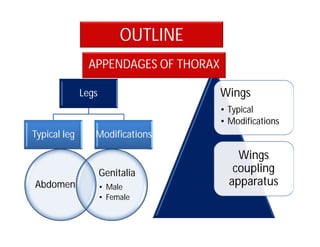
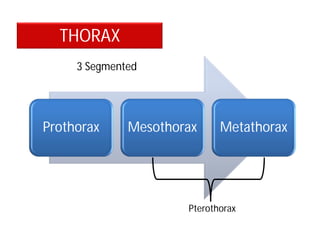
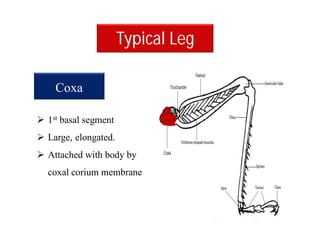
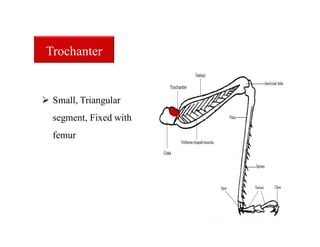
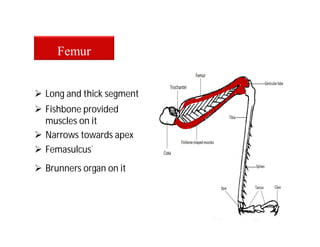
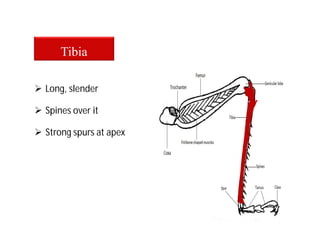
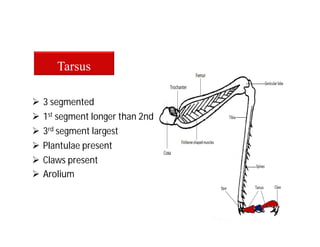
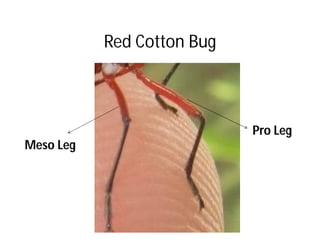
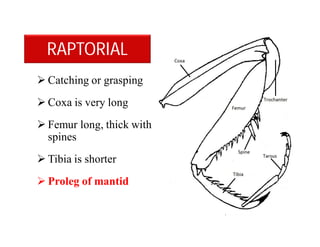
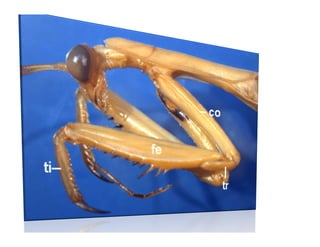
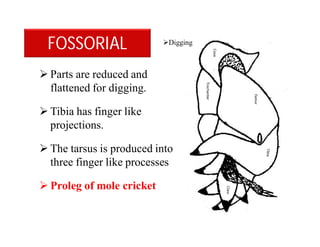
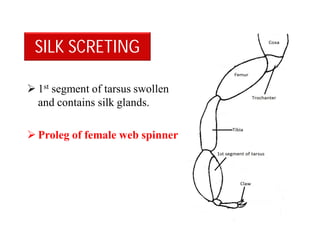
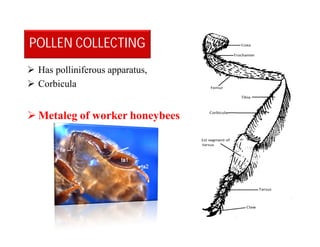
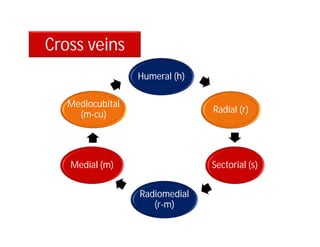
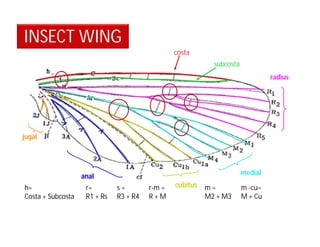
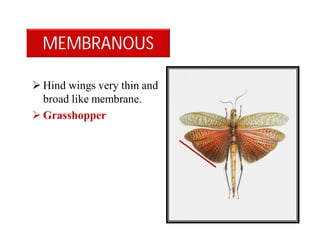
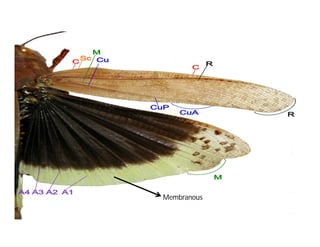
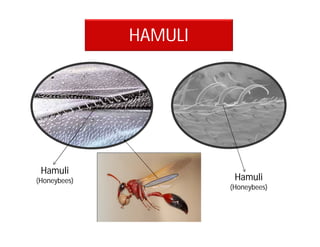
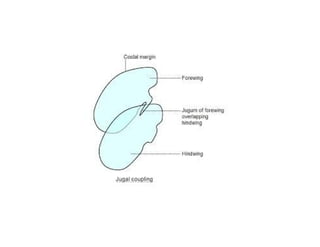
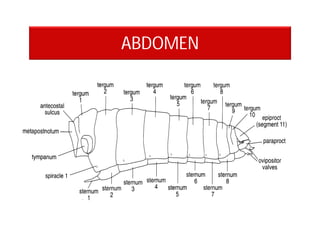
