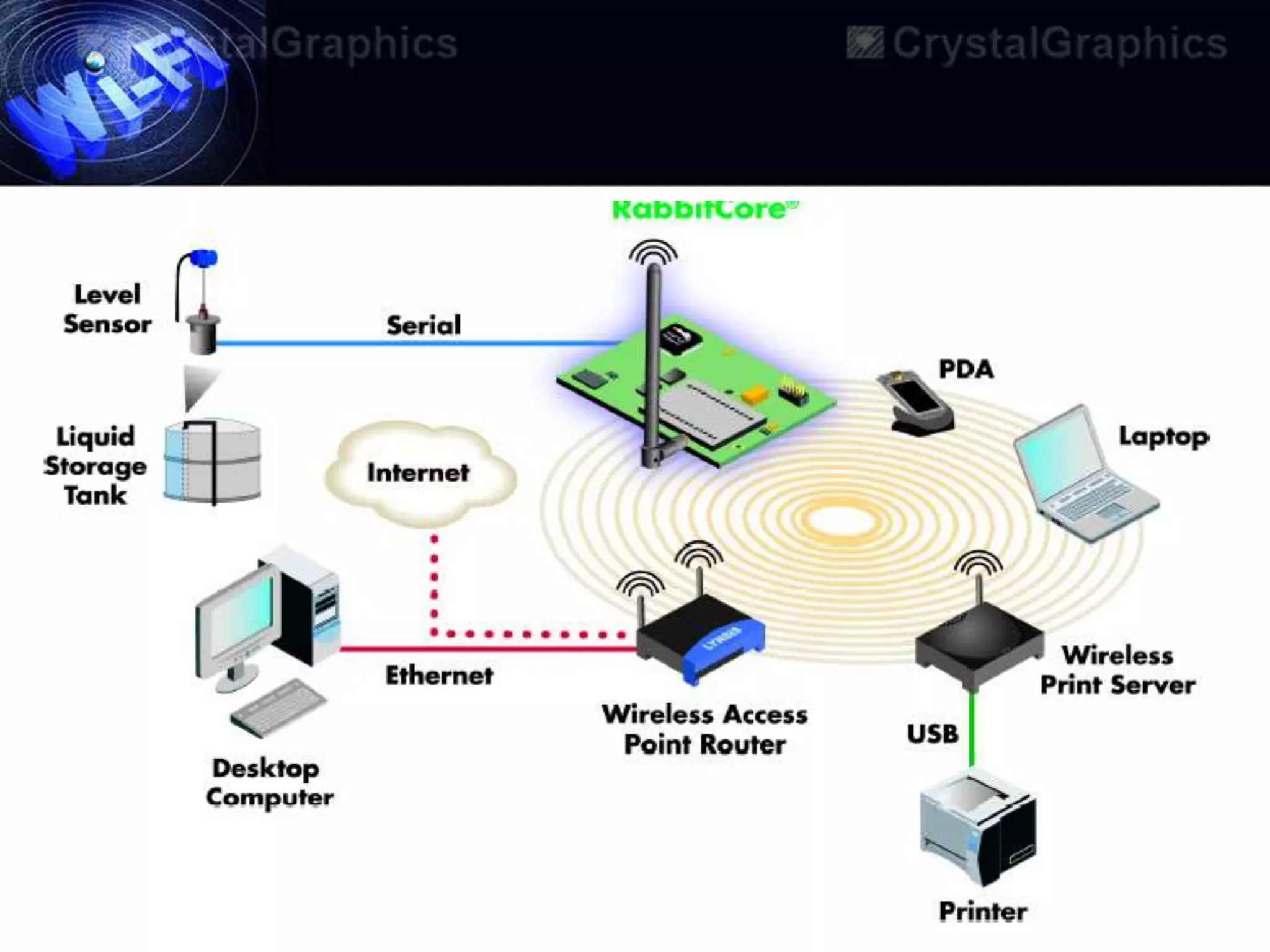
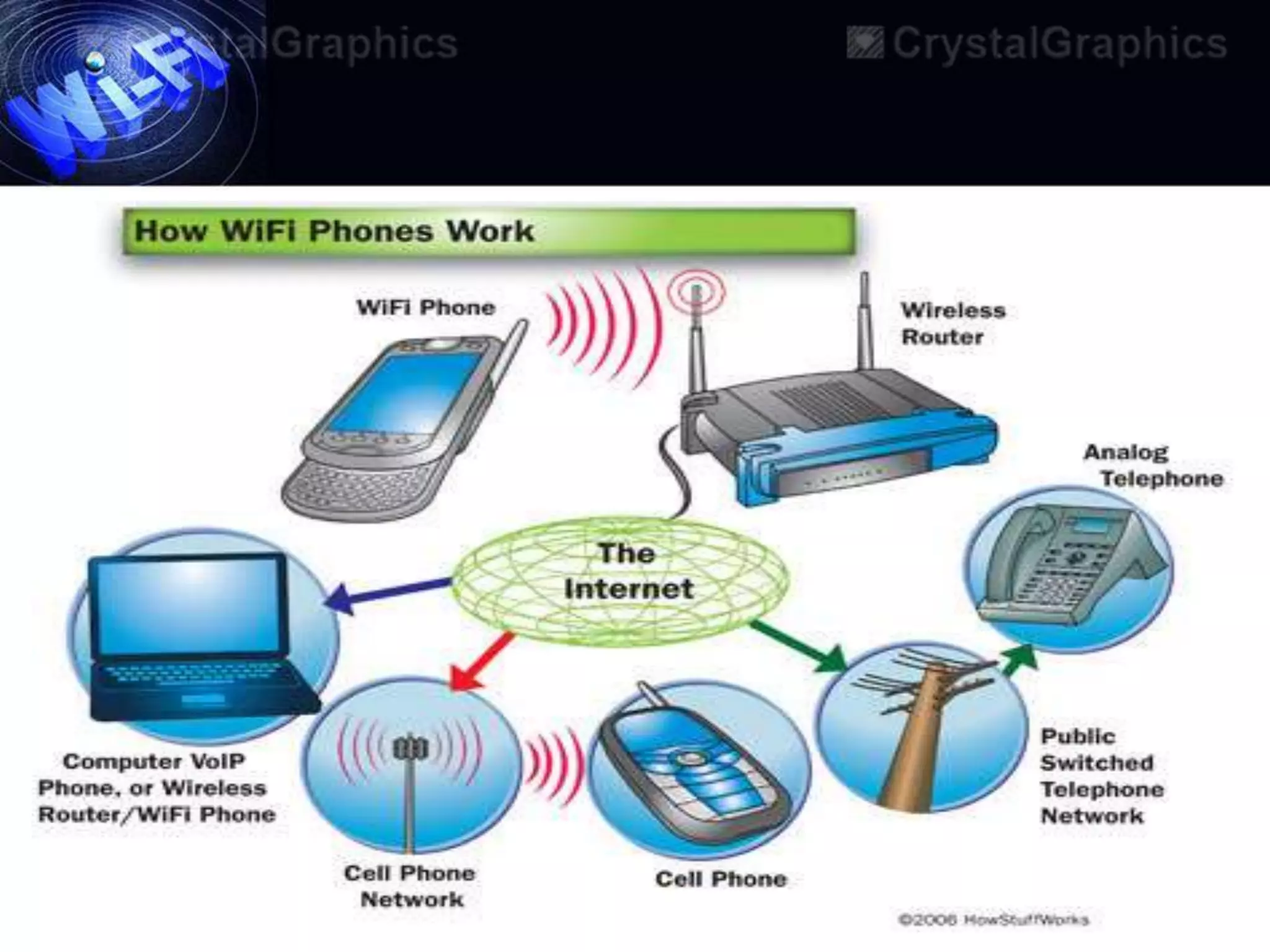
