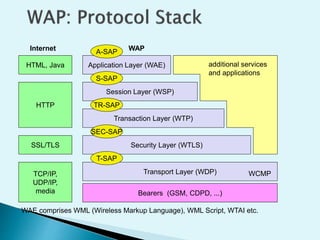
WAP is a standard that allows users to easily access information and services on the internet from their mobile phones. It was created by wireless and internet companies to provide a common protocol for internet access from cellular devices. The WAP architecture is based on web standards and aims to deliver internet content and applications to a wide range of mobile technologies in a scalable, interoperable, efficient and secure manner. However, future user demands for transmitting pictures and video may challenge WAP's capabilities and it could be overtaken by technologies like GPRS or UMTS that can better handle multimedia content.