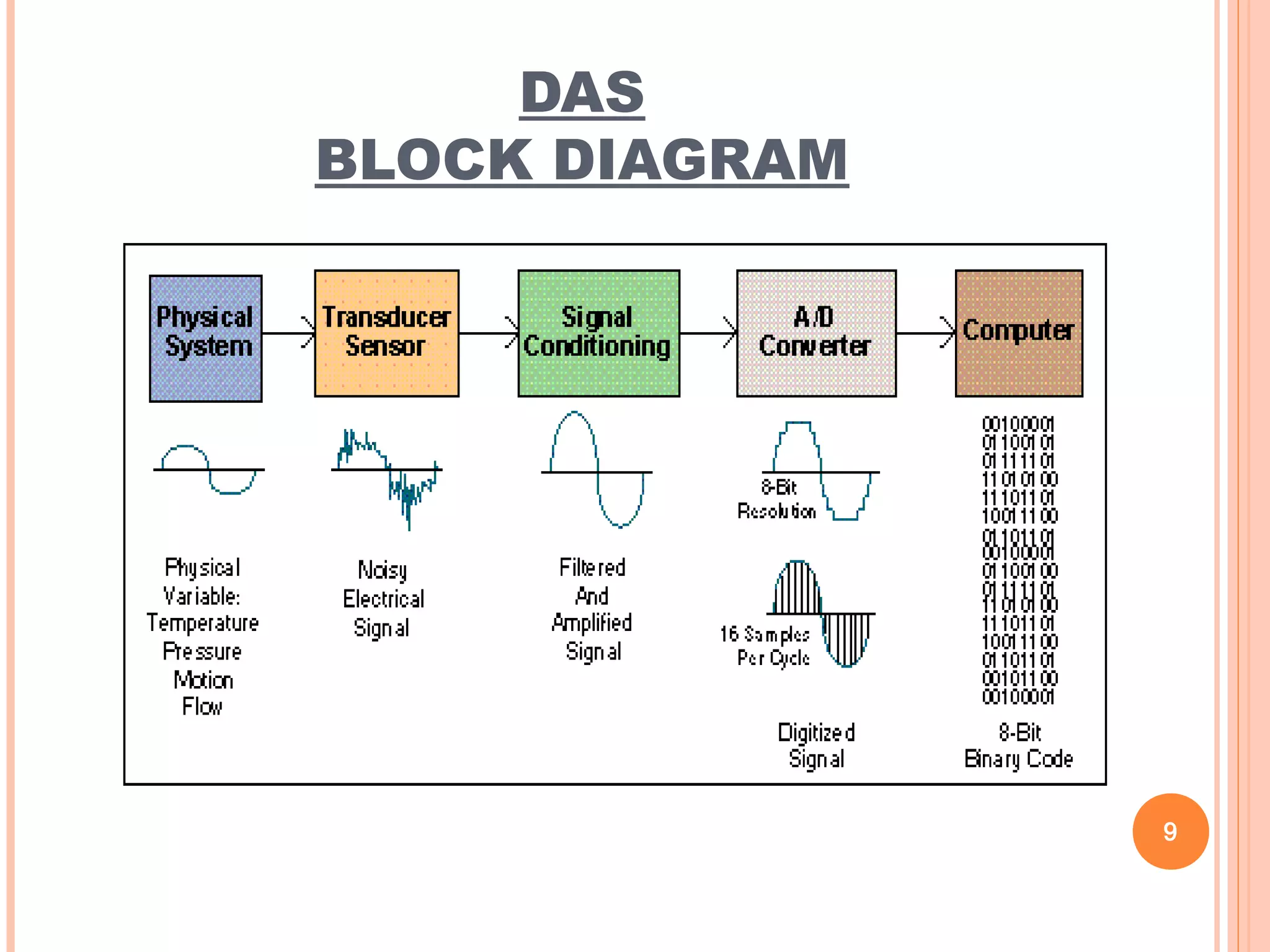
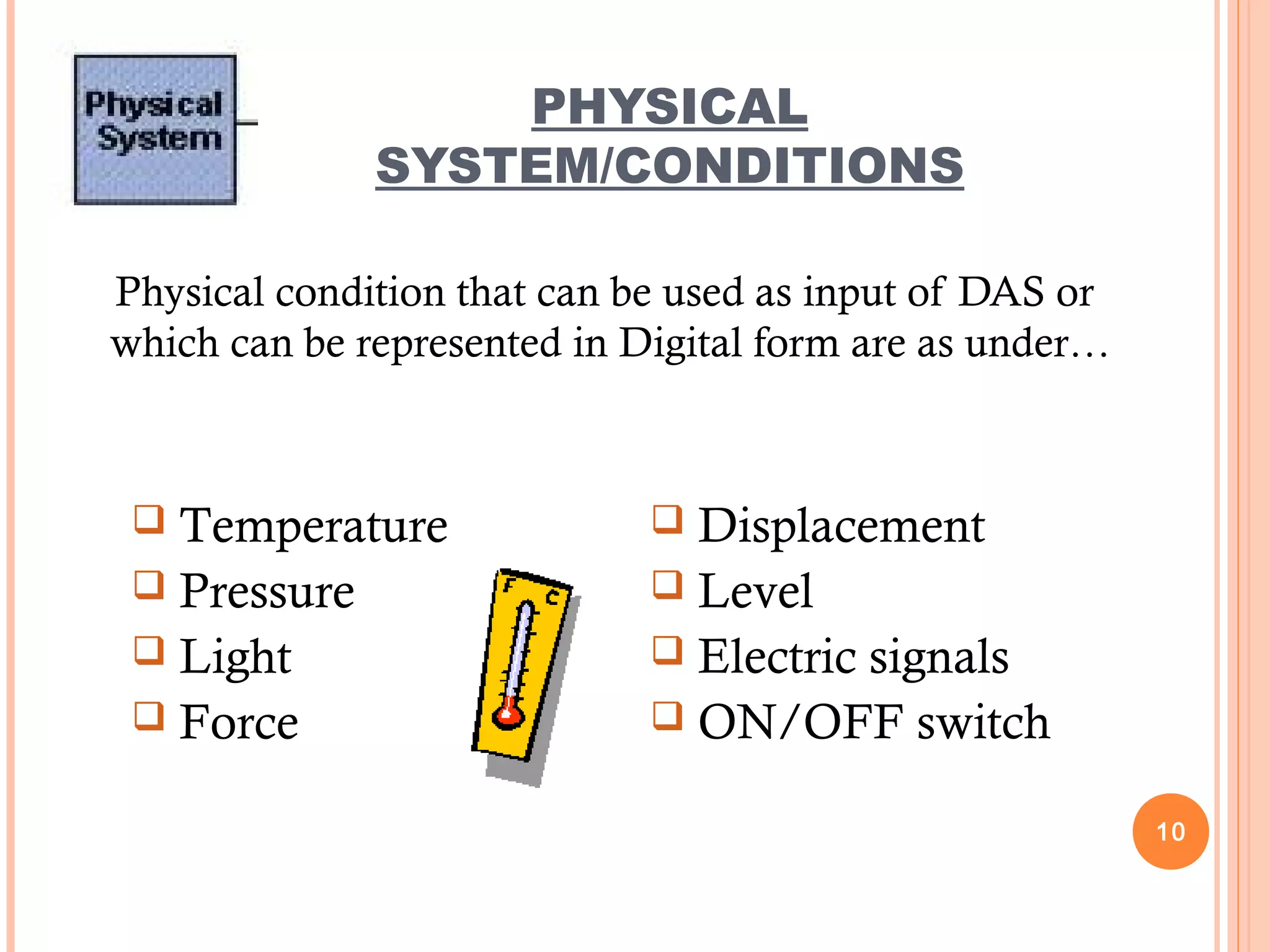
The document discusses data acquisition systems (DAS), which sample and convert real-world physical conditions into digital values for processing. It highlights the components, objectives, methodology, hardware and software involved in DAS, as well as its merits and demerits. DAS is essential in various fields for efficient data storage and processing.