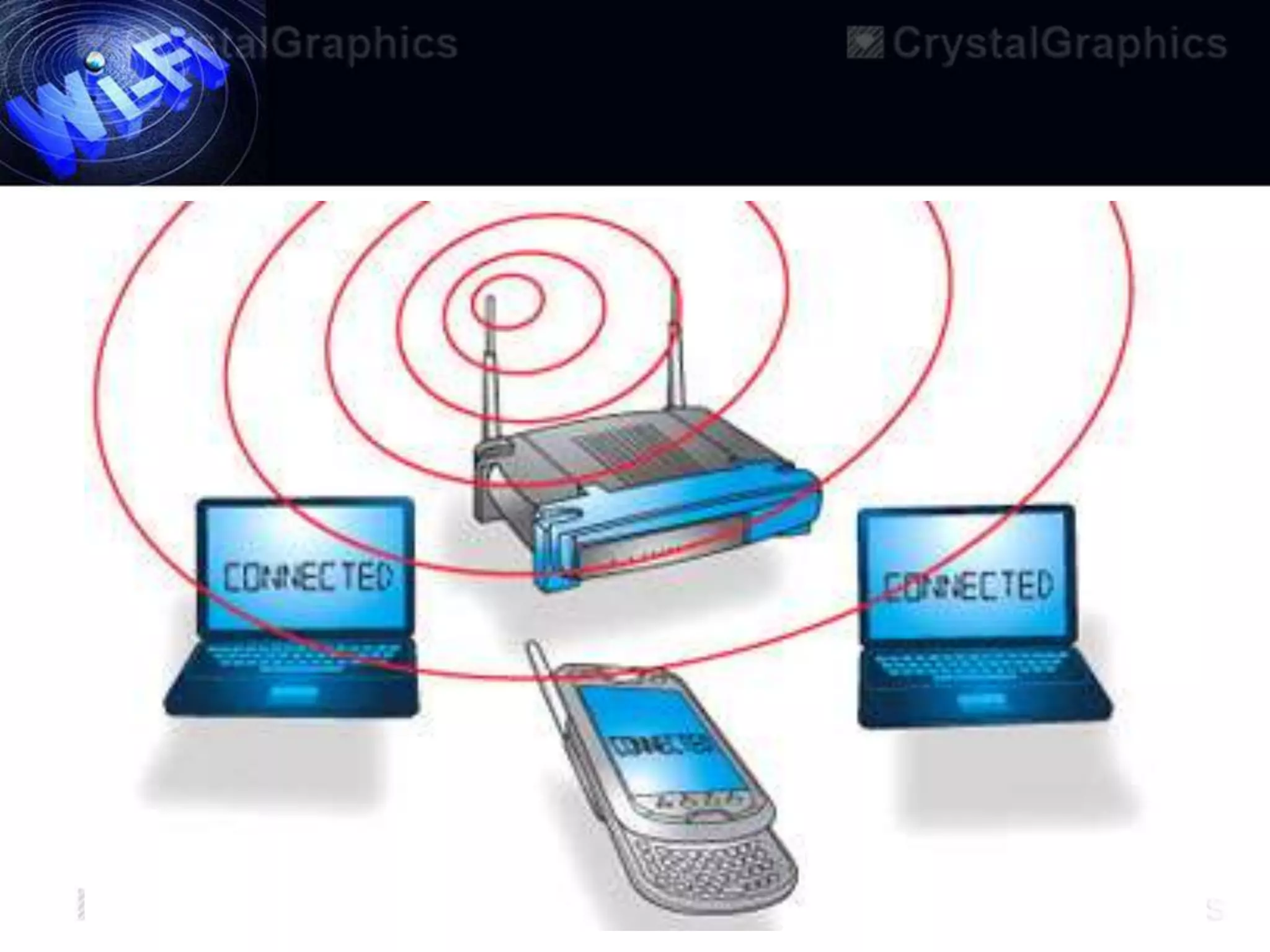
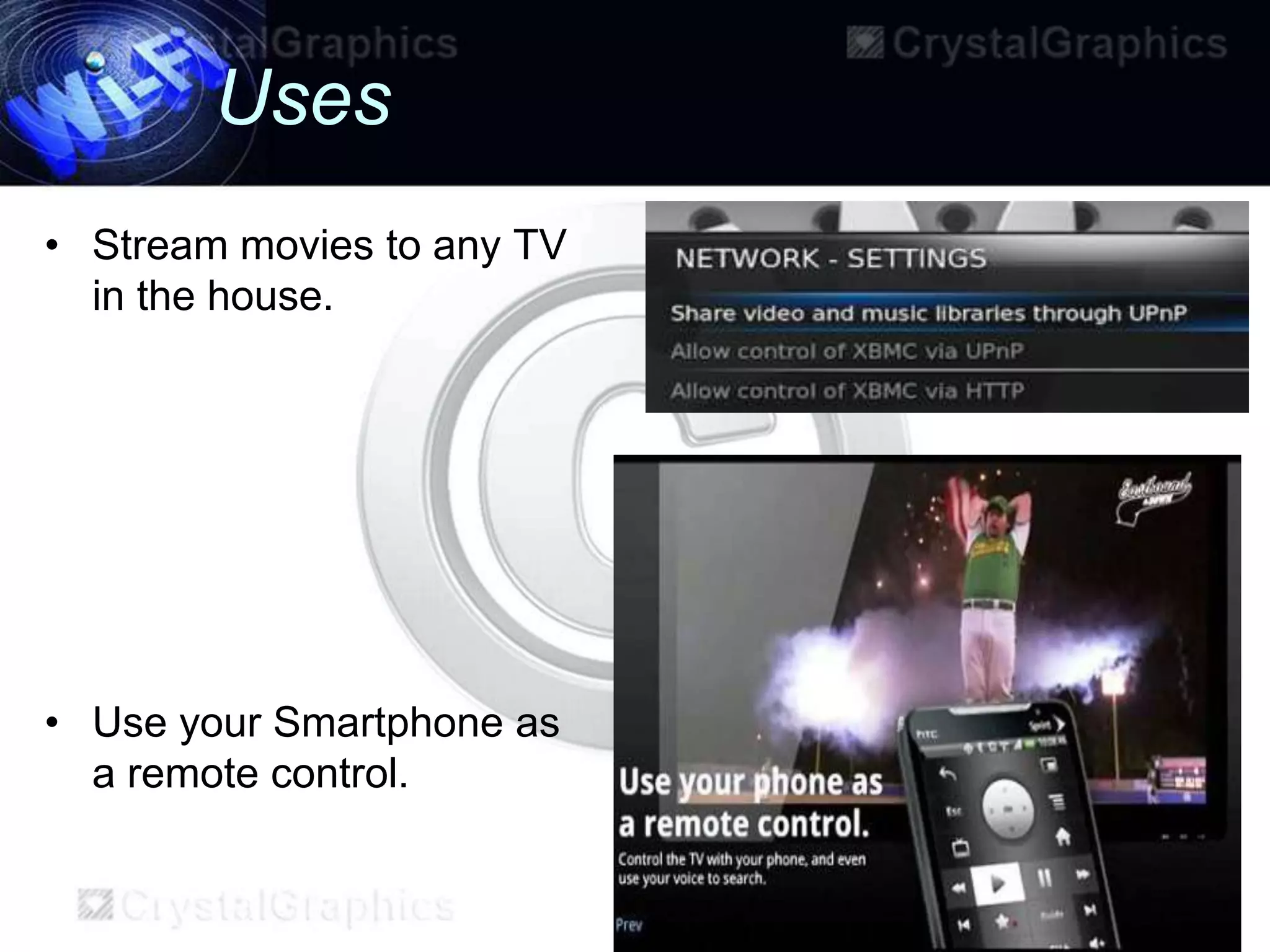
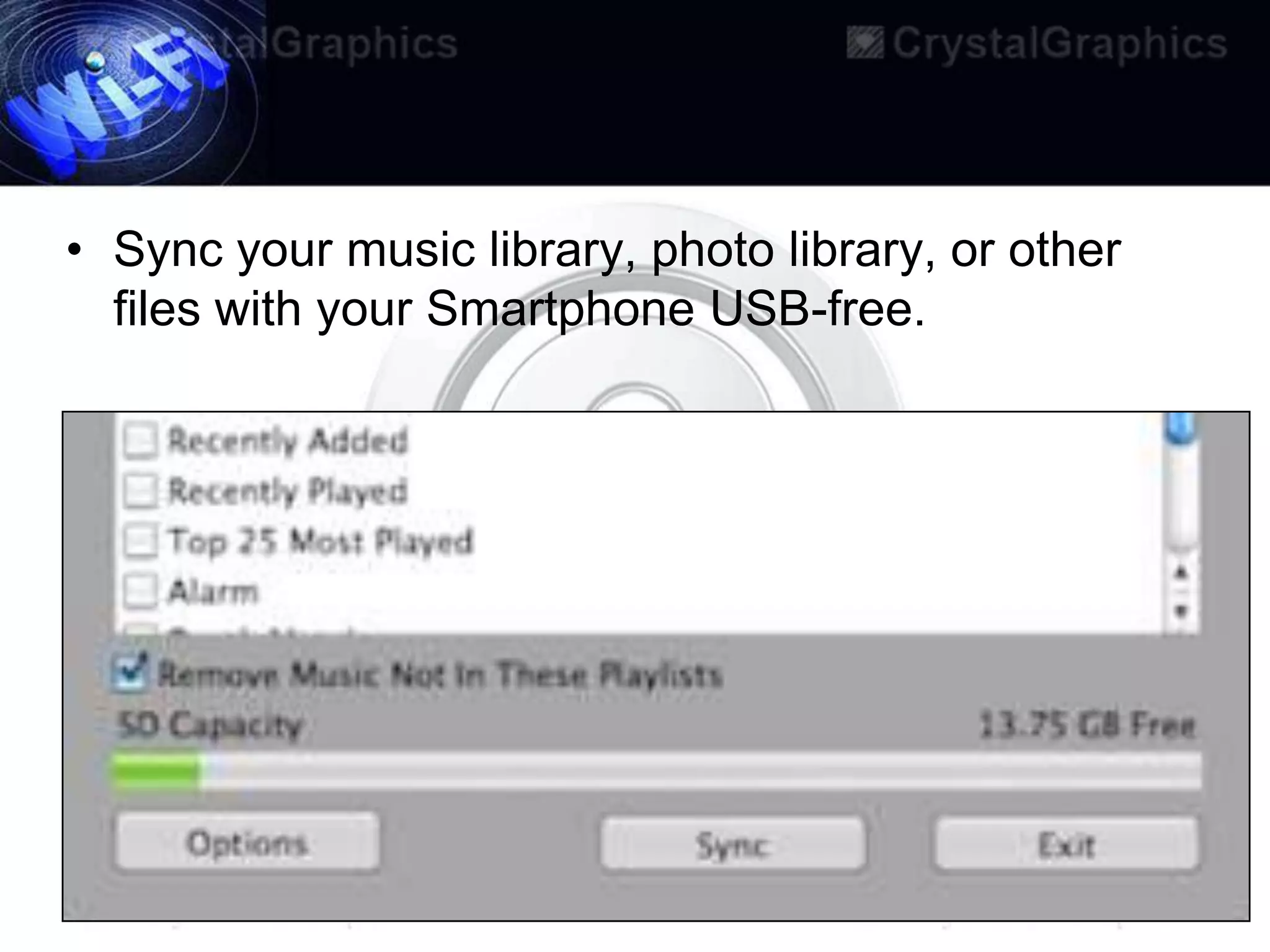
