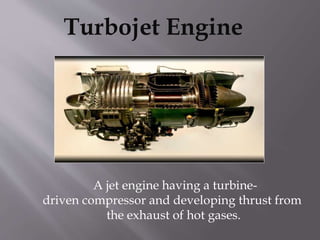
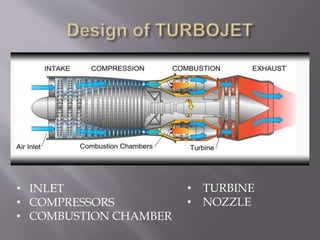
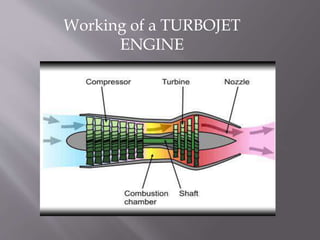
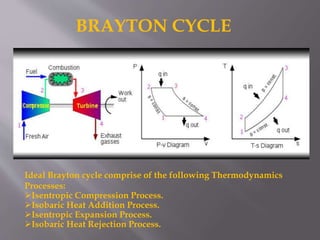
This document discusses the design and operation of a turbojet engine. It begins with an introduction and history, describing the first aircraft to use turbojet engines in the late 1930s and 1940s. The main components of a turbojet engine are then outlined, including the compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, and nozzle. The document explains that the turbine drives the compressor and thrust is produced by exhaust gases. It provides details on the Brayton cycle and discusses advantages like high power-to-weight ratio but also disadvantages such as high fuel consumption at low speeds. Applications mentioned include commercial aviation and use in high speed vehicles.