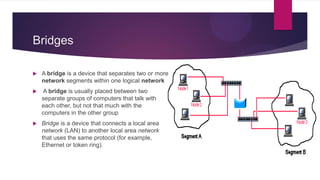
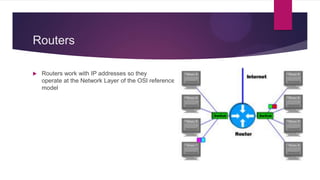
This document discusses various networking devices and wireless technologies. It describes how hubs operate at the physical layer by flooding traffic to all ports, while switches operate at the data link layer by examining packets and only sending to necessary ports. Modems convert between analog and digital signals. Bridges separate network segments, while routers connect different networks and use IP addresses. Wireless technologies discussed include Wi-Fi Direct for device-to-device connections, Wi-Fi HaLow for low power long range connections, Miracast for cable-free display sharing, ZigBee for mesh networks, and WiMax for high speed wireless broadband.