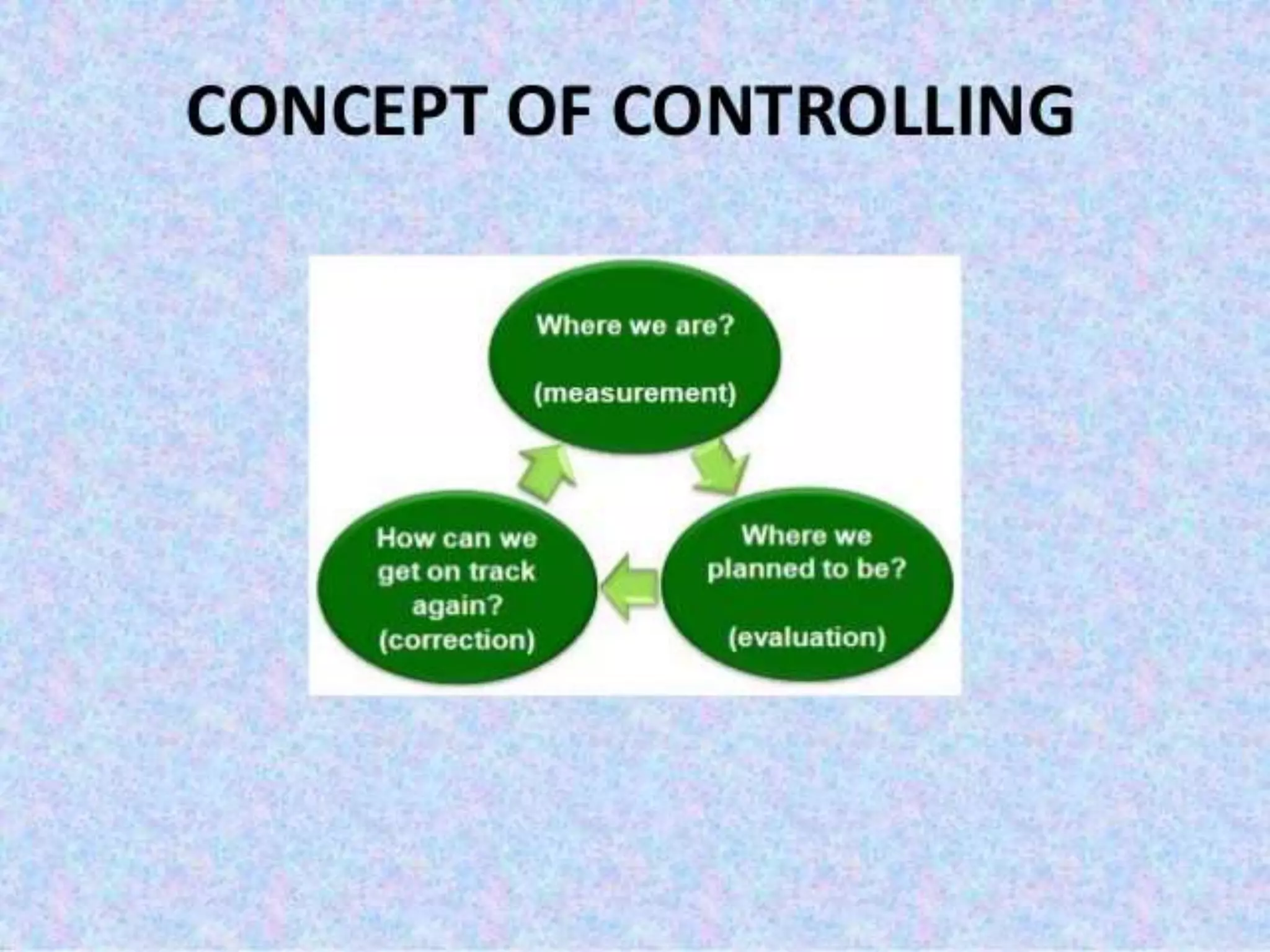
The document outlines the importance and functions of controlling in management, defining it as the process of monitoring performance to ensure alignment with plans and objectives. It details types of control, areas of control, and effective control characteristics, emphasizing the relationship between controlling and planning. Additionally, it addresses methods for employee performance management, organizational control systems, and the significance of coordination for achieving organizational efficiency and effectiveness.