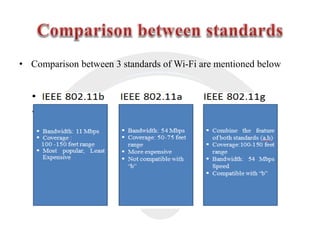
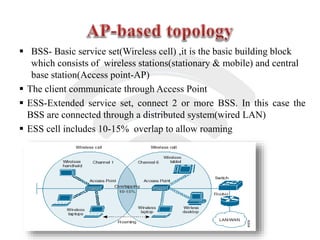
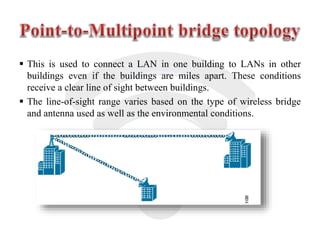
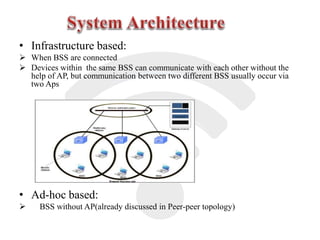
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that allows devices to connect to the internet and each other without being physically connected with cables. It uses radio waves to enable wireless network access across multiple devices. The Wi-Fi Alliance tests and certifies products for interoperability and compliance with IEEE 802.11 wireless standards. Wi-Fi provides the benefit of mobility and flexibility without cables but has disadvantages such as slower speeds and potential security risks compared to wired connections.