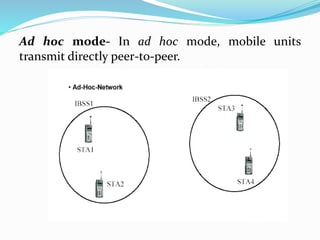
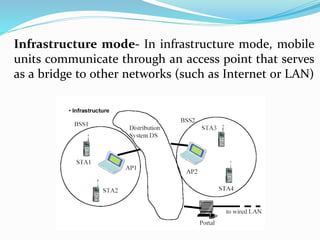
WLAN allows devices to connect to the internet and each other wirelessly using radio waves or infrared signals. It provides flexibility, portability, mobility, and ease of installation compared to wired networks. Common applications of WLAN include use in medical, education, temporary situations, airlines, and emergency centers. WLANs operate in either ad hoc mode for direct peer-to-peer connections or infrastructure mode which uses an access point to connect to other networks. Technologies used include infrared, radio waves that comply with FCC regulations, and microwaves. WAP allows access to internet content and services on mobile devices by compressing web pages for smaller screens.