This document provides an overview of aircraft wings, including their:
- Historical development from ancient kites to the Wright brothers' fixed-wing aircraft.
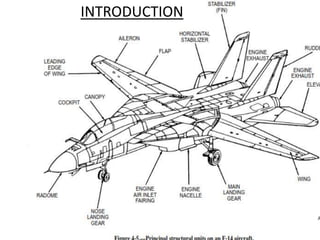
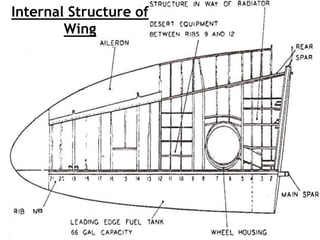
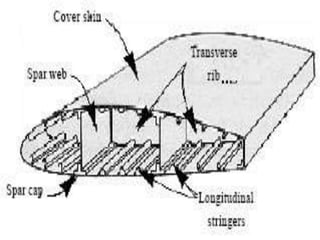
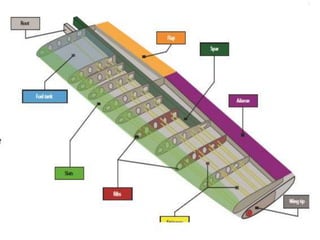
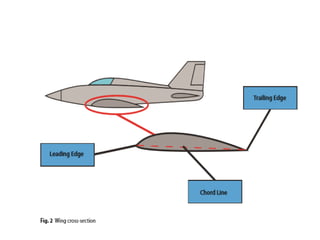
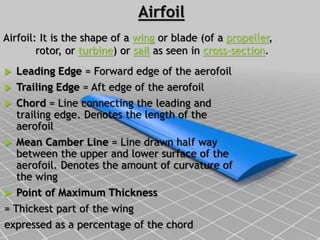
- Construction, with internal structures like ribs, spars, stringers, and skin covering the framework. Wings also contain fuel tanks, flaps, and other devices.
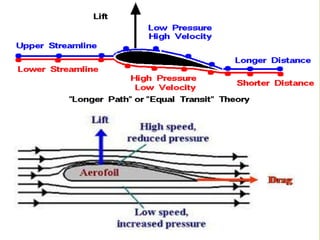
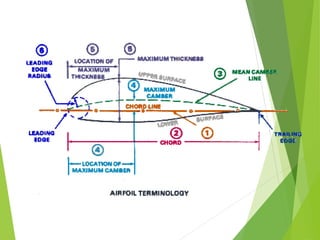
- Functions, as wings generate lift through Bernoulli's principle and critical angle of attack. Wing design factors like aspect ratio and camber also affect lift.
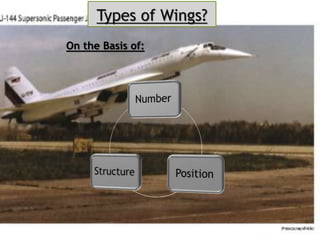
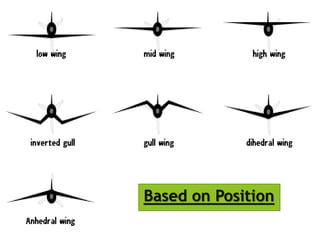
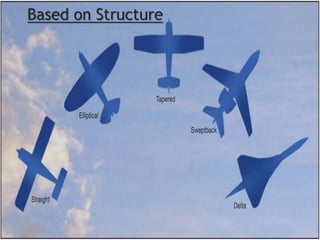
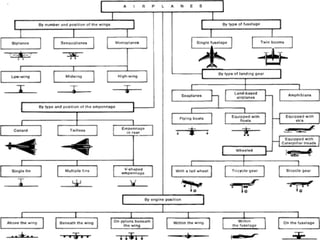
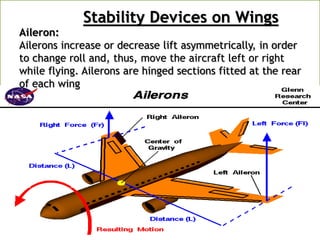
- Types based on position (fixed or movable) and structure (cantilever or strut-braced). Stability devices like ailerons and flaps are also described.
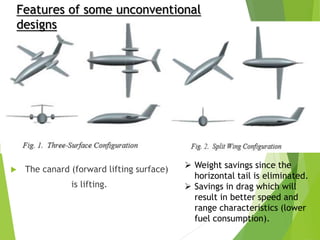
- Unconventional designs that