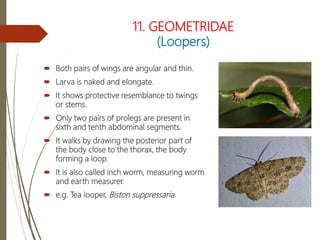
This document provides information on the order Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies). It describes their key physical characteristics including scales covering the body and wings. It also summarizes the characteristics of common moth and butterfly families, including their larvae. Key families described are Nymphalidae, Lycaenidae, Papilionidae, Pieridae, Satyridae, Arctiidae, Bombycidae, Noctuidae, and Hesperiidae.