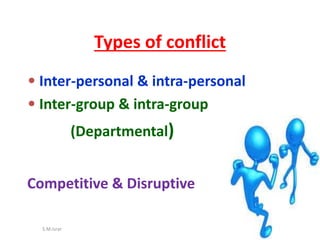
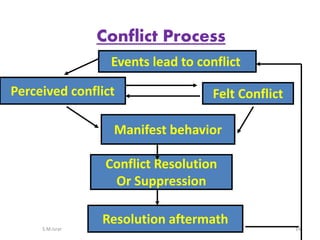
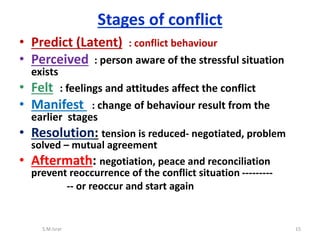
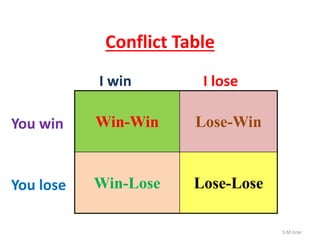
The document discusses conflict, including its definition, types, causes, stages, and strategies for management and resolution. It defines conflict as a state of incompatibility or disagreement between parties that begins when the goals of one are obstructed by another. Conflict can be inter-personal, inter-group, and arise from scarce resources, differing perceptions or goals. Effective conflict management includes open communication, understanding different perspectives, and finding solutions that address everyone's needs.