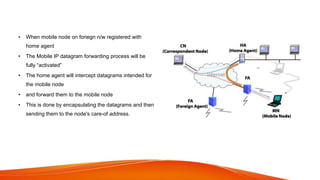
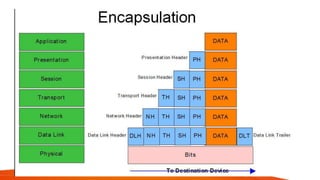
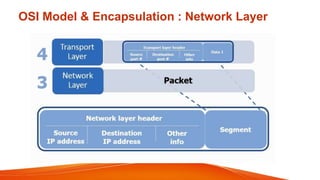
Mobile IP uses encapsulation and tunneling to forward data to mobile nodes. When a mobile node registers with its home agent while connected to a foreign network, the home agent intercepts datagrams for the mobile node and encapsulates them by adding a new IP header. This creates a tunnel to the mobile node's care-of address. Common encapsulation methods include IP-in-IP, minimal encapsulation, and GRE. Tunneling allows datagrams to be forwarded across networks while hiding the details of the encapsulated datagram. Loops can occur if the source IP matches the tunnel endpoint, so routers discard these datagrams.