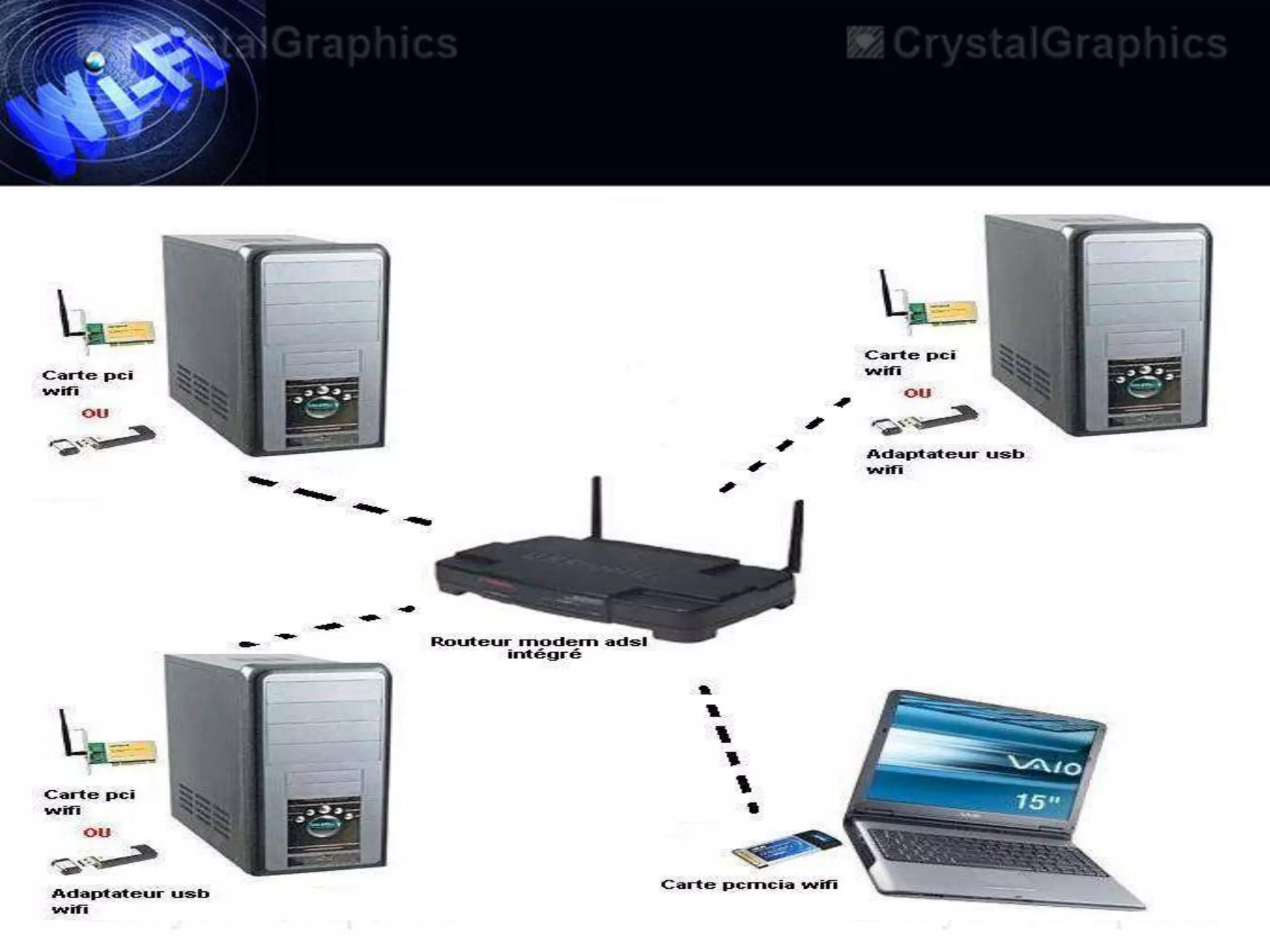
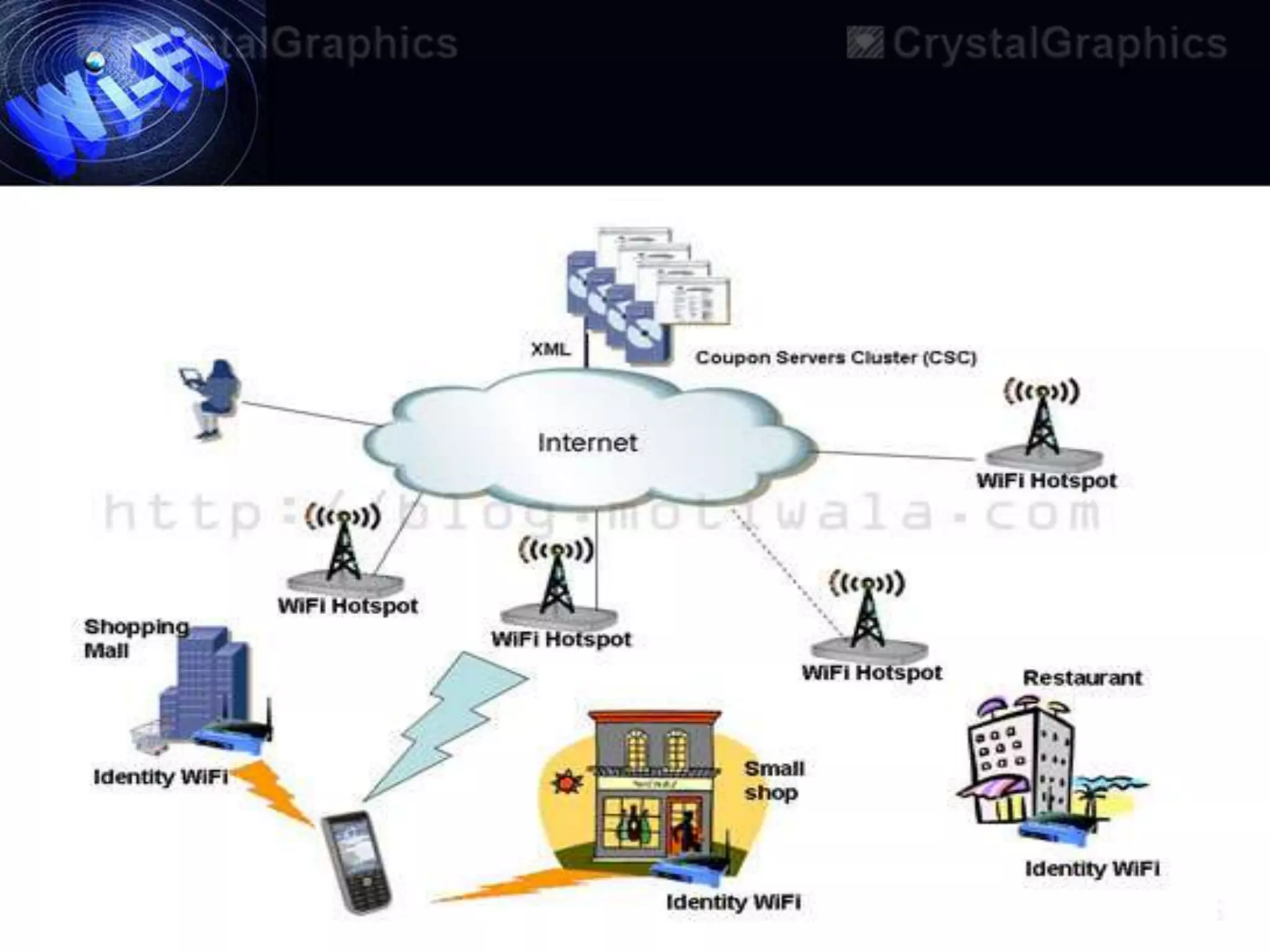
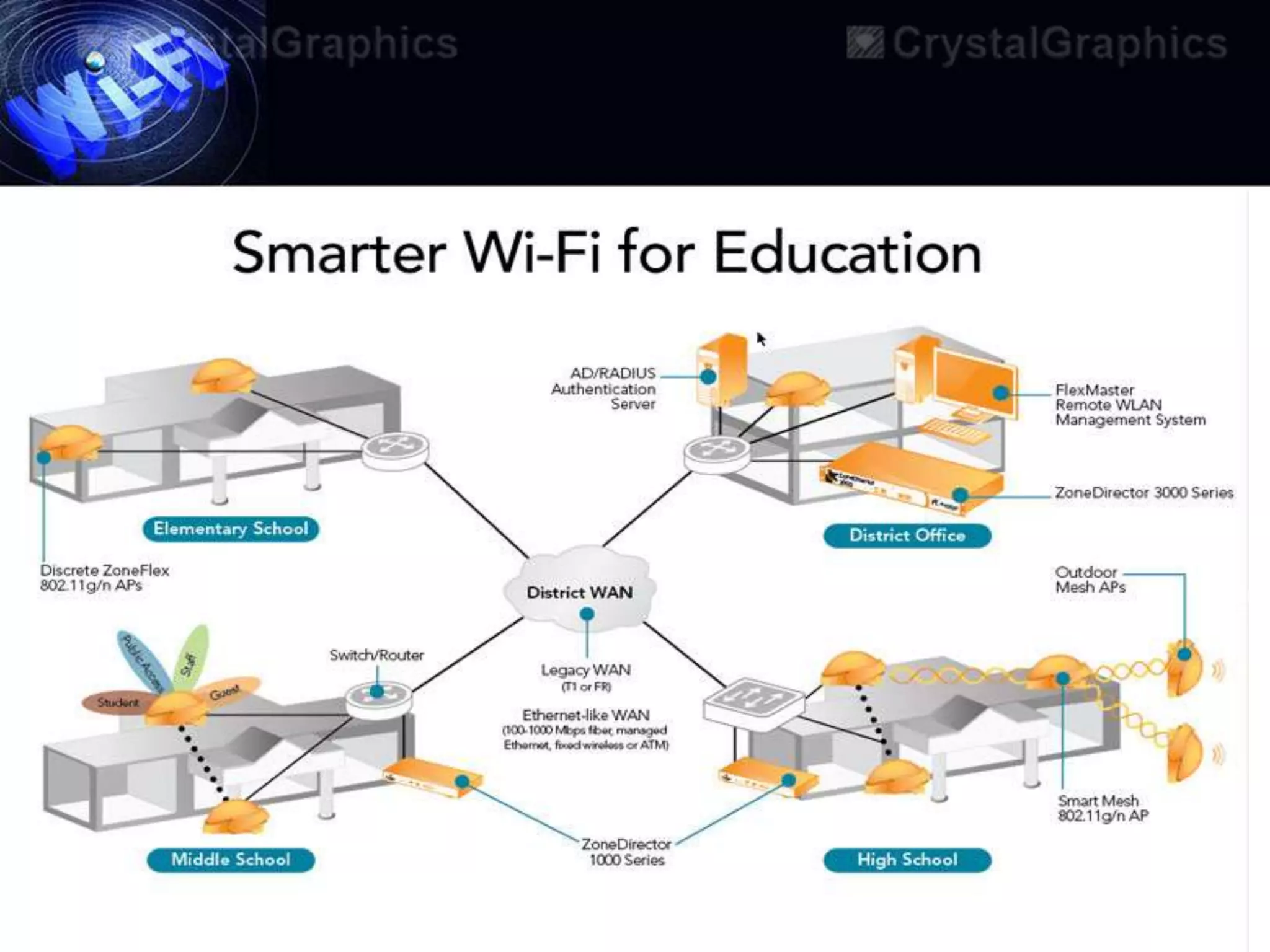
This document discusses Wi-Fi and its applications. It defines Wi-Fi as a wireless technology brand owned by the Wi-Fi Alliance that uses IEEE 802.11 standards for interoperable wireless local area network (WLAN) products. The document outlines the history of Wi-Fi, its common uses like sharing files and streaming media, benefits such as mobility and reduced costs, security goals, typical ranges, and applications like enabling collaboration and providing internet access in public spaces.