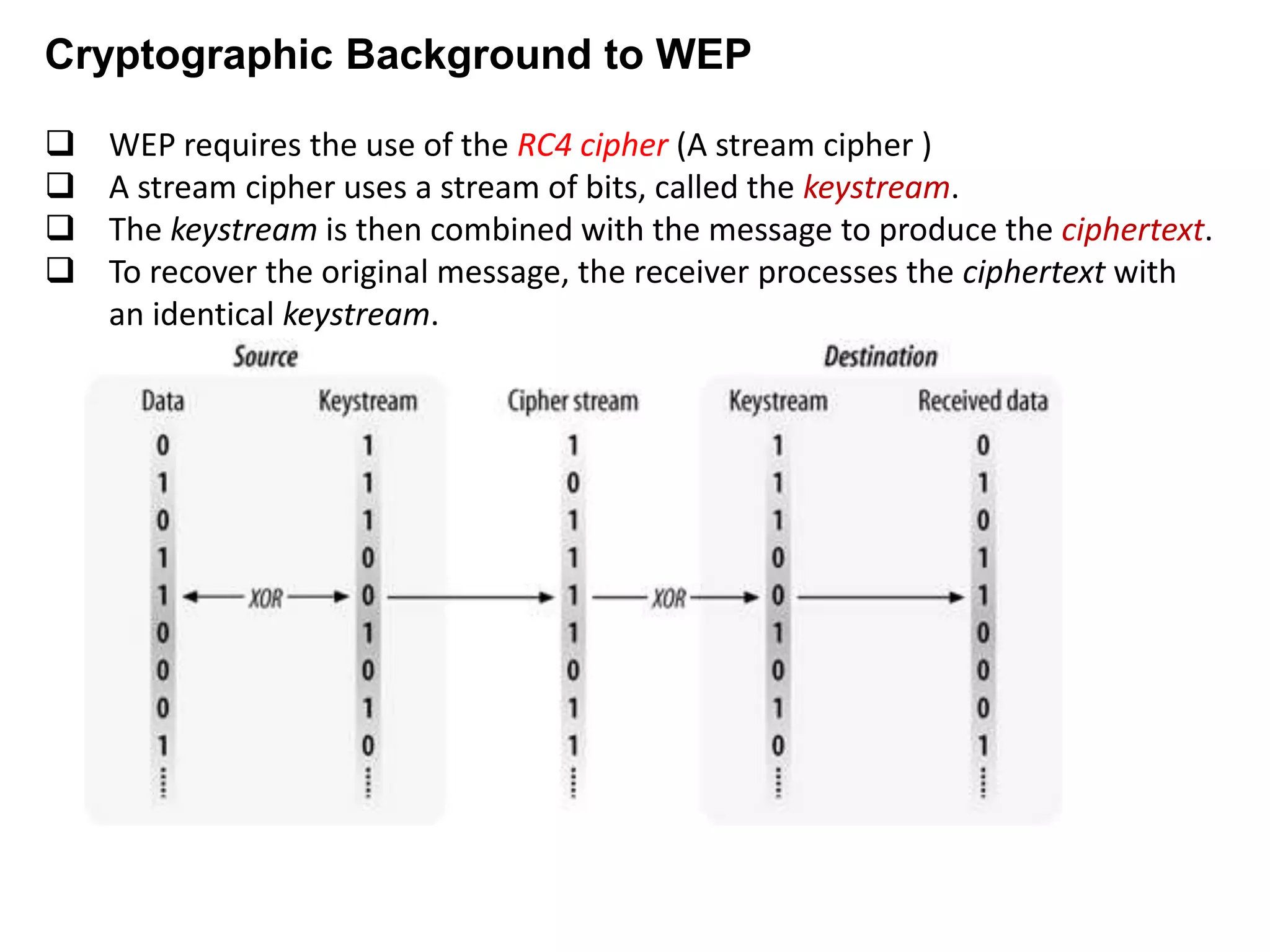
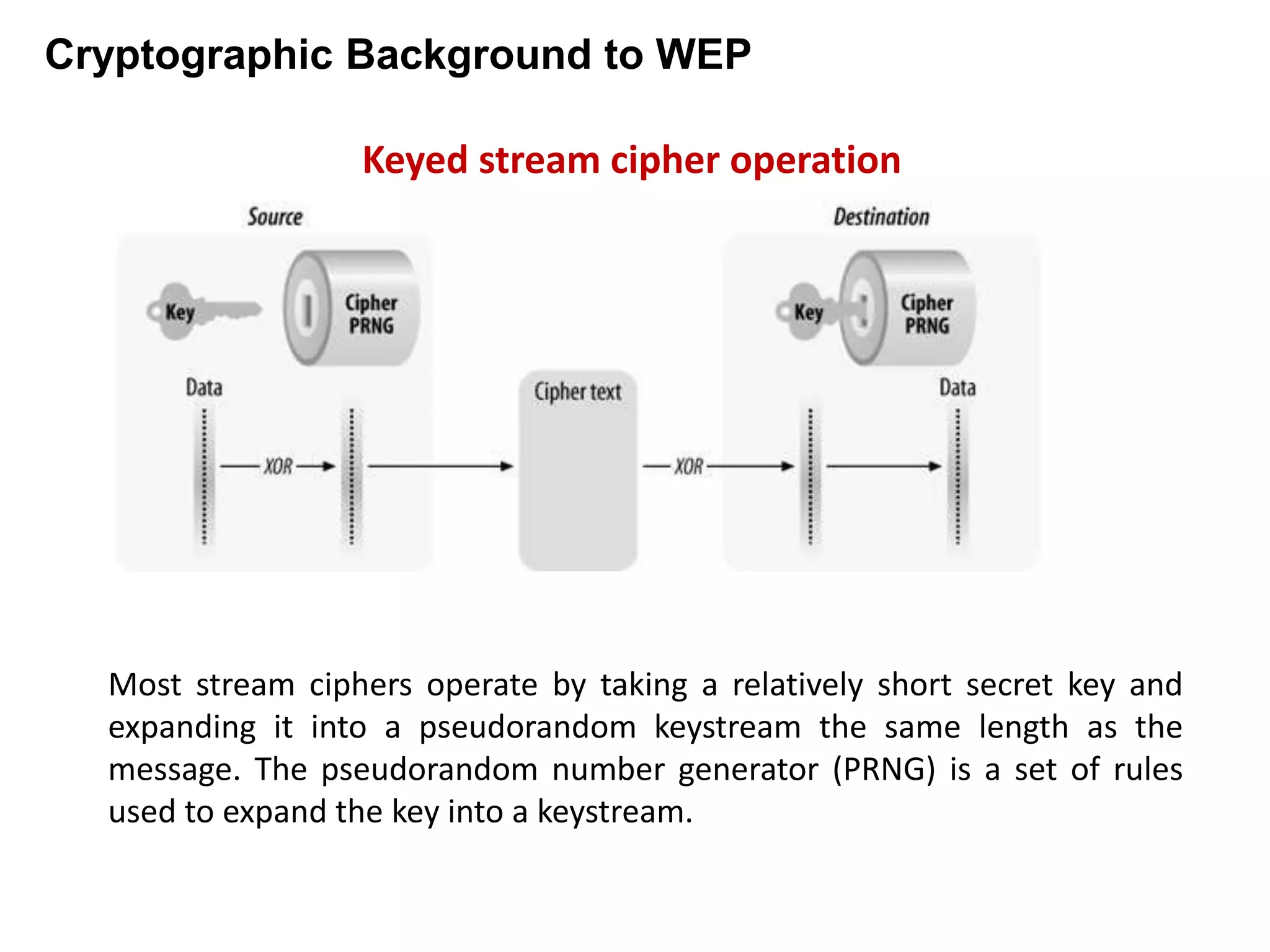
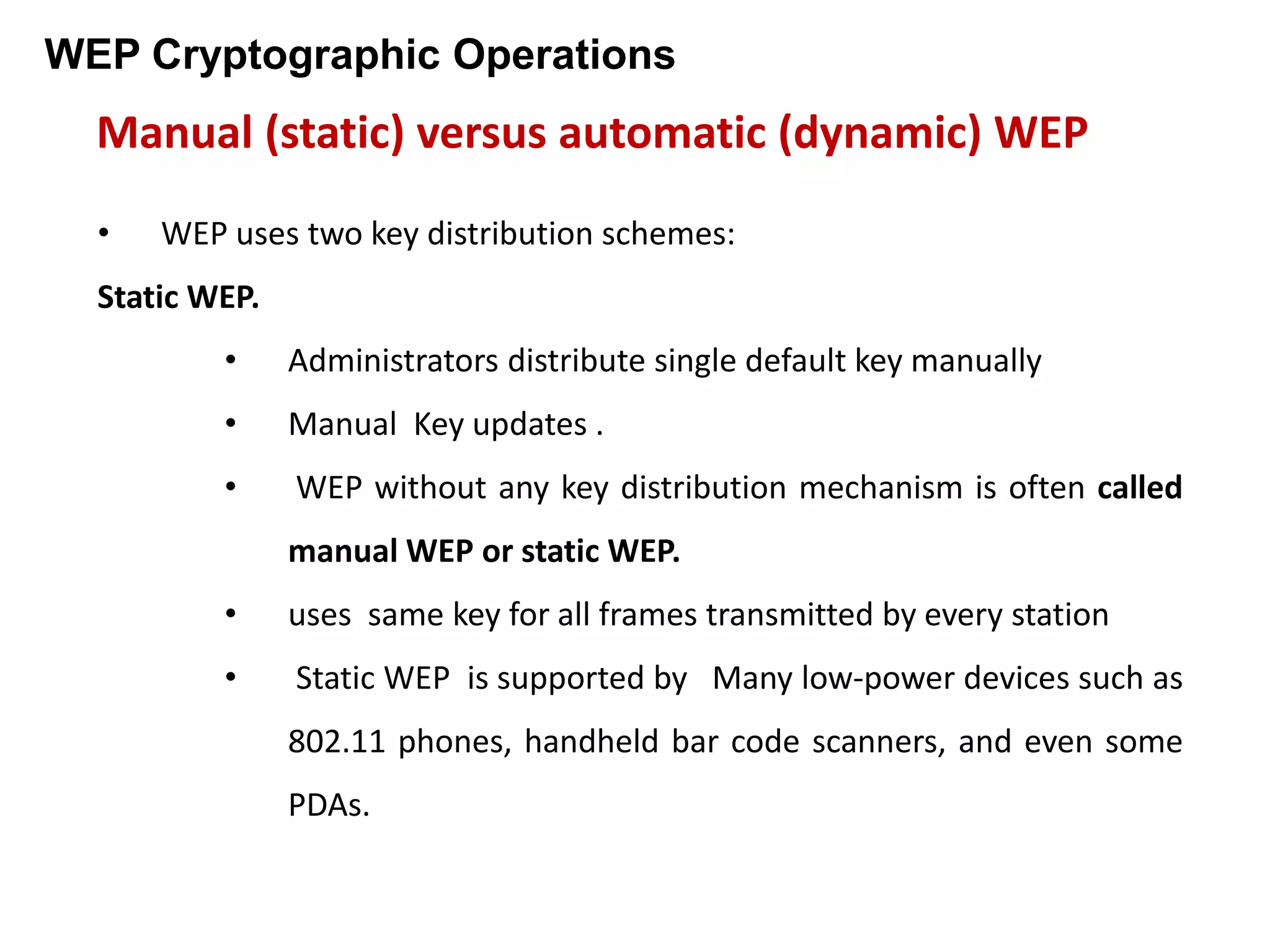
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) was an early protocol for wireless network security. It aimed to provide confidentiality through encryption and integrity through a checksum. However, WEP had several flaws:
1. It reused encryption keys too frequently due to a small initialization vector space, allowing the same encryption to be used for multiple packets.
2. It used a weak integrity checksum that could be predicted, allowing packets to be modified without detection.
3. Its short secret key provided insufficient security against brute force attacks to recover keys from captured network traffic.