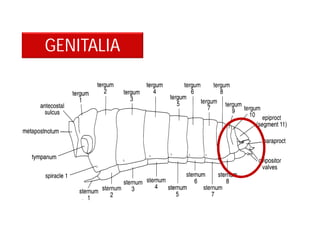
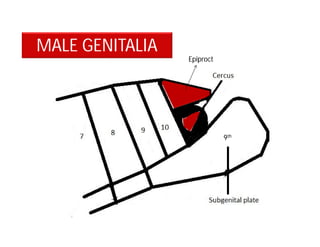
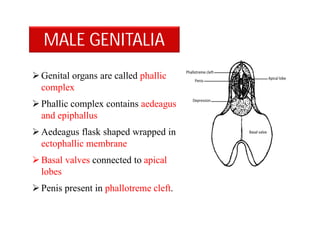
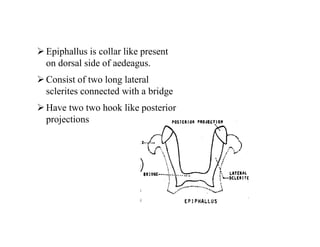
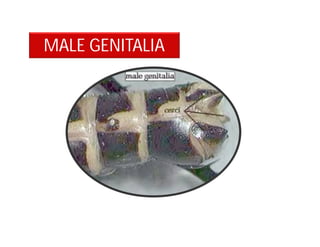
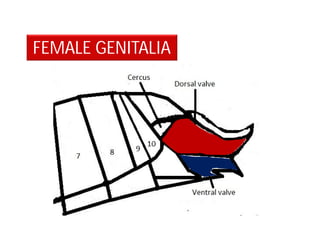
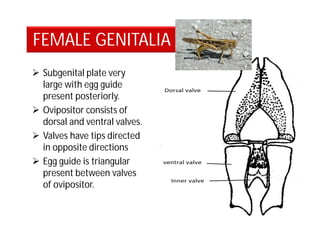
This document discusses the appendages of the thorax (legs and wings) and abdomen (male and female genitalia) in insects. It describes the typical structure of insect legs, and various modifications including cursorial, saltatorial, raptorial, fossorial, natatorial, clinging, silk secreting, antenna cleaner, pollen collecting, and basket-like legs. Wing structures are also summarized, including typical wings, wing modifications like elytra and hemelytra, and wing coupling apparatuses. Finally, the document provides an overview of male and female genitalia in insects.