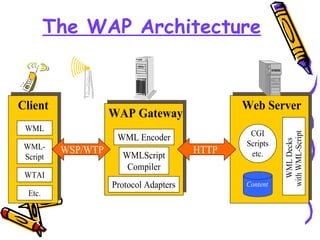
WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) allows for data exchange on mobile networks. It uses existing standards and defines a layered architecture to optimize access to information on devices like phones. The goal of WAP is to provide a web-like experience on small devices. It uses proxies to connect wireless networks to the internet and transports requests from mobile devices to web servers using protocols like WSP and WML, which is optimized for small screens. While higher bandwidth networks may reduce its need, WAP compliance with future standards could expand its usage for online services, productivity, and more.