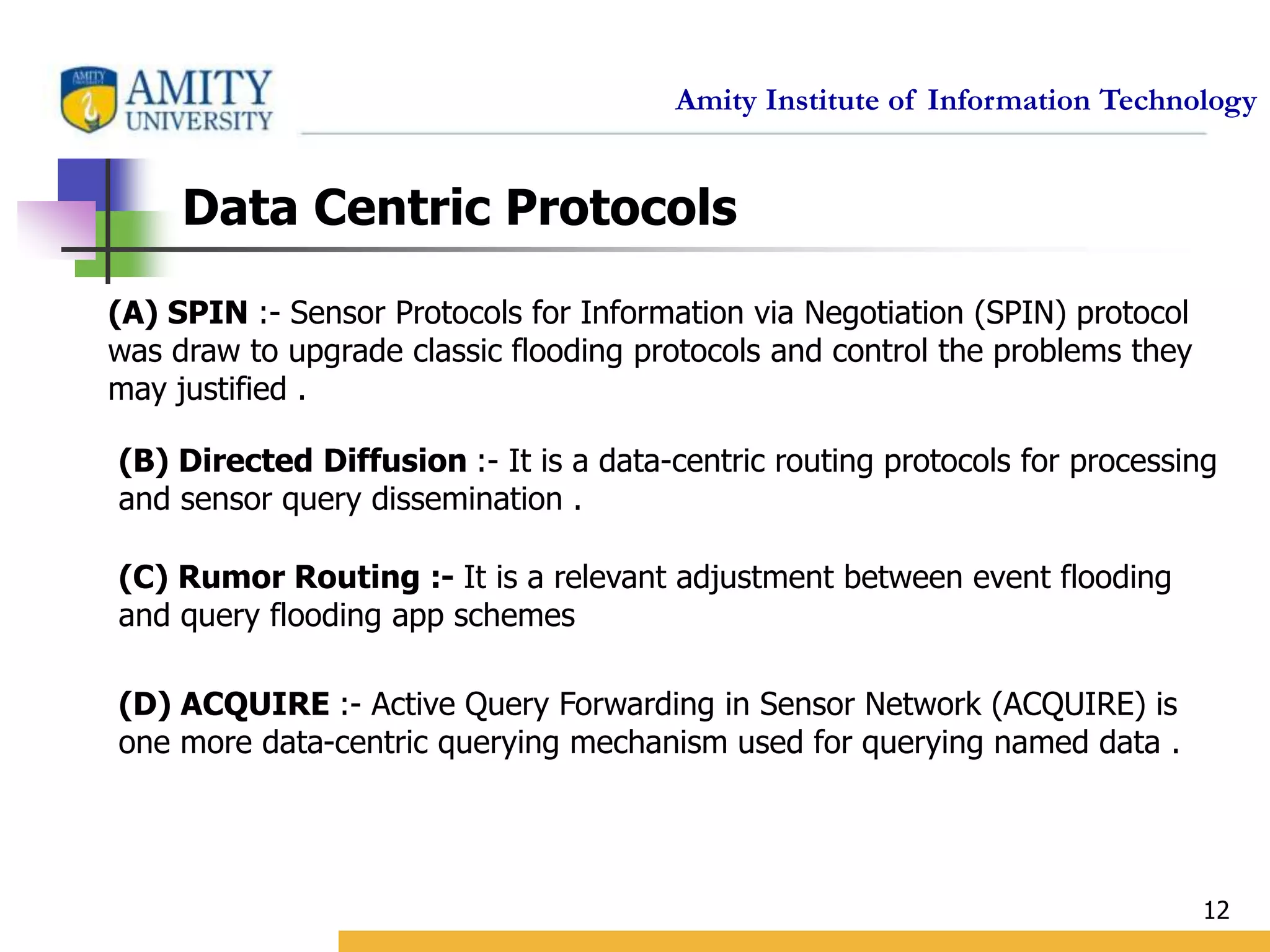
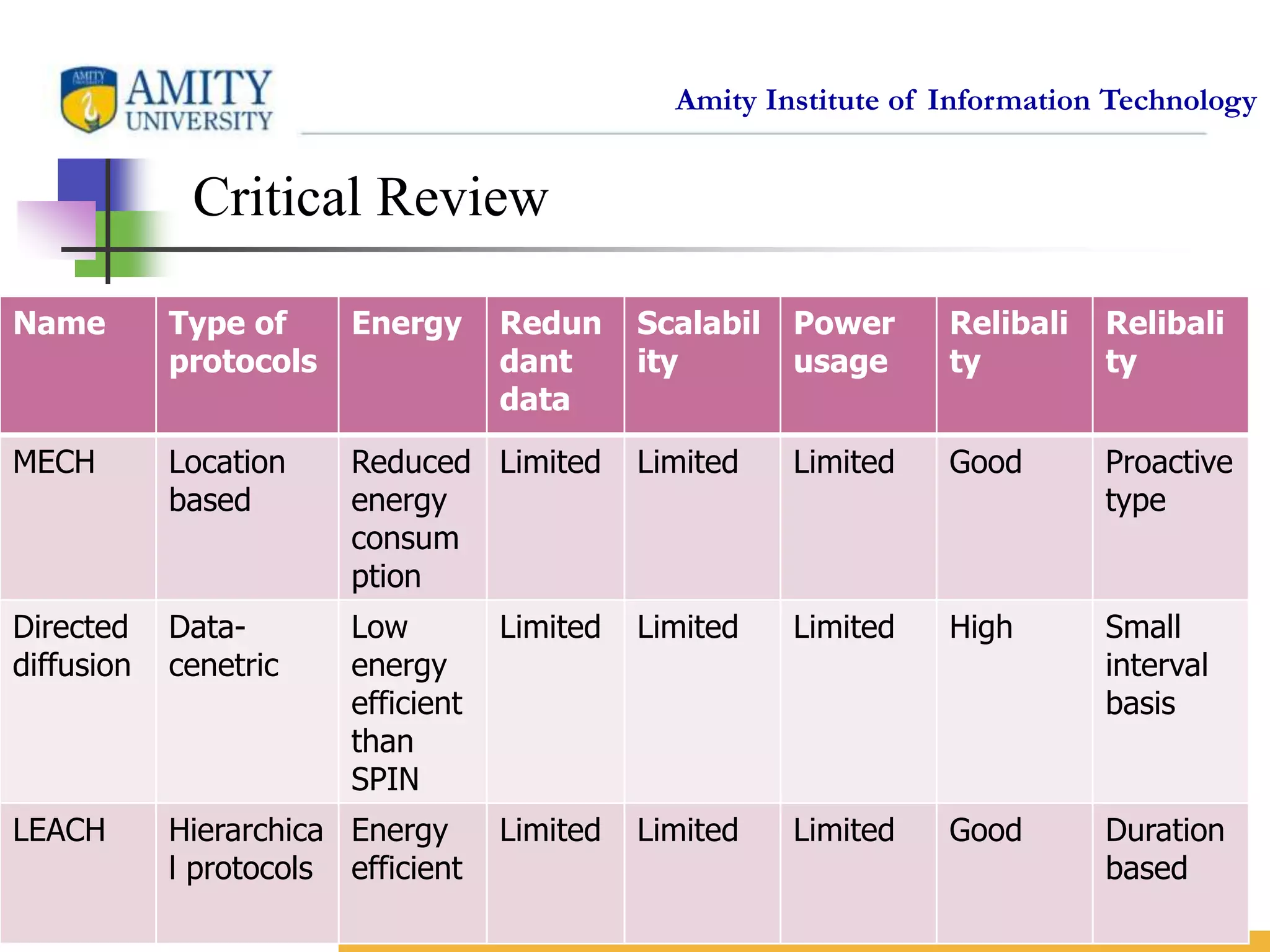
This document provides an overview and critical review of routing protocols in wireless sensor networks. It begins with an introduction to wireless sensor networks and their applications. It then discusses several related works on routing protocols. The main body discusses different types of routing protocols, including location-based protocols like MECN and GEAR, hierarchical protocols like LEACH and PEGASIS, and data-centric protocols like SPIN and Directed Diffusion. It provides examples of each type and evaluates them based on factors like energy efficiency, scalability, reliability and more. Finally, it lists references for further reading on routing protocols in wireless sensor networks.