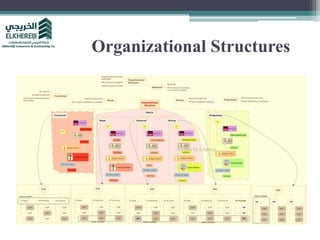
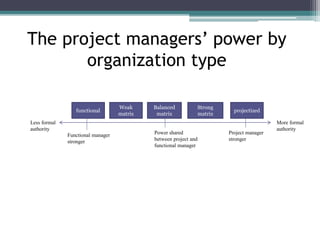
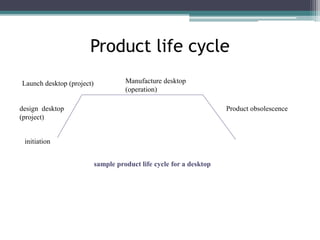
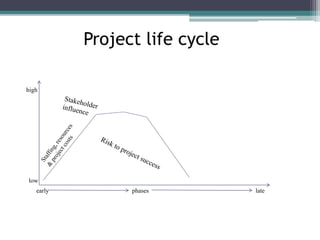
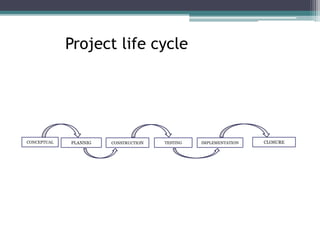
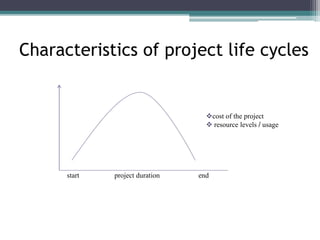
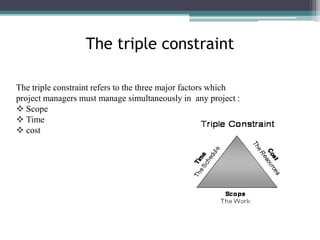
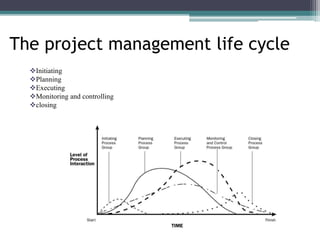
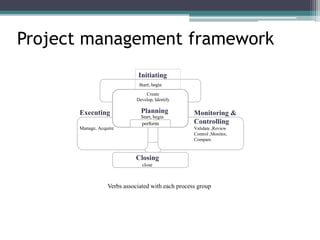
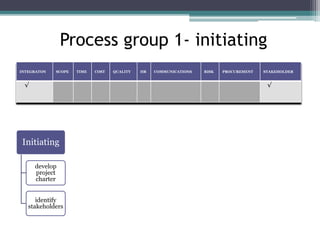
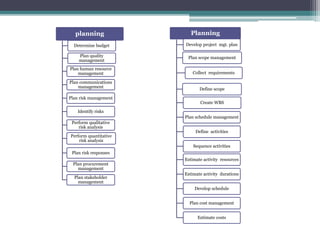
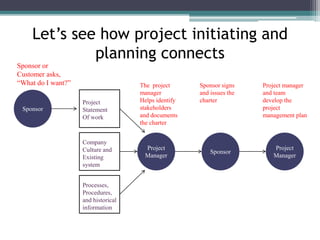
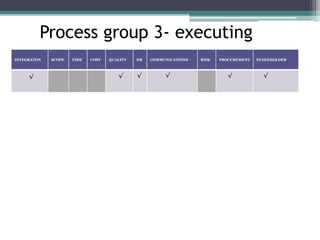
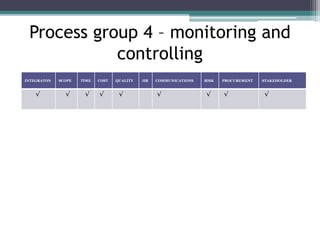
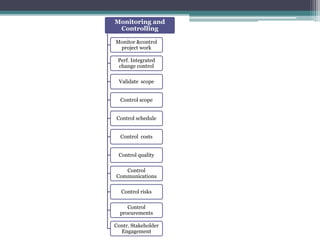
This document provides an overview of project management and the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification. It defines what constitutes a project, describes the five process groups of project management, and explains the project life cycle and management framework. The five process groups are initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. Project management balances the triple constraints of scope, time and cost. The document also recommends several books for PMP exam preparation.