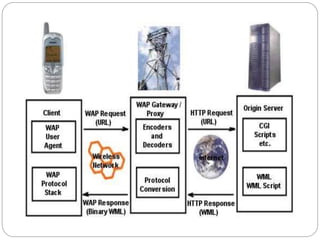
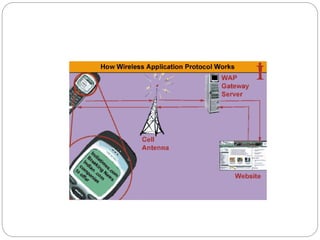
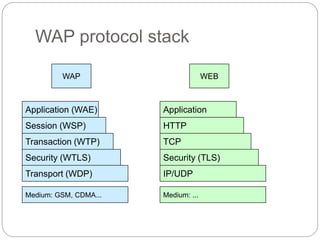
This document provides an overview of the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) which enables delivery of internet content and services to mobile devices. WAP uses open standards like HTML, XML and TCP/IP adapted for wireless networks through specifications for WML, WMLScript and WTAI. A key component is the WAP Gateway that connects the wireless domain to the internet and compresses content using a binary version of HTTP called WSP. The Wireless Markup Language (WML) is used to develop optimized mobile applications that can be efficiently encoded for transmission. WAP enables core mobile services like banking, shopping and messaging through standardized access across different wireless networks and devices.