This document discusses the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP), which allows hosts to report their multicast group memberships to neighboring multicast routers. It describes the different versions of IGMP, including IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3. It also covers IGMP messages like membership queries, reports, and leaves. IGMP snooping is defined as a switch feature that optimizes multicast traffic delivery by only forwarding traffic to ports with interested receivers. Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) serves a similar purpose for IPv6 as IGMP does for IPv4.




![IGMP messages
MEMBERSHIP QUERY [ 0x11 ]
Membership Query messages are used by multicast enabled routers running IGMP to
discover which hosts on attached networks are members of which multicast groups.
Membership Query messages are sent to the 'all-systems' multicast group address of
224.0.0.1.
There are two sub types of Membership Query:
General Query(every 60s) - used to learn which groups have members on an attached network.
Group-Specific Query - used to learn if a specific group has any members on an attached network.
Router sends query membership message to a single group rather than all hosts(reduce traffic)
MEMBERSHIP REPORT (v1/v2) [ 0x12 / 0x16 ]
A membership report message is sent by a host whenever it joins a multicast group, and
when responding to Membership Queries sent by an IGMP router that is functioning as a
Querier.
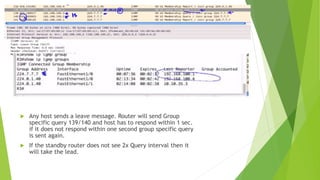
LEAVE GROUP [ 0x17 ]
This message is sent when a host leaves a multicast group. This message is sent to the 'all-
routers' multicast address of 224.0.0.2. The router then sends out a group-specific
membership query to the network to verify if the last member of a group has left.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igmp-140606020139-phpapp01/85/IGMP-5-320.jpg)