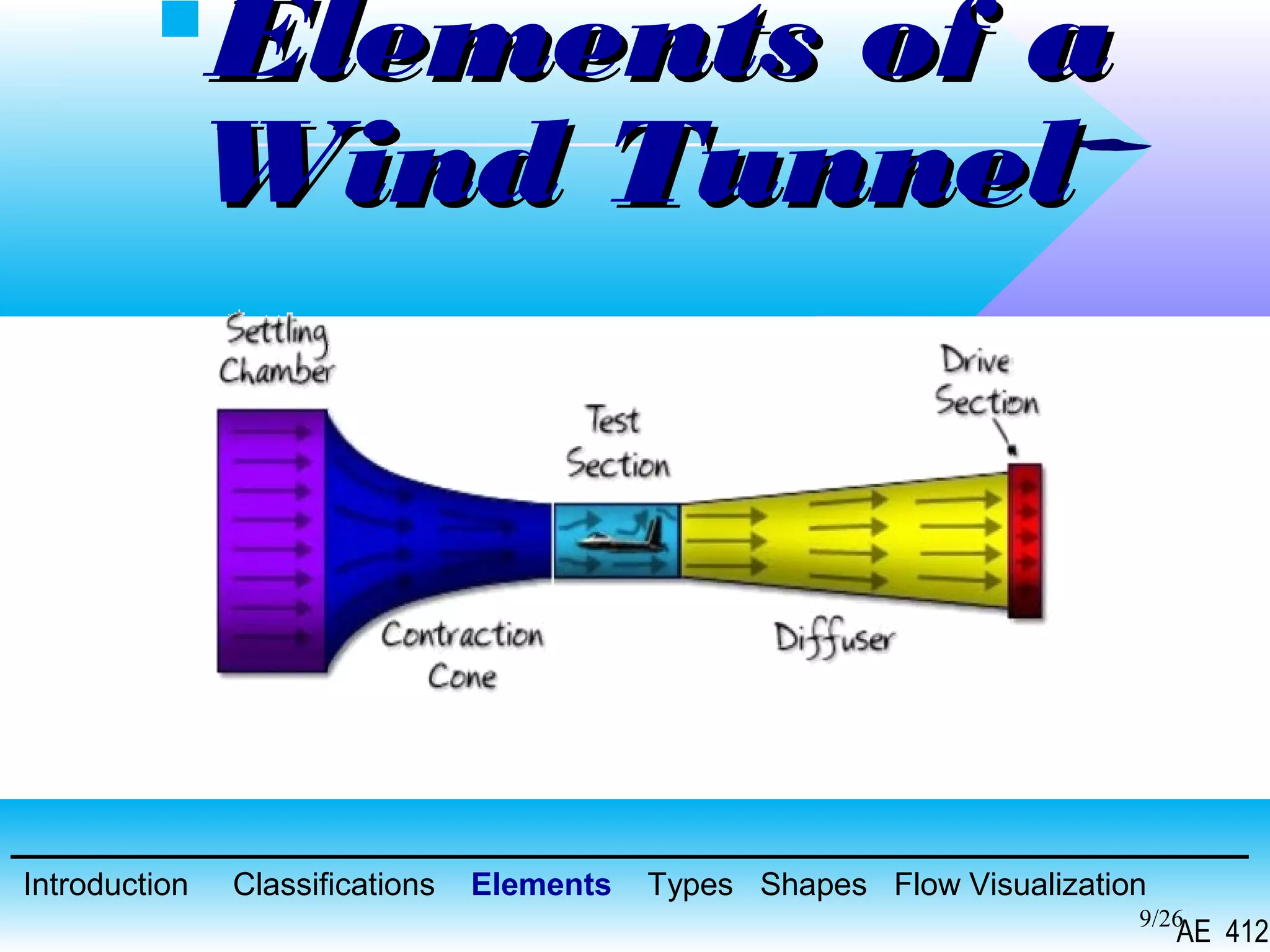
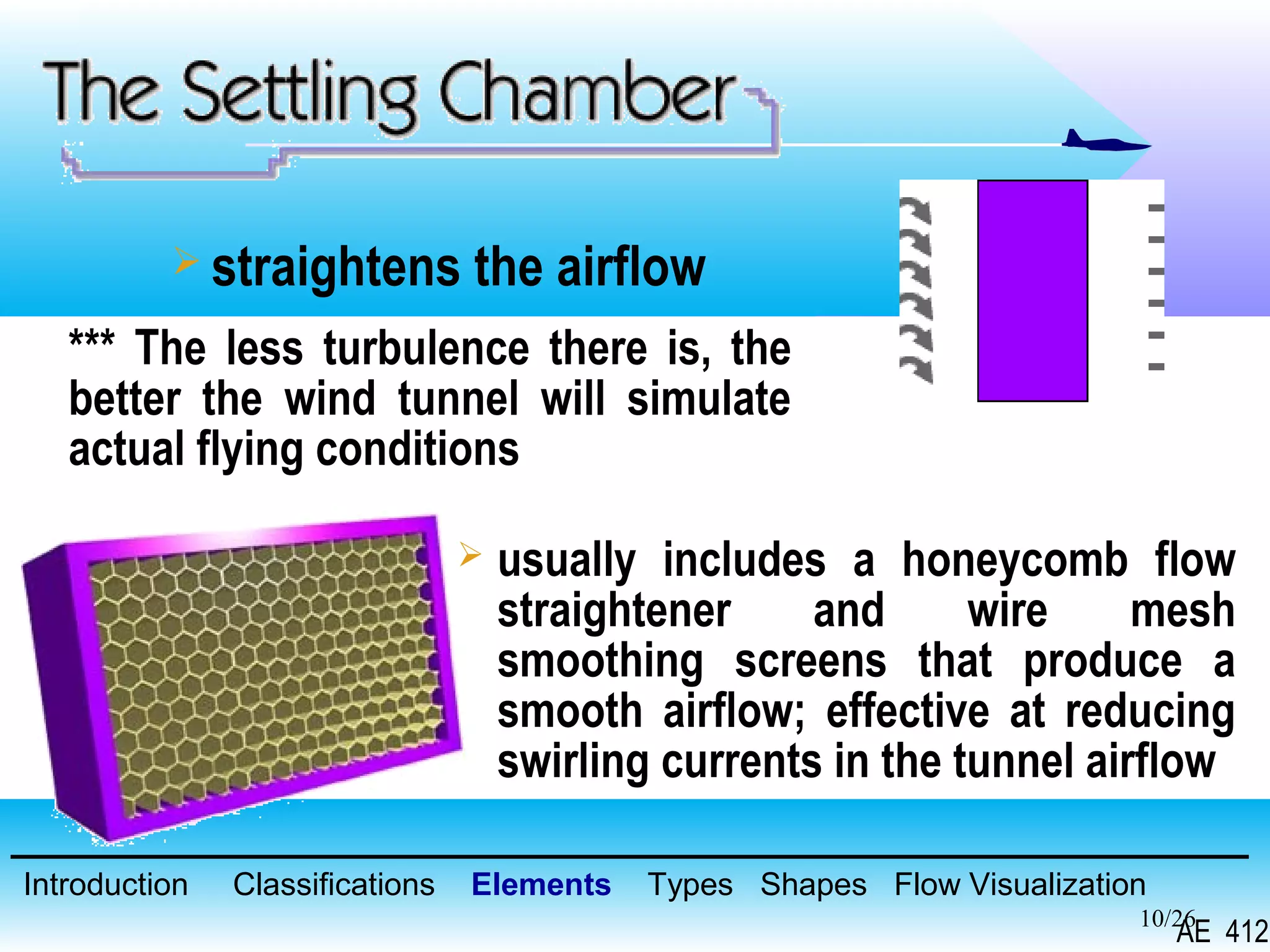
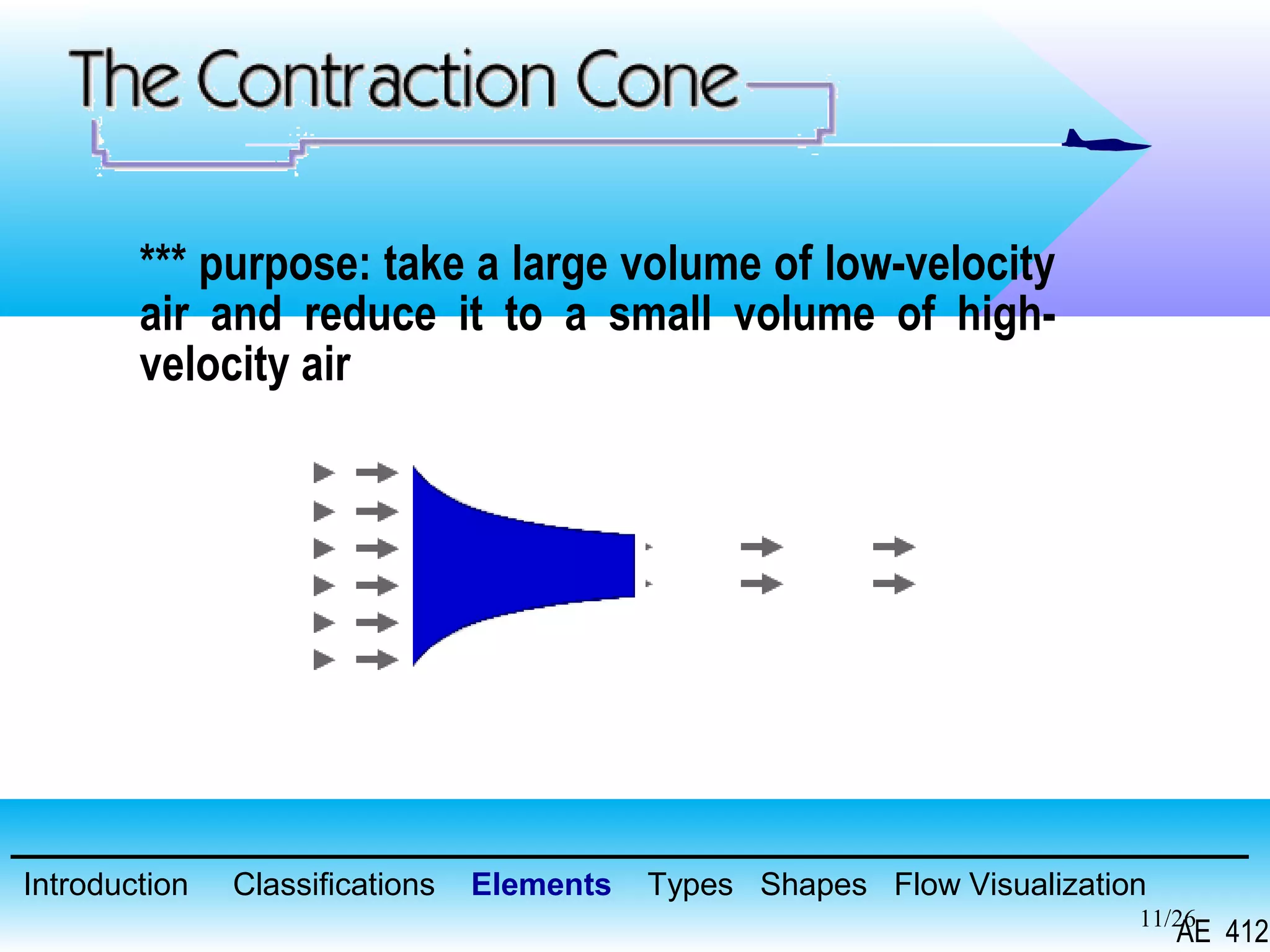
