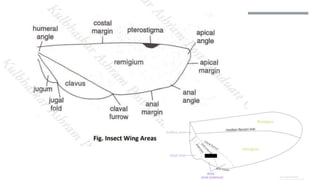
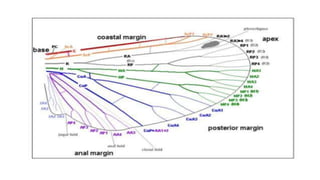
The document discusses the structure and modifications of insect wings. It defines wings as flattened double-layered expansions of the body wall with the same constituents as the body wall. The wings contain six to eight longitudinal veins that branch and are named based on a standardized system. The insect wings are highly modified for different habits, and distinct names describe these forms, including tegmina, elytra, hemelytra, halteres, pseudohalteres, brachypterous, membranous wings, and scaly wings. Each wing type is exemplified by the order it is found in.