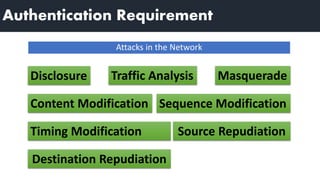
1) Message authentication can be achieved through message encryption, message authentication codes (MACs), or hash functions.
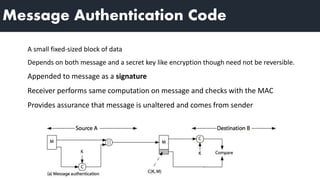
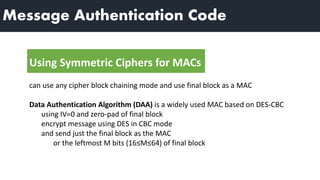
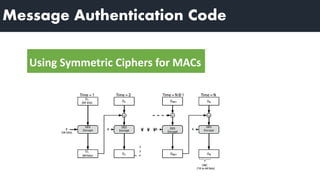
2) MACs provide authentication by appending a fixed-size block that depends on the message and a secret key. Receivers can verify messages by recomputing the MAC.
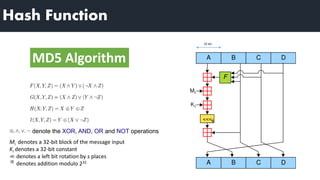
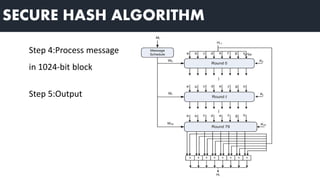
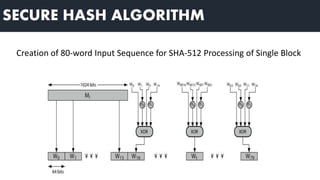
3) Hash functions map variable-length data to fixed-length outputs and are easy to compute but infeasible to reverse or find collisions. Common hash functions include MD5 and SHA-512.