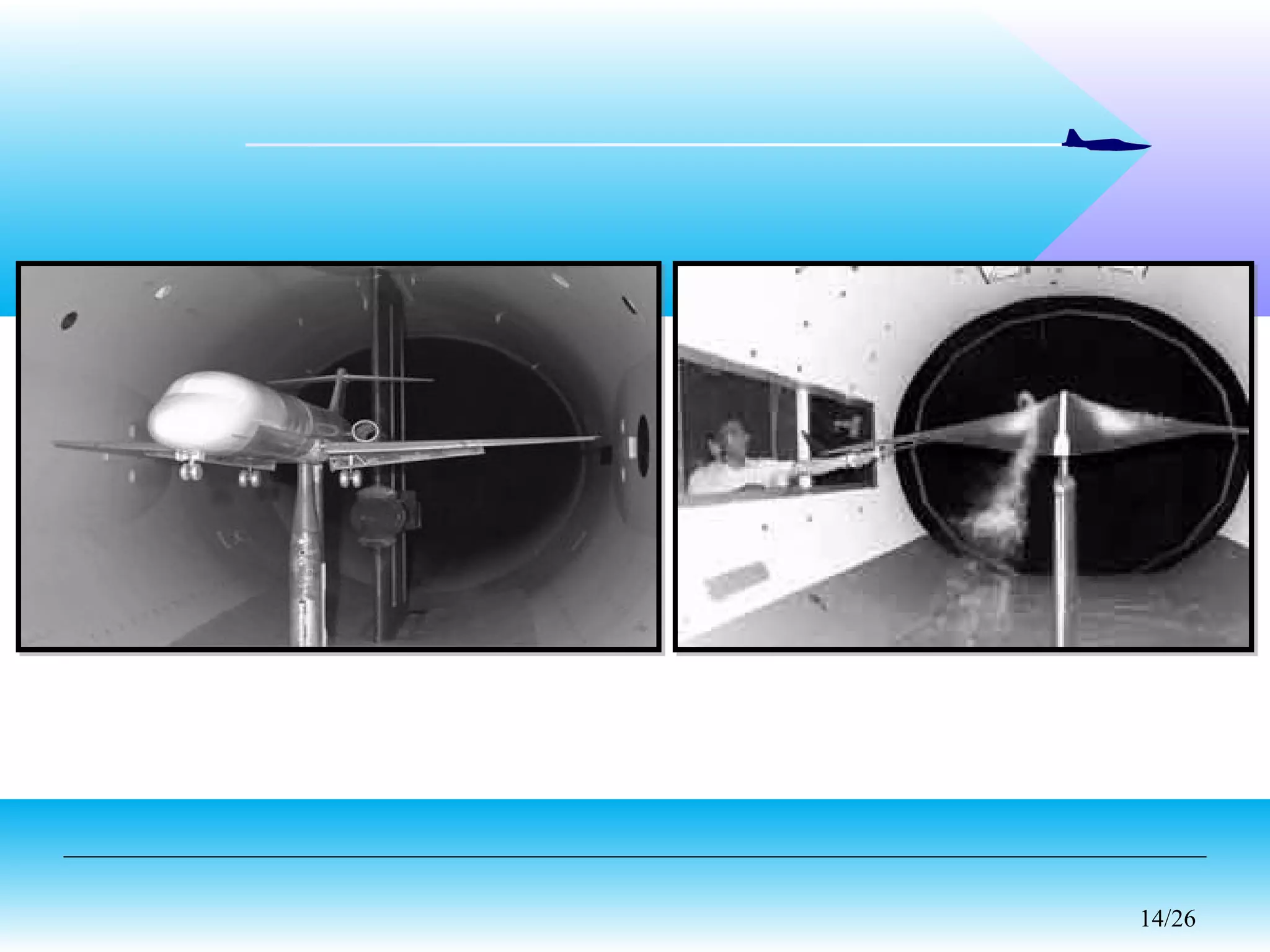
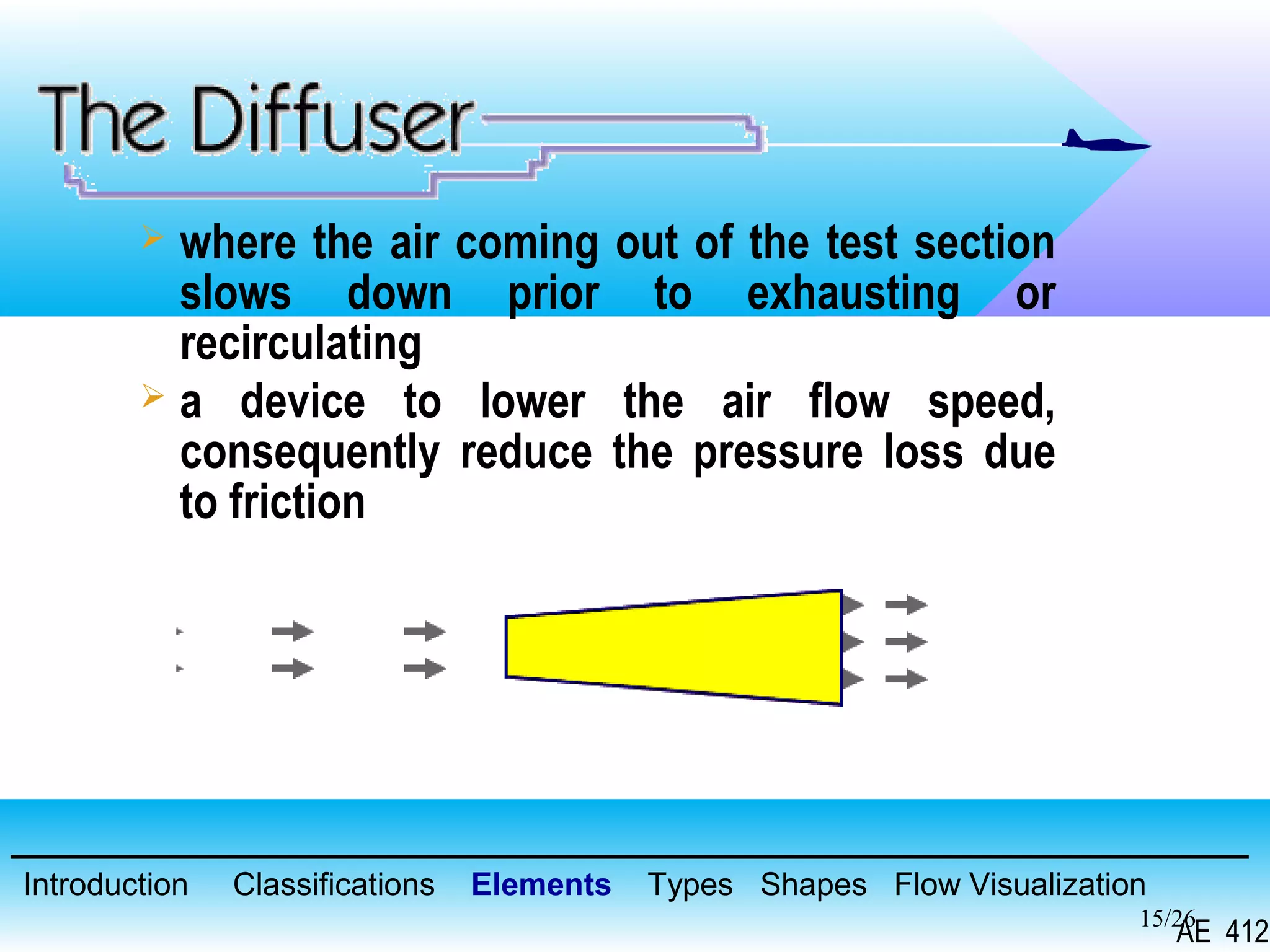
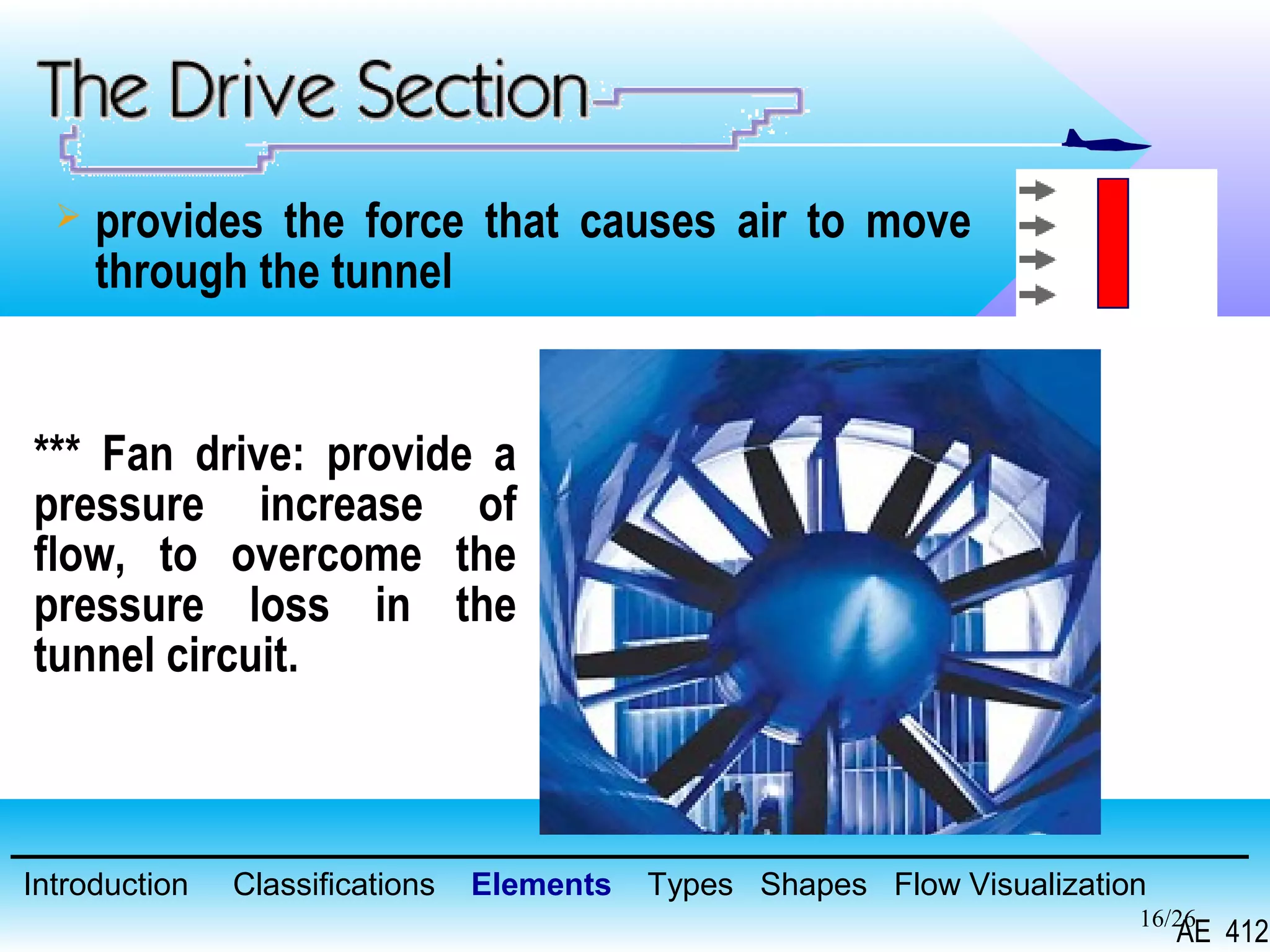
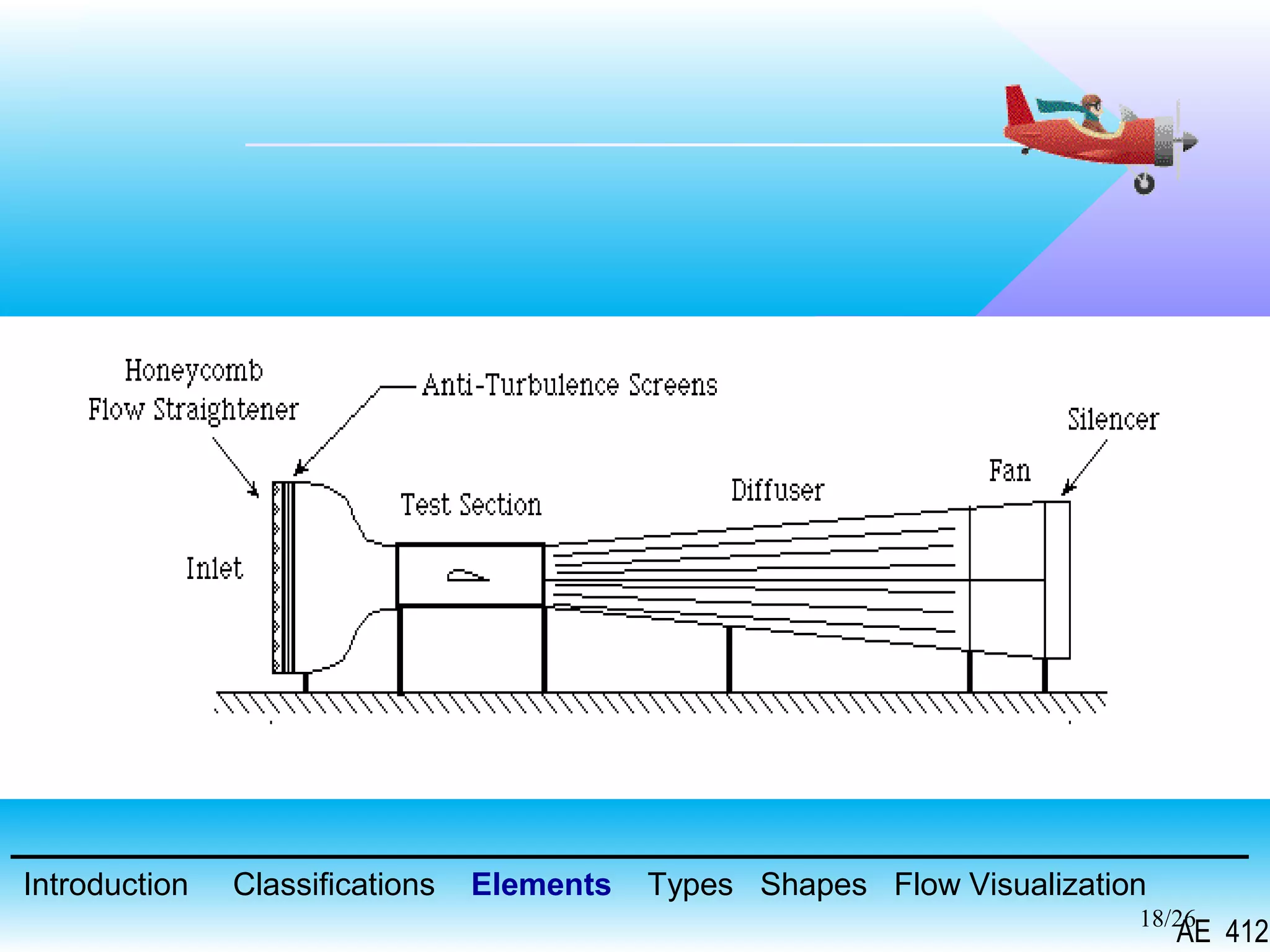
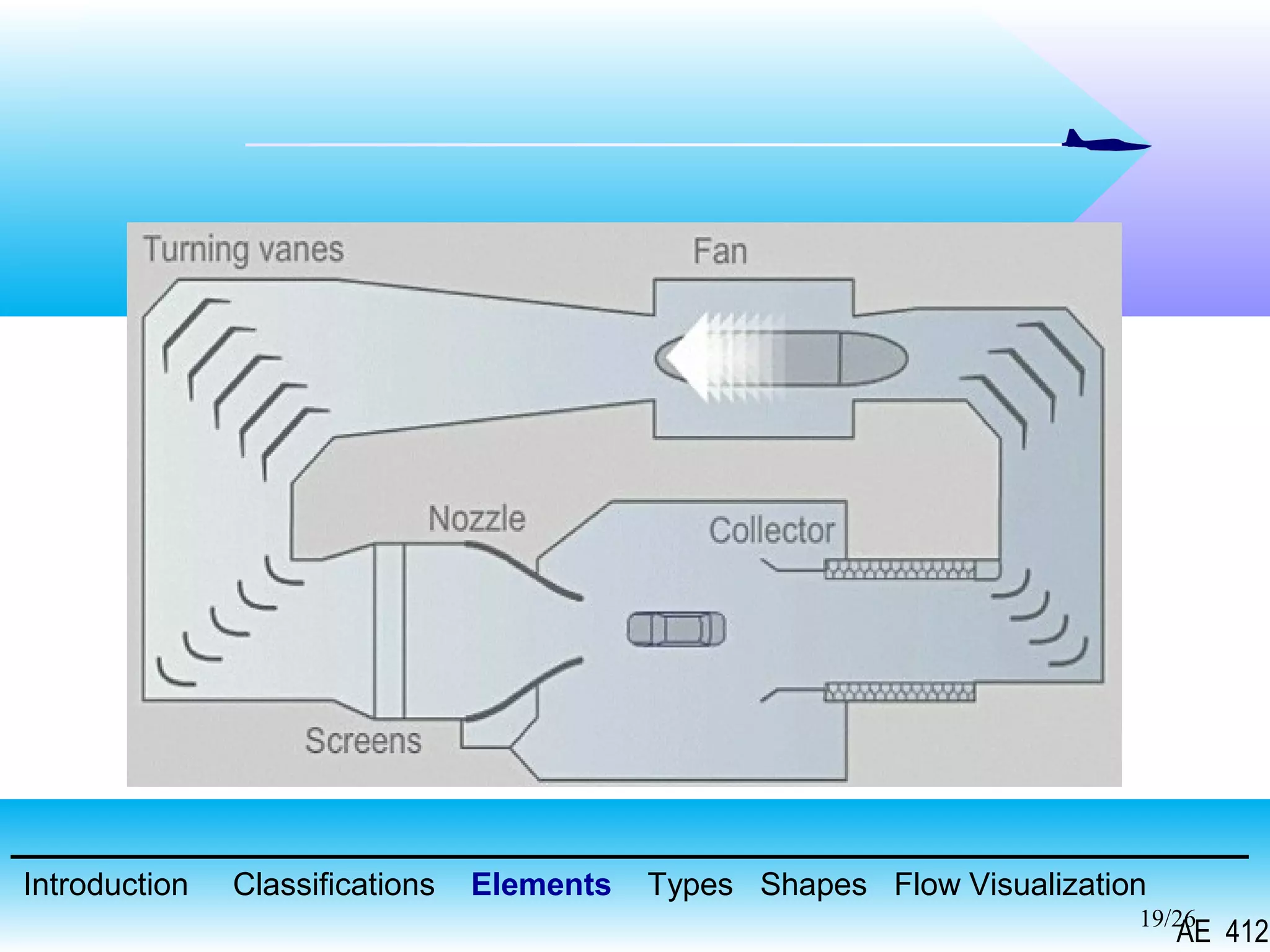
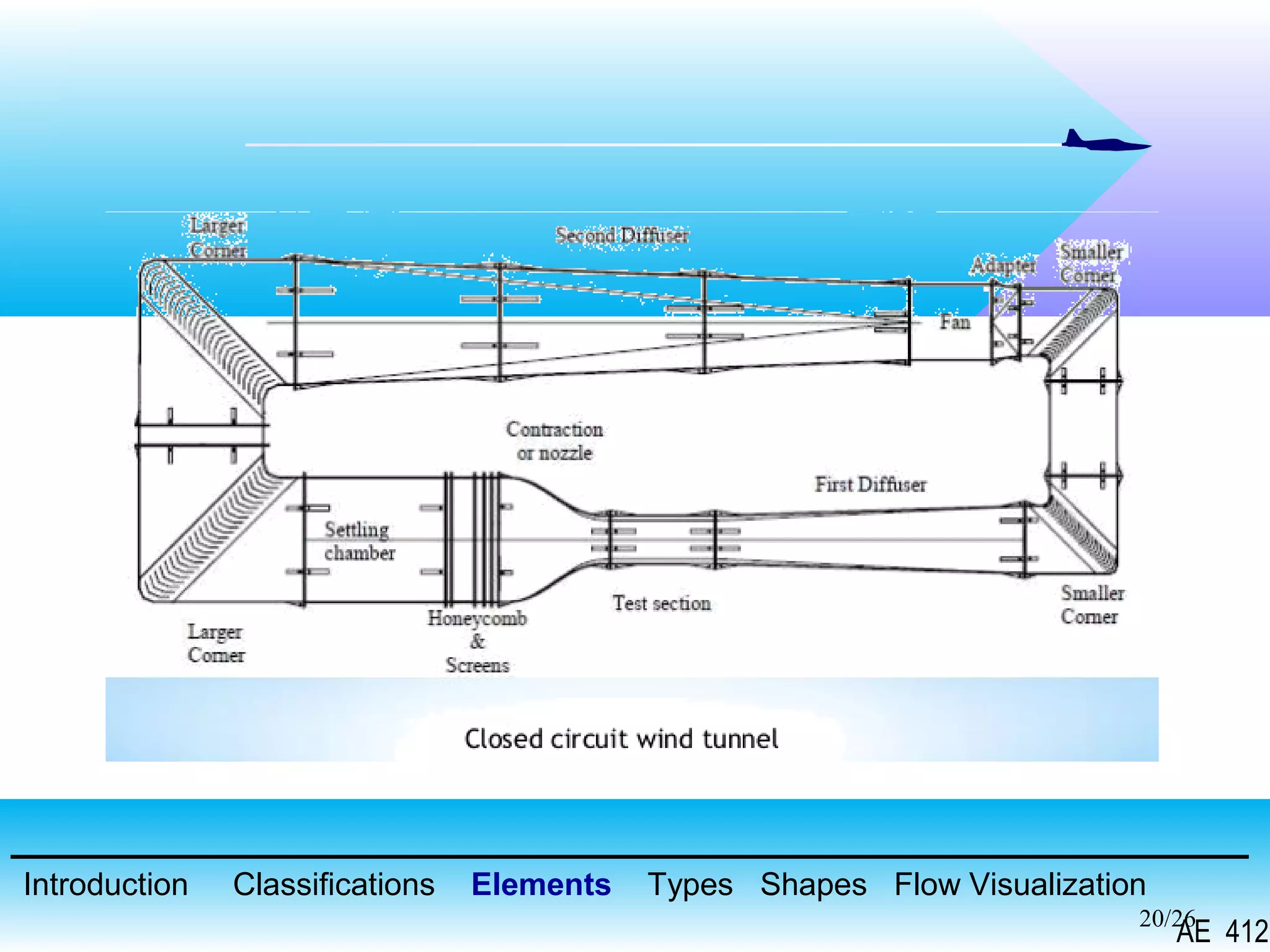
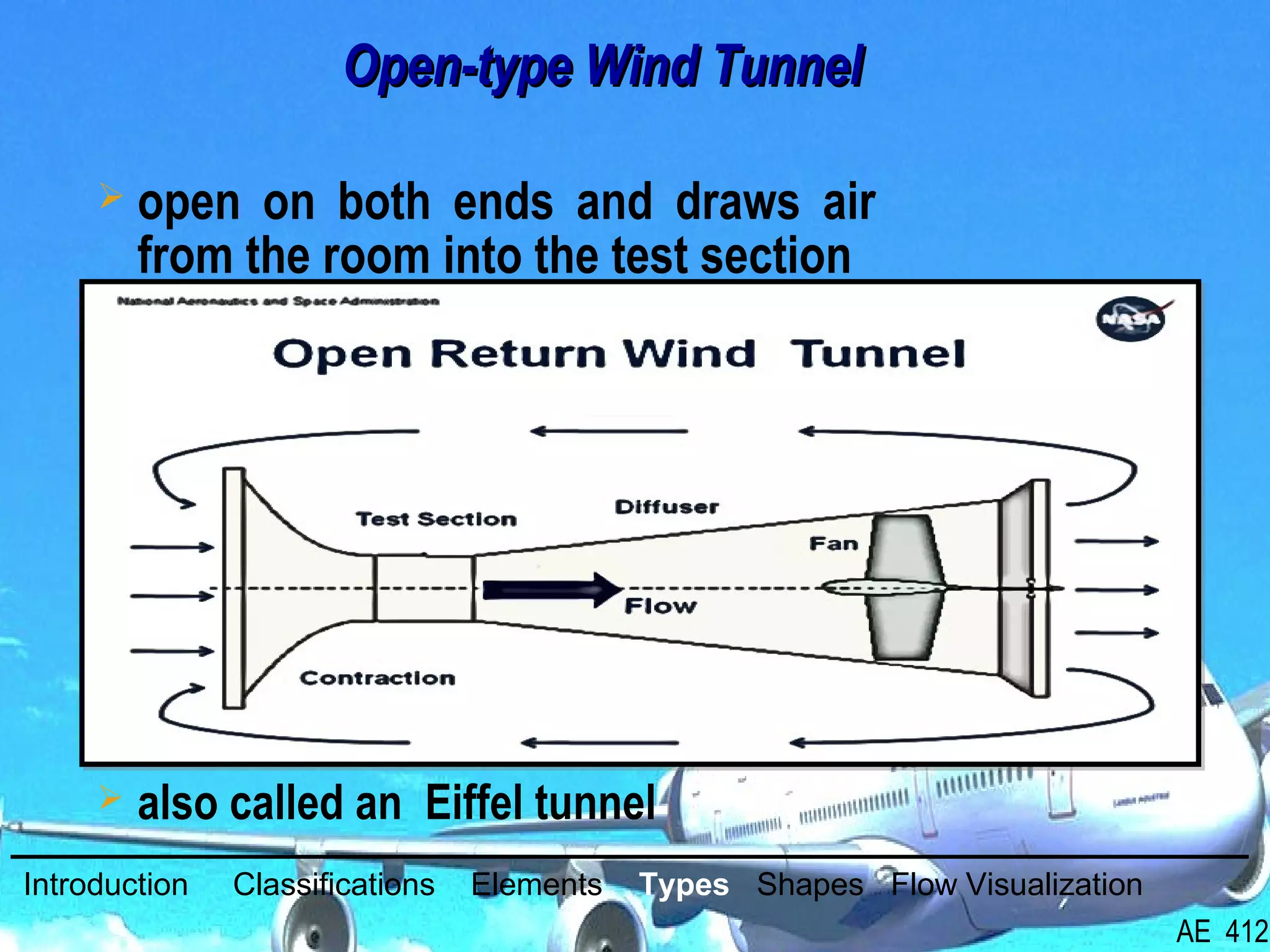
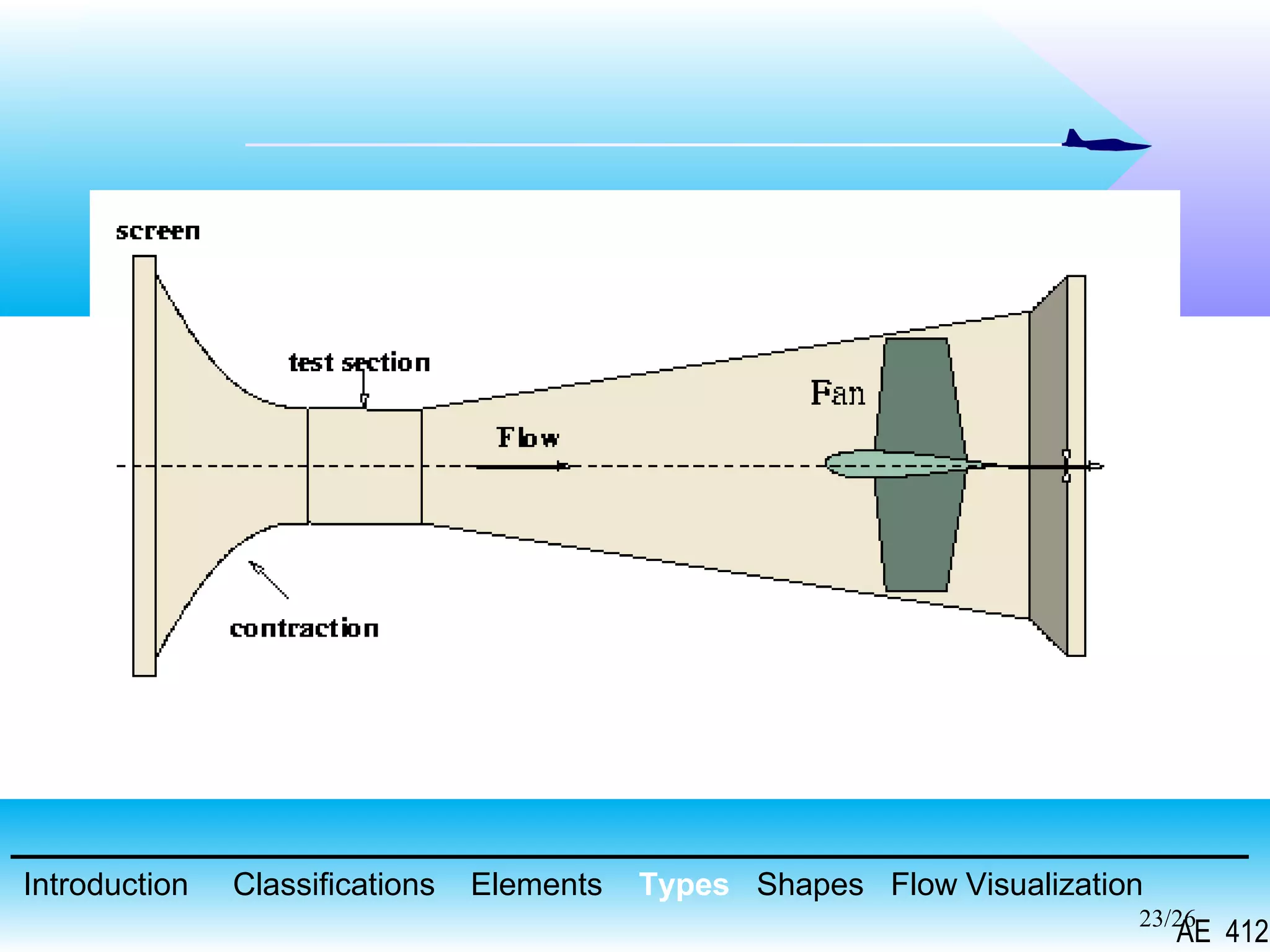
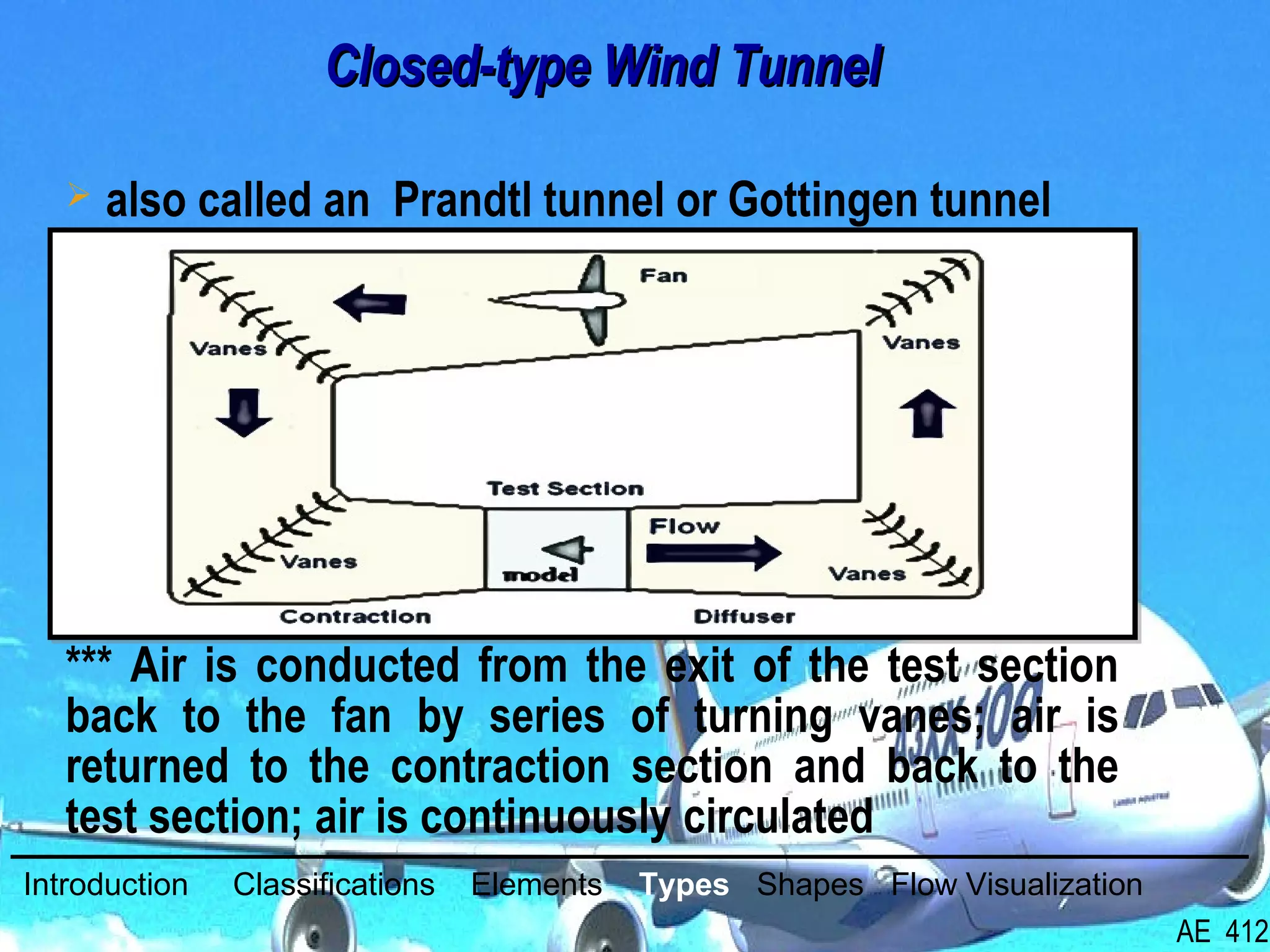
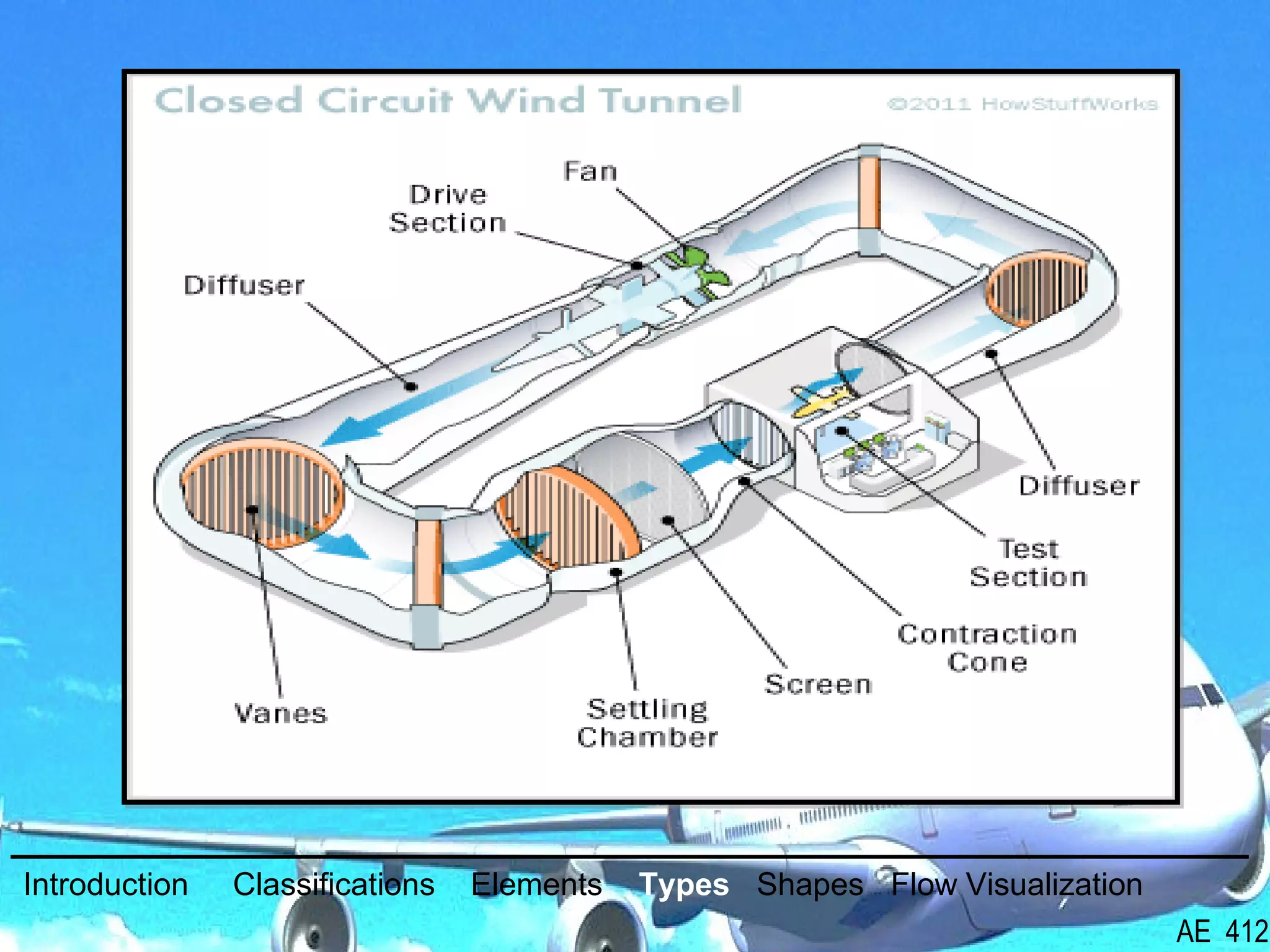
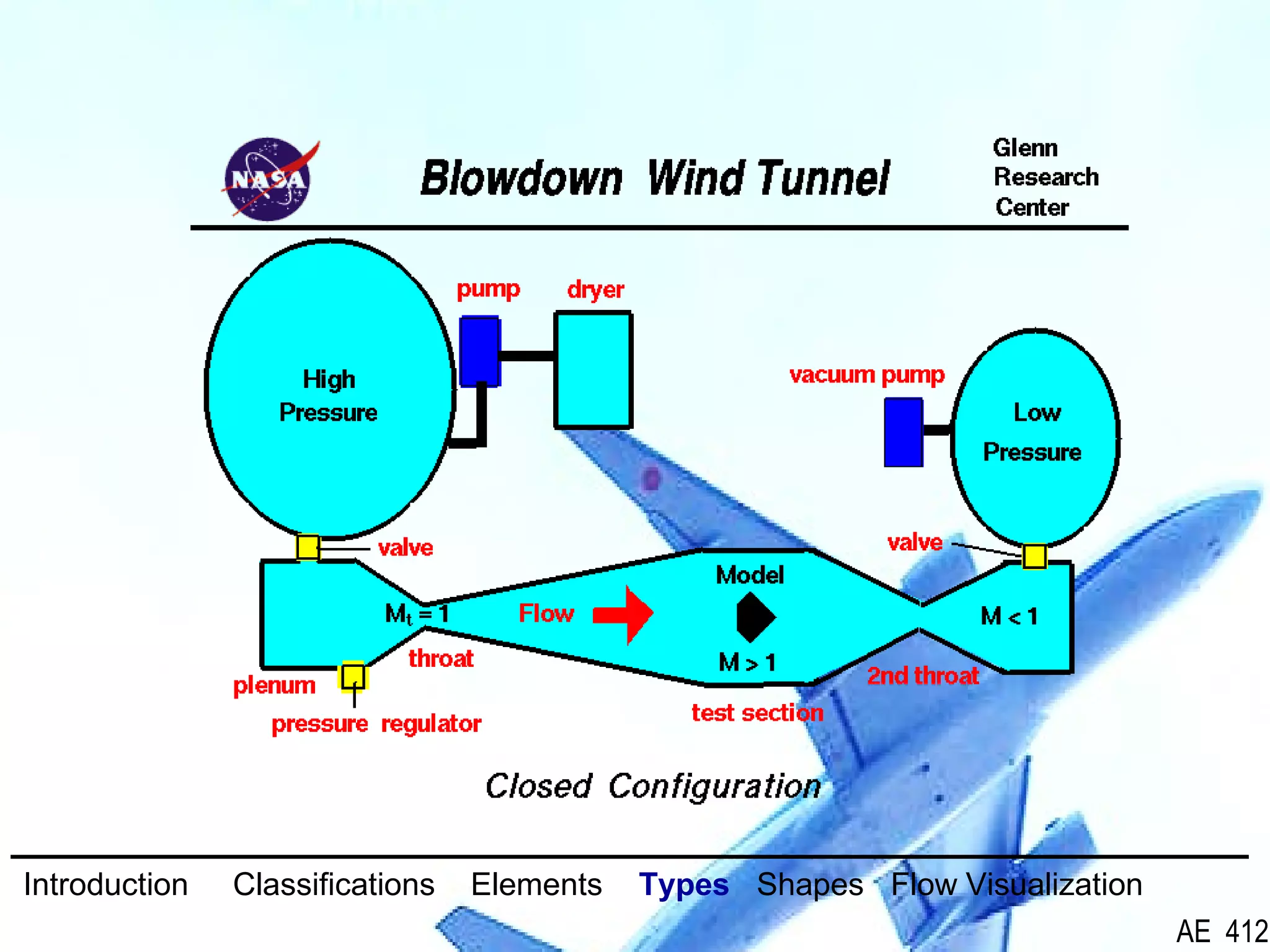
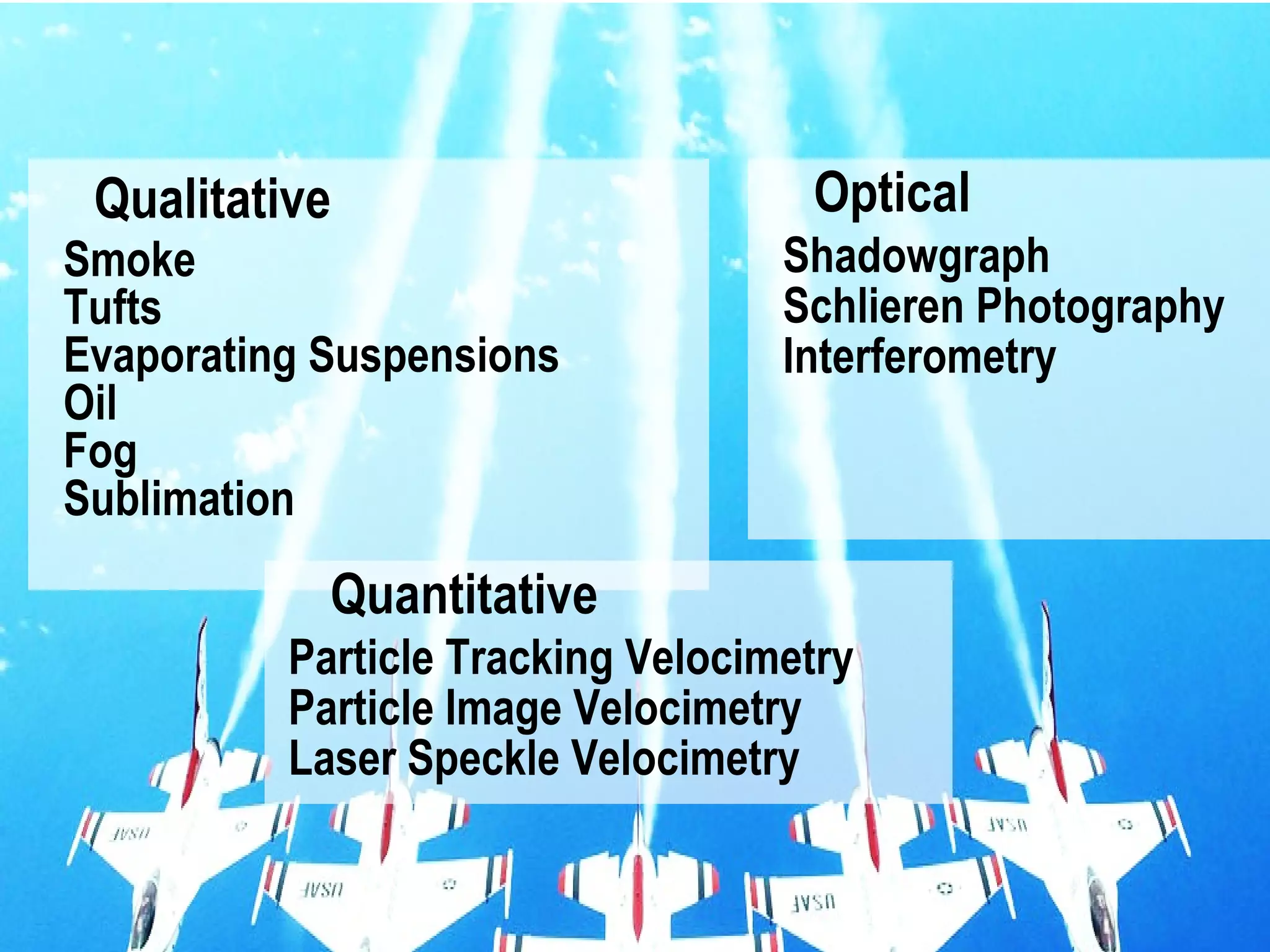
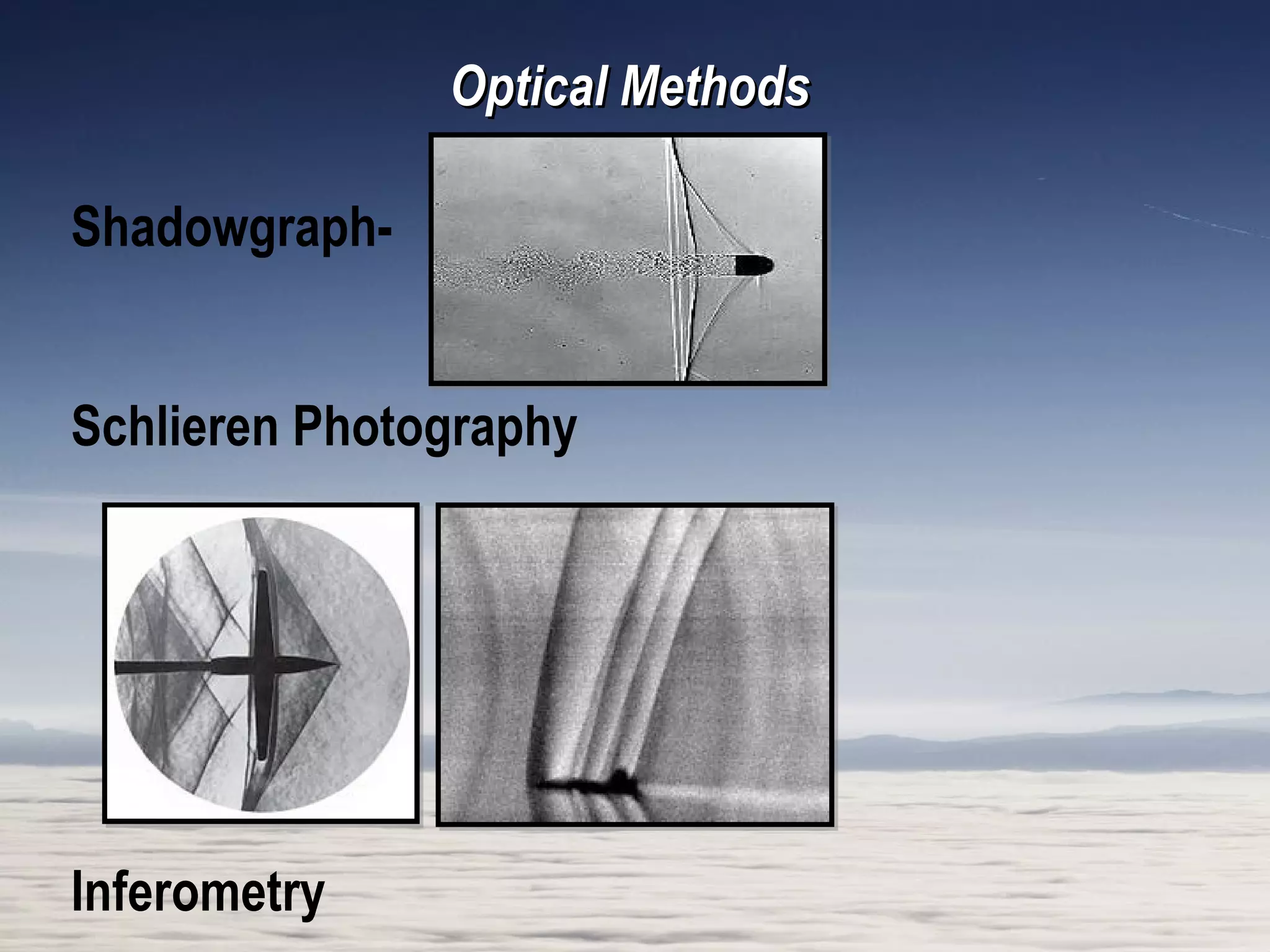
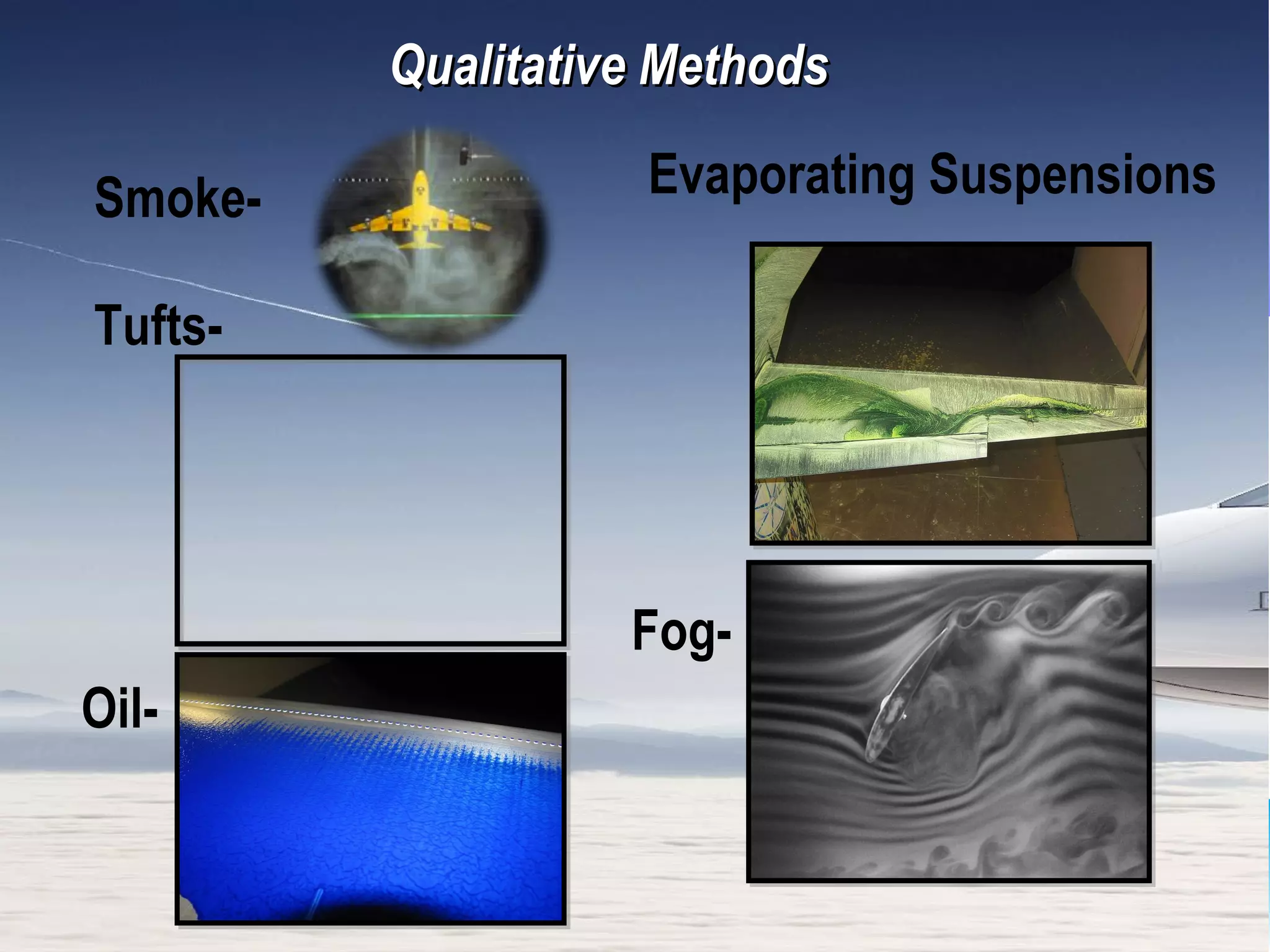
A wind tunnel is a facility that provides a controlled airflow for testing aerodynamic models. It has a test section where models are placed and sensors measure forces like lift and drag. Wind tunnels are classified based on speed of airflow, air pressure, and size. They can have open or closed designs and use various flow visualization techniques to study airflow patterns.