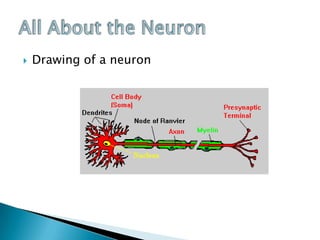
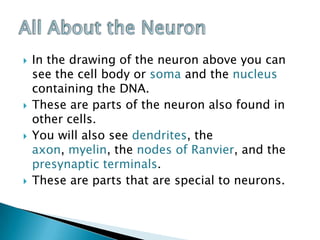
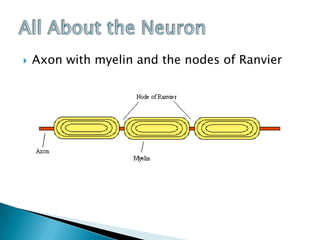
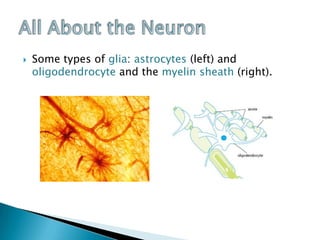
Neurons are specialized cells that carry messages through the body via electrochemical processes. They have extensions called dendrites that receive information and axons that carry information to other neurons or structures. At the junction between neurons called the synapse, chemicals called neurotransmitters relay messages. Neurons have irregular shapes and specialized structures that allow them to communicate rapidly and coordinate the body's thinking and behavior. Support cells called glia aid neurons by insulating axons, removing waste, and regulating blood flow in